Lecture
The process of abstract design consists in the transition from the source firmware (or a set of firmware) to one of the traditional forms of the automaton specification: matrix, table, or graphical (graph). The stage of transition to the task of the automaton is also necessary, since ensures the implementation of the structural design process by using a sufficiently efficient apparatus of the theory of finite automata.
Structural design is the process of transition from the above task forms to its functional scheme.
So, an abstract automaton at the input has a certain sequence of input signals, depending on which it goes from one state to another, producing a certain sequence of output signals (Fig. 5.1).
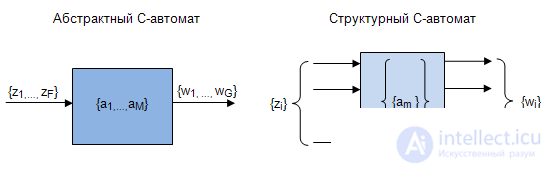
The structure of the machine takes into account the structure of the input and output signals, that is, their specific representation in the form of binary vectors. The states of the automaton are also encoded by binary vectors.
Consider the combined automaton (Fig.5.2). Every state  abstract automaton is encoded by a binary vector:
abstract automaton is encoded by a binary vector:
 ,
,
 ;
;
 - the number of states of an abstract automaton;
- the number of states of an abstract automaton;
 - the number of memory elements.
- the number of memory elements.
Input and output signals are also represented by binary vectors:
 ,
,  ,
, 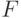 - the number of input signal abstract machine,
- the number of input signal abstract machine, 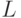 - the number of inputs of the structural machine;
- the number of inputs of the structural machine;  ,
,  - the number of output signals of type 1,
- the number of output signals of type 1, 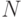 - the number of outputs of the 1st type of structural automaton;
- the number of outputs of the 1st type of structural automaton;  ,
,  - the number of output signals of type 2,
- the number of output signals of type 2, 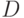 - number of outputs 2 types of structural automaton
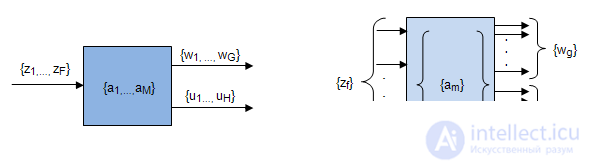
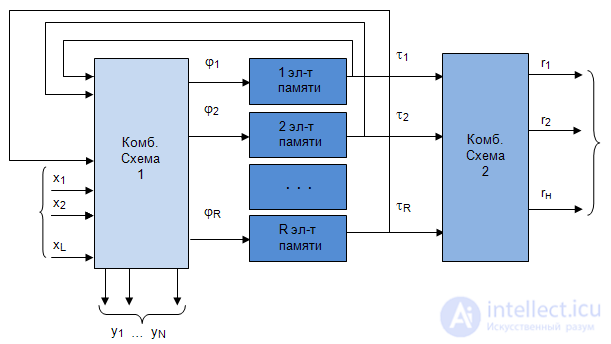
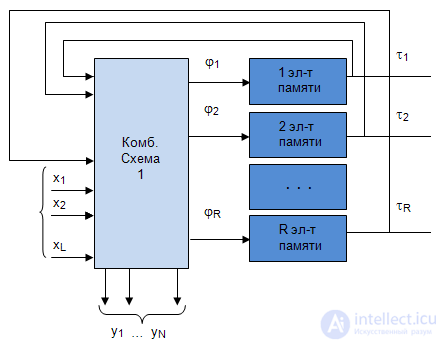
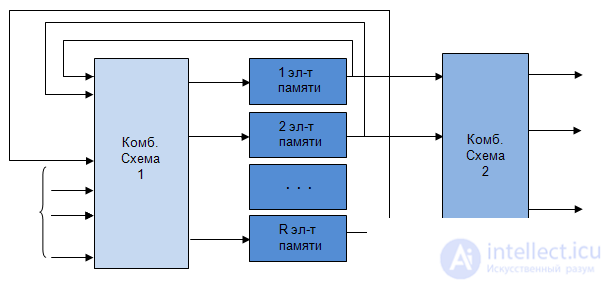
- number of outputs 2 types of structural automaton Structural diagram 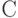 an automaton with the canonical method of synthesis appears to consist of three parts: two-combination schemes and the memory of the automaton (Fig. 5.3). Combination scheme 1 is designed to form the excitation functions
an automaton with the canonical method of synthesis appears to consist of three parts: two-combination schemes and the memory of the automaton (Fig. 5.3). Combination scheme 1 is designed to form the excitation functions 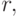 arriving at the inputs of the memory elements, and output signals of type 1
arriving at the inputs of the memory elements, and output signals of type 1 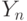 depending on input signals
depending on input signals 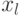 and signals from the outputs of the memory elements
and signals from the outputs of the memory elements 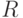 .
.
Combination scheme 2 is designed to generate output signals of type 2 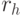 as functions from the outputs of the memory elements
as functions from the outputs of the memory elements 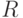 .
.
Since the type 2 signals are absent in the Miles automatic machine, then, accordingly, there is no combinational circuit 2 in the structural diagram. The scheme of the Mile structural automaton is shown in Fig. 5.4.
In Moore's automaton, type 1 signals are absent, therefore, in the block diagram in combinational circuit 1, there are no output signals of type 1 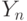 . The scheme of the structural automaton of Moore is shown in Fig.5.5.
. The scheme of the structural automaton of Moore is shown in Fig.5.5.
Thus, in order to synthesize a structural automaton, it is necessary to synthesize two combinational circuits using a system of canonical equations. The system of canonical equations for  -automat looks like this:
-automat looks like this:
 ;
;  ;
; 






 , (
, (  - the number of states of the abstract automaton) and we encode the states of the abstract automaton (Table 5.1).
- the number of states of the abstract automaton) and we encode the states of the abstract automaton (Table 5.1). a m \  |  |
|---|---|
| a 1 | |
| a 2 | |
| ... | |
| a M |
 , (
, (  - the number of input signal abstract machine);
- the number of input signal abstract machine);  ; (
; ( 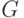 - the number of output signals of type 1);
- the number of output signals of type 1);  , (
, ( 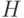 - the number of output signals of type 2) and encode the input (table 5.2) and output signals (table 5.3) and (table 5.4) of the abstract automaton.
- the number of output signals of type 2) and encode the input (table 5.2) and output signals (table 5.3) and (table 5.4) of the abstract automaton. | z f / x 1 | x L x 1 x 2 ... x 1 |
|---|---|
| z | |
| z | |
| ... | |
| z |
| w f / y 1 y 2 ... y N | y 1 y 2 ... y N |
|---|---|
| w 1 | |
| w 2 | |
| ... | |
| w G |
| u h / r 1 r 2 ... r D | r 1 r 2 ... r D |
|---|---|
| u 1 | |
| u 2 | |
| ... | |
| u H |
 ;
;  ;
;  ;
;  ;
;  ;
;  ;
;  ;
;  ;
;  ;
;
Comments
To leave a comment
Theory of Automata
Terms: Theory of Automata