Lecture
Efficiency is determined by the power ratio 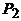 given by the transformer to the load, to the power
given by the transformer to the load, to the power 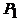 Consuming *** from the network:
Consuming *** from the network:
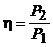 .
.
Efficiency characterizes the efficiency of voltage conversion in a transformer. In practical calculations, h is calculated by the formula
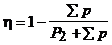 , (20)
, (20)
Where 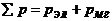 - total loss in the transformer.
- total loss in the transformer.
Formula (20) is less sensitive to errors in determining 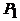 and
and 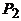 and therefore allows us to obtain a more accurate value of h. Net power is calculated by the formula
and therefore allows us to obtain a more accurate value of h. Net power is calculated by the formula
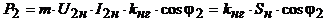 , (21)
, (21)
Where 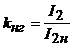 - the load factor of the transformer.
- the load factor of the transformer.
The electrical losses in the windings are determined from short circuit experience.
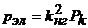 , (22)
, (22)
Where 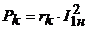 - loss of short circuit at rated current.
- loss of short circuit at rated current.
Losses in steel 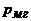 determined by the experience of idling
determined by the experience of idling
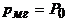 . (23)
. (23)
They are assumed to be constant for all operating modes of the transformer, since 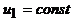 Emf
Emf 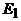 in operating mode changes slightly.
in operating mode changes slightly.
Substituting relations (21) - (23) into formula (20), we obtain
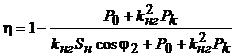 . (24)
. (24)
 |
Analysis of this expression shows that h has a maximum value under load, when the losses in the windings are equal to the losses in steel,
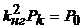 .
.
From here we get the optimal value of the load factor.
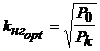 .
.
In modern power transformers, the loss ratio 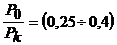 therefore, the maximum h occurs at
therefore, the maximum h occurs at 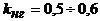 (Fig.21).
(Fig.21).
Out of the curve 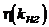 It can be seen that the transformer has almost constant efficiency in a wide range of load variation from 0.5 to 1.0. At low loads, the sharp transformer h decreases.
It can be seen that the transformer has almost constant efficiency in a wide range of load variation from 0.5 to 1.0. At low loads, the sharp transformer h decreases.
Comments
To leave a comment
Power supplies for electronic equipment
Terms: Power supplies for electronic equipment