Lecture
Electromagnetic radiation in the human environment is created by both natural and artificial sources.
Natural sources include:
- electromagnetic radiation of the sun, which creates a flux density of power over the atmosphere of the Earth 1400 W / m2 in a wide range of radio frequencies, and on the Earth's surface - no more than 100 W / m2;
- electrostatic (up to several V / m) and magnetic fields (up to 40 A / m) emitted by terrestrial sources;
- electromagnetic radiation caused by natural phenomena on Earth, for example, lightning discharges, turbulent flows in the ionosphere, etc.
Natural emitters create throughout the entire existence of mankind on Earth an electromagnetic background (less than 1 μW / cm2), to which mankind has long adapted itself. Over the past 100 years, an increase in the electromagnetic background level has been observed due to the rapid development of artificial sources of electromagnetic radiation, and they can be divided into two large groups:
- radio systems: radio and television stations, radars, radio navigation systems, radio relay communication lines, mobile communication systems, technological installations in industry, physiotherapy installations, etc .;
- devices that are not intended to radiate electromagnetic energy into space, but in which electrical currents flow, which are sources of parasitic electromagnetic fields: transformer substations, high-voltage power lines, electric stoves, electric heaters, refrigerators, televisions, microwave ovens, etc.
Electromagnetic fields of different wavelength ranges are biologically active and can affect living organisms in different ways, including humans.
The human body consciously responds only to electromagnetic waves of the optical range (eyes, / - 1014 Hz), while for other wave bands people do not have sensitive organs. However, as practice and studies show, the following organs are most sensitive to electromagnetic radiation: eyes, central nervous system, cardiovascular, harmonious and reproductive systems. Despite numerous studies of the effects of electromagnetic fields on human health, to date there is only scattered information about the effect of the respective electromagnetic wave ranges with the corresponding power flows and exposure time. Therefore, to ensure safety in all countries of the world, standards for safe exposure to electromagnetic radiation have been developed and adopted.
The following parameters were chosen as parameters with the help of which the electromagnetic field effect on the human body is evaluated:
- Power Density (PD) - power flux density P (mW / cm2);
- Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) - specific absorption capacity (degree of specific absorption): SAR (mW / g, W / kg);
- Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) - the maximum possible exposure (usually expressed in units of PD (mW / cm2);
- exposure time t (min).
SAR and PD values are related by the following simple relation:

Thus, it is possible to use the PD and SAR values as standard parameters, however, the SAR value is more suitable for estimating the levels of electromagnetic field effects that cause tissue heating processes, while the PD value allows for evaluating the effects of weak and strong electromagnetic fields. .
It should be noted that usually the standard safety standards are divided into two groups:
- safety standards for personnel working with installations emitting electromagnetic fields;
- safety standards for the public.
Therefore, below we will consider the standard norms adopted in European countries, the USA, Japan and Russia for the two groups mentioned.
Staff safety standards
Consider the safety standards of being in the zone of electromagnetic radiation for personnel, developed by various institutes and committees of countries of the world.
1. CENELEC {Committee European de Normalization Electro-technique) ES 59005, October 1998. According to the SAR value in the frequency range from 30 MHz to 6 GHz:
- for tissues of arms, legs, the average SAR value for a time period of ^ 6 min should not exceed the values: SAR ^ 20 mW! g (for fabric t = 10 g);
- for other tissues (and not limbs), the average SAR value for m ^ 6 min should not exceed SAR ^ 10 mW! g (for fabric m = 10 g);
- for the whole body of personnel working in the radiation zone, at m ^ 6 min, the average value should be SAR ^ 0.4 mW! g.
2. ANSI / IEEE C95.1 - 1992 (ANSI - American National Standards Institute) / (SHEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers):
- in the frequency range 300 ... 3000 MHz, the PD value is determined by the approximate formula - 77 ^ \ f (MHz)! 300 (MHz)], with an exposure time of t ^ 6 min, that is, for the frequency / = 900 MHz, the value of P < s 3 mW / cm2, this is the allowable PD level for personnel monitoring equipment and radiation levels;
- for a similar case, only with uncontrolled radiation, the value of PD will be: П «S f / 1500 = 900/1500 = 0.6 mW / cm2 with t <6 min.
3. FCC (Federal Communication Commission), 1996:
- MPE for the case of controlled radio equipment in the frequency range 300 ... 1500 MHz, the PD value is determined by the approximate formula: P f / 300 = 900/300 = 3 mW / cm2 with m ^ 6 min.
4. Latvian Standard LVS ENV 50166.2: Elektromagnetiska lauka iedarblba uz cilveku. Augstas frekvences (10 kHz lldz 300 GHz):
- MPE for the range 400 ... 2000 MHz: P <G20.4 / (MHz) = 20.4 * 900 = 18360 mW / cm2 (an extremely large value, since when P ^ 100 mW / cm2 the temperature of a human tissue at t 6 minutes rises above 41 ° С).
- admissible PD rate in the range of 400 ... 2000 MHz: P / 400 (MHz) = 900/400 = 2.25 mW / cm2 with an exposure time of 6 min.
So, the allowable values of electromagnetic exposure of the entire body of personnel in the frequency range used by the mobile communication should not exceed when the exposure time is 6 min: by PD: P <(0.6-3) mW / cm2; no SAR: SAR £ 0.4 mW / g.
It should be noted that in Russia for personnel working in the zone of electromagnetic radiation for a time of t 20 min, the value of PD according to the standard should not exceed P «S1 mW / cm2.
Electromagnetic exposure safety standards for the public.
The safety standards for the population are usually about 5 (and preferably 10 times) should be less than the permissible standards adopted for staff. Consider the permissible safety standards of electromagnetic radiation for the population, adopted in various standards.
1. CENELEC ES 59005,1998:
- for the tissues of the feet, hands, etc. The average SAR value during the time t <s 6 min should not exceed the values: SAR <r4 mW / g (at t = 10 g);
- for other tissues (muscles, etc.), the average SAR value over time t 6 minutes should not exceed the values: SAR <, 2 mW / g (at t = 10 g);
- for the whole human body with m <s 6 min, the average SAR value <g0.08 mW / g, that is, 5 times less (0.4 / 5 mW / g) than for the staff.
Similar SAR values are adopted in the Latvian standard LVS ENC 50166.2: 1995.
2. ANSI / IEEE С95.1-1992: in the frequency range 300 ... 3000 MHz, the PD value at the exposure time is 30 min П ^ f / 1500 (MHz) = 900/1500 = 0.6 mW / cm2.
3. FCC, 1996: MPE for the public with uncontrolled radio equipment:
MPE = P = [f / 1500 (MHz)] - 900/1500 = 0.6 mW / cm2 for x <> 30 min.
4. Latvian Standard LVS ENC 50166.2: 1995: for the frequency range 400 ... 2000 MHz, the PD value at exposure time t 6 min is defined as П = / (MHz) / 200 (MHz) W / m2, i.e.
- at / = 900 MHz: П g 4.5 W / m2 = 0.45 mW / cm2 - 450 μW / cm2;
- at / = 1800 MHz: P <g9 W / m2 = 0.9 mW / cm2 - 900 μW / cm2;
- at f = l900 MHz: P <g 9.5 W / m2 = 0.95 mW / cm2 = 950 μW / cm2.
5. Standard of Russia. With continuous radiation and the constant presence of the population in the electromagnetic field in the frequency range 300 MHz ... 3000 GHz: the value of PD should not exceed P ^ 10 μW / cm2.
Thus, for the public, a safe level of electromagnetic radiation in the frequency range used in cellular mobile communication systems (900 ... 1800 MHz) is:
- no SAR ^ 0.08 mW! g ^ 80 μW / g;
- by PD P ^ 10 m kW / cm2 (Russia);
- no PD P z400 ... 1000 μW / cm2 (Europe, USA).
It should be noted that the values of PD from 400 to 1000 μW / cm2 are large enough for the population to remain permanently in the zone of electromagnetic radiation. They should be reduced by two orders of magnitude, i.e. from 4 to 10 μW / cm2 [7.20]. It should be noted that in Italy the level of a safe background for the population should be 1.5 µW / cm2.
The levels of electromagnetic radiation of mobile phones.
In tab. 7.2 shows the maximum and minimum SAR values, experimentally found by DoMode.com specialists for mobile phones manufactured by leading companies.
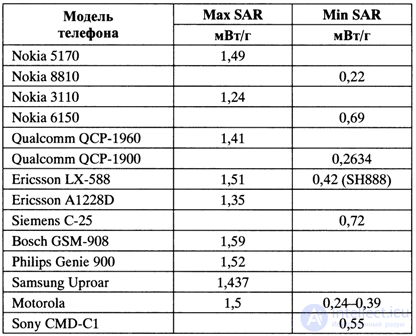
As follows from a comparative analysis and permissible SAR values, which were discussed above, the SAR safe level should be equal to or less than 80 µW / g.
SAR values for mobile phones are in the range from 220 to 1600 µW / r, which indicates that the safe background effect of the electromagnetic field is exceeded from 3 to 20 times.
The maximum value of SAR ^ 1.6 mW! G for mobile phones exceeds the permissible norms defined by the standards:
- ANSI / IEEE: 900/1500 = 0.6 mW / cm2; 1900/1500 = 1.26 mW / cm2;
- CENELEC: SAR * 0.4 mW / g.
Therefore, when mobile phones are used by mobile cellular subscribers at cell borders (that is, at a significant distance of MS mobile stations from basic BTS, for GSM standard at distances of 10 ... 30 km from BTS), when the mobile station transmitter operates at maximum power , it is advisable to have a short talk time mode, not exceeding 1 ... 2 minutes.
Comments
To leave a comment
GSM Basics
Terms: GSM Basics