Lecture
The term “multiple access” is associated with the organization of sharing of a limited portion of the frequency spectrum by many users. Currently, five options for multiple access are known:
- FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) - multiple access with frequency division communication channels;
- TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access ) - multiple access with time division of communication channels;
- CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access ) - multiple access with code division of communication channels;
- SDMA (Spase Division Multiple Access ) - multiple access with spatial separation of communication channels;
- PDMA (Polarization Division Multiple Access ) - multiple access with polarization division of communication channels.
Of practical interest for cellular mobile communications are the first three of them.
The fourth method is actually used in the implementation of the principle of frequency reuse, in particular when dividing cells into sectors using directional antennas, but this is not referred to as a multiple access method.
 Since the GSM standard uses TDMA, partly in combination with FDMA, consider the first two methods of multiple access.
Since the GSM standard uses TDMA, partly in combination with FDMA, consider the first two methods of multiple access.
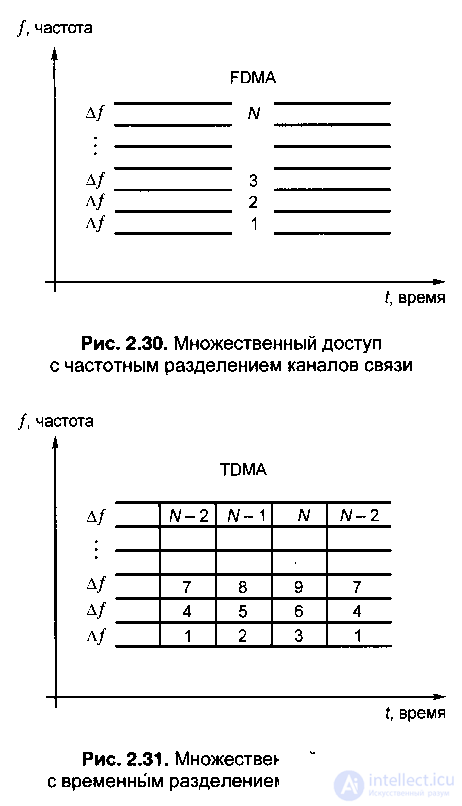
1. The FDMA method is a multiple access with the separation of communication channels by frequency, the easiest to implement, since in this method each user is allocated a separate frequency band A / (frequency channel) for the duration of the communication session, which he uses all
time (Fig. 2.30). The FDMA method is used in all analog cellular communication systems (first generation), while the allocated frequency band A / is 10 ... 30 kHz. The main disadvantage of FDMA is the insufficiently efficient use of the frequency band allocated for communication.
2. TDMA method - time division multiple access, consists in the fact that each frequency channel
divided between users in time - frequency channel
in turn, it is provided to several users for certain periods of time, that is, for example, several physical channels are implemented in one frequency channel. As an example in fig. 2.31 presents the case where each frequency channel is divided between three users.
The practical implementation of the TDMA method requires the conversion of an analog speech signal into a digital sequence, which is subjected to coding and encryption, which is necessary to protect information from errors during transmission and reception.
Comments
To leave a comment
GSM Basics
Terms: GSM Basics