Lecture

Alkaline batteries of size C from various manufacturers.
The alkaline cell is a manganese-zinc galvanic cell, which uses manganese dioxide as the cathode, powdered zinc as the cathode, and an alkali solution, usually potassium hydroxide, as the electrolyte.
For the first time, the use of alkaline electrolyte in chemical current sources was proposed independently from each other by Waldemar Jungner ( Eng. ) In 1899 and Thomas Edison in 1901 [1] [2] . They used an alkaline electrolyte in nickel-cadmium batteries.
In the manganese-zinc elements, alkaline electrolyte was first used by Canadian engineer Lewis Urry (Eng.) Russian. in the mid-1950s, he worked at Union Carbide ( Eng. ), producing batteries under the brand name "Eveready". Lewis Urry used the workings of Thomas Edison [3] . In 1960, Urry, along with Karl Cordesch and Paul Marshall, received a patent for the construction of an alkaline element [4] .
Typical characteristics of an alkaline battery [5] [6] :
Zn + 2OH - → Zn (OH) 2 + 2e -
Which then decomposes into zinc oxide and water.
Zn (OH) 2 → ZnO + H 2 O
At the cathode, in turn, reactions of reduction of manganese (IV) oxide in (III) occur:
2MnO 2 + H 2 O + 2e - → Mn 2 O 3 + 2OH -
In general, chemical processes inside the cell using KOH as an electrolyte can be described by the following equation:
Zn + 2KOH + 2MnO 2 + 2e - → 2e - + ZnO + 2KOH + Mn 2 O 3
In contrast to the salt cell, the alkaline electrolyte is practically not consumed in the process of discharging the battery, which means that its quantity is rather small. Therefore, in the alkaline element on average 1.5 times more than manganese dioxide.
Work on the improvement of consumer properties of primary current sources led in the sixties to the beginning of the production of alkaline batteries. The name of this type of battery received by the substance of the electrolyte - a concentrated alkaline solution. For the production of electrolyte is used potassium hydroxide, less sodium hydroxide. Today alkaline batteries are often called alkaline batteries because of the inscription on the case of batteries manufactured abroad “Alkaline” (alkali). Other participants in the electrochemical reaction in an alkaline battery are the same as in a salt battery - a negative zinc electrode and a positive manganese oxide electrode. The use of an alkali solution as an electrolyte instead of a salt solution can significantly improve the performance properties of batteries. The voltage of various types of batteries ranges from 1.5 to 12 volts. There are alkaline batteries designed for a variety of discharge currents. Low alkaline batteries have a low discharge current. The battery in case 164 has a capacity of only 8 milliamp-hours, and the disk battery in the PX625A case contains 190 milliamp-hours. The discharge current of these small batteries is measured when working on a high-resistance load. The capacity of the batteries depends on the discharge current. This illustrates the discharge graph of a Duracell MN1500 cylindrical battery in an AA package.
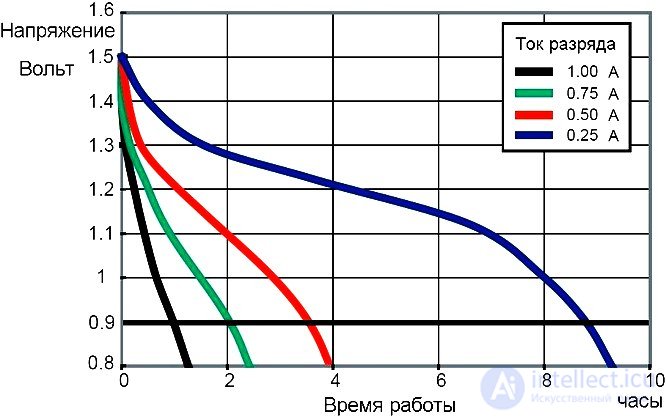
The schedule of discharge of an alkaline battery Duracell MN1500 at a temperature of 210 C.
The graph shows that at a discharge current of 1 amp, the battery can work for 1 hour to reduce the voltage to 0.9 volts, and at a discharge current of 0.25 amp, the battery works 9 hours. There are alkaline batteries with a much larger capacity. Duracell MN903 at a voltage of 7.5 volts operating at a load of 2.7 ohms, at the beginning of the discharge gives a current of 2.7 amperes. Duration of work when the voltage drops to 3.5 volts reaches 18 hours, and with an initial discharge current of 750 milliamperes per load of 10 ohms, the battery can last more than seventy hours.

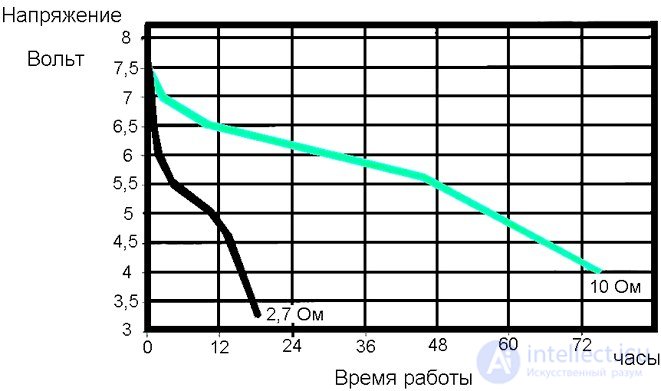
Battery Duracell MN903 and its discharge at a temperature of 210 C.
During the reaction, the electrolyte is consumed very slightly, so it is required less than in a salt battery. The reaction does not emit gases, which allows to exclude from the design of the chamber for the collection of gases. These features of an electrochemical reaction involving an alkaline electrolyte make it possible to better utilize the volume of the battery. The negative electrode is a zinc powder, occupying 20-30% of the volume, and not a glass like a salt battery. The design of the battery makes it possible to significantly increase the service life and increase the maximum current delivered to the load.
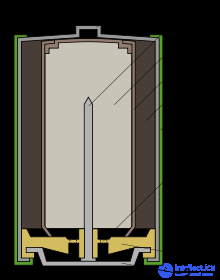
Basic parts of an alkaline element
By construction, the alkaline element is similar to the salt, but the main parts in it are arranged in reverse order. The anode paste (3) in the form of zinc powder, impregnated with a thickened alkaline electrolyte, is located in the inner part of the cell and has a negative potential, which is removed by a brass rod (2). From the active mass, manganese dioxide mixed with graphite or soot (5), the anode paste is separated by a separator (4), also impregnated with electrolyte. The positive conclusion, unlike the salt element, is made in the form of a steel nickel-plated glass (1), and the negative one - in the form of a steel plate (9). The shell (6) is insulated from the cup and prevents short circuits that may occur when several cells are installed in the battery compartment. Gasket (8) perceives the pressure of gases generated during operation. The emission of gases in the alkaline element is much less than in the salt, therefore the volume of the chamber for their collection is also less. To prevent a battery from exploding if used improperly (for example, a short circuit), it has a safety membrane (7). When the gas pressure is exceeded, a rupture of the membrane and depressurization of the element occur - usually the result is electrolyte flow.
To increase the shelf life in the early structures of the elements, amalgamation of zinc powder was carried out; however, this method of extending the shelf life of the elements makes the elements dangerous for domestic use. Therefore, special organic corrosion inhibitors are introduced into modern elements.
The design of alkaline disk batteries is described in the battery design section.


The technological scheme for the production of alkaline cylindrical elements (A-343, etc.) includes procurement and assembly sections. In the procurement areas, parts of the element are made - steel nickel-plated housings, reinforced caps, down-conductors, insulating gaskets, granulated sinter-mixture. In the assembly area, the agglomerate mixture is pressed into the steel bodies and
take the elements. The fabrication of the negative electrode, the filling of the interelectrode space of the element with a thickened electrolyte and the assembly of the element are technologically integrated and are carried out by an assembly machine.
A label is attached to the elements, and after controlling the voltage, the elements are packed.
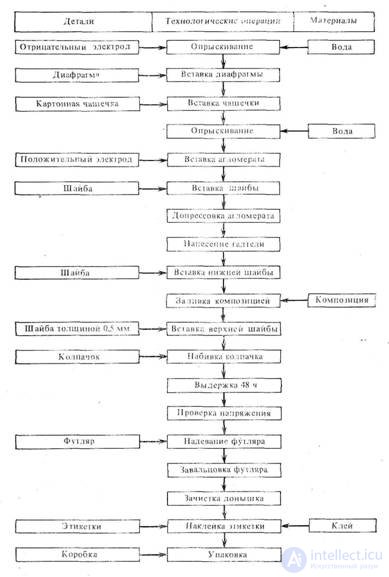
Below is a flow chart for the manufacture of cylindrical alkaline elements.
The assembly of cup-shaped elements consists in connecting the components of the element - zinc and manganese dioxide electrodes, a pasta diaphragm, centering washers into a single structure, sealing the element and appearance design.
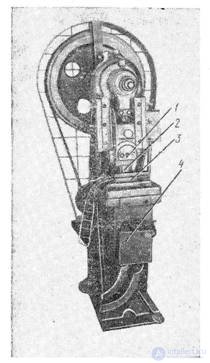
Fig. . Eccentric Press
for punching zinc electrodes and diaphragms of galette elements: 1 — press slider, 2 — punch shank, 3 — die matrix, 4 — box for stamped electrodes
The diagram shows the sequence of individual operations in assembling cup elements No. 373 (“Mars”).
Unlike salt elements, alkaline ones can operate at a higher discharge current. In addition, there is no effect of "fatigue" of the element, when after working at a large load there is a significant voltage drop on the terminals of the element, and to restore its performance it takes a certain time to "rest". However, when a short circuit or installation in the wrong polarity is also possible leakage of electrolyte.
The alkaline element has the same operating voltage as the usual manganese-zinc, but has a large capacity, discharge current, shelf life and operating temperature range. Alkaline elements are available in the same sizes as salt, and therefore can be used in the same devices, for example, in lanterns, electronic toys, portable tape recorders, etc. However, due to the best bit characteristics, it is possible to use them both in devices that consume significant current (photo flash, radio-controlled models) and in devices that consume a relatively small current for a long time (electronic clock).
Thanks to this design, the alkaline element has the following features:
From here, the following advantages and disadvantages can be distinguished:
Due to the design features, an alkaline battery has advantages and disadvantages. The main advantage is the increased discharge current. Compared with salt batteries, alkaline batteries have a significantly increased service life due to a large supply of reagents. Shelf life has also increased and can be several years. After a year of storage capacity is reduced by no more than 10%. Batteries work well over a wide temperature range. During operation, the battery voltage does not change for a long time and decreases sharply only at the end of its service life.
Alkaline batteries are more expensive than salt batteries, their weight is greater due to the design features. Salt battery recovery methods are not applicable to alkaline batteries. Since the capacity of alkaline batteries significantly exceeds the capacity of salt, they must be used in devices with medium and high energy consumption. This electric shavers, players, voice recorders, as well as flash and powerful lights.

Rechargeable alkaline battery, size AA.
There are ways to recharge alkaline batteries, prolonging their service life, but manufacturers are not recommended for such actions, the result of recharging may be the most unpredictable. The possibility of a small charge of alkaline batteries gives the reversibility of the electrochemical reaction that occurs during discharge, but the design does not provide safe charging. Therefore, special rechargeable alkaline batteries have been developed, named as half-volt batteries, rechargeable alkaline batteries or RAM (Reusable Alkaline Manganese, Rechargeable Alkaline Manganese - reusable alkaline manganese batteries) that exclude electrolyte leakage or depressurization that can occur during repeated recharging. A patent for the first generation of such batteries was obtained in Canada. Their release was launched in the late eighties.
The undoubted advantages include the possibility of acquiring a chemical power source ready for operation without pre-charging. If, after purchasing a battery, you first need to charge it, and then use it, then the rechargeable batteries can be immediately installed home appliances, without having a charger at hand. By purchasing a rechargeable battery, we get the primary current source. After the first discharge, the battery can be charged and it becomes a secondary current source. Thus, rechargeable batteries occupy an intermediate position between the primary and secondary current sources. The battery voltage is 1.5 volts and almost does not change until full discharge. These batteries can operate in the mode of discharge currents up to 600 milliamperes. AA battery capacity reaches 2 ampere hours. Their internal resistance is higher than the internal resistance of conventional batteries. Active substances zinc and manganese oxide. Rechargeable alkaline batteries are a good substitute for nickel-cadmium and nickel-magnesium batteries. Charged batteries can be stored in charge for several years. The price of rechargeable batteries is twice the price of ordinary alkaline, but lower than the price of batteries. A long shelf life that exceeds the performance of nickel-cadmium, nickel-magnesium batteries, the absence of harmful substances allows chargeable alkaline batteries to compete with batteries used in household appliances.
If batteries are discharged by less than 25%, then they can be recharged several hundred times to a voltage of 1.42 volts, if they are discharged by more than 25% and less than 50%, then overcharging is possible up to 50 times to voltage level 1, 32 volts. A heavily discharged battery can be recharged no more than 20 times. Batteries can be used in any device that supports standard dimensions (AA, AAA, C, D, and others). Batteries of this type are most suitable for devices with low current consumption in standby mode, which are used periodically. For example: remote controls, portable radio stations, flashlights and others. In some countries, rechargeable batteries are widespread. There are household appliances in which they are recommended in the instructions. Some devices oriented to this type of batteries are equipped with a power supply unit that provides two charging options - a battery or a battery. The power supply of such devices, designed for AA size, maintains a charging current in the range of 10 ... 20 milliamperes to avoid consequences due to possible confusion between rechargeable batteries and conventional ones. At low temperatures, these batteries are suitable only for low-power devices.
Alkaline batteries have many advantages over other types of batteries. This allowed them to gain popularity all over the world.
Comments
To leave a comment
Power supplies for electronic equipment
Terms: Power supplies for electronic equipment