Lecture
Web hosting is the physical placement of web pages on a server. This is a virtual analogue of renting a room, but space is leased on a disk, which is calculated in megabytes. The quality characteristics depend on where the site is located, so it is important to choose the best site for the site that meets the criteria of reliability and stability.
Depending on the country of location, hosting may be, for example: Ukrainian (the technical platform is located in Ukraine), Russian (in Russia), American (in the USA), etc.
Hosting can be divided into free and paid.
Free hosting provides a hosting provider free disk space to host the site on the Internet. Free hosting, as a rule, exists due to advertising placed on the pages of sites. This advertisement can be in the form of banners, text links, advertising frames, pop-up windows, although there are free hosting services that do not place any advertising on the websites.
Dear companies, as a rule, do not use the services of free hosting, as it has features that are unacceptable for a serious Internet project.
Thus, free hosting is suitable if the novice developer needs to host a low-value, small and static HTML project. For more serious projects, if the site is aimed at a long and stable existence, it is worth thinking about reliable and fast commercial hosting.
In a paid hosting, the site owner pays a certain amount for the use of disk space and services to him services.
Web hosting is the most affordable service for hosting simple websites. During web hosting the user has the opportunity to upload via FTP the source codes of his site to the server of the hosting provider and get access to the total for all users of the MySQL DBMS. There are no additional functions usually in the web hosting service - server and software settings, the availability of available applications and supported programming languages are beyond the user's control. One of the negative aspects of this is the impossibility of self-diagnosis of some of the possible problems without contacting technical support.
VPS (Virtual Private Server) is a virtual server, for the operation of which virtualization is used based on the operating system. The most commonly used implementations are OpenVZ, FreeBSD Jail and the like. The user has a separate software environment (called userspace) and superuser rights, but cannot change the kernel or OS family (change Linux to FreeBSD), use some network functions. Because of this, there are restrictions on the versions of guest operating systems, and often the constant availability of the stated resources cannot be guaranteed. Note that the latter is more dependent on the policy of the hosting provider.
VDS (Virtual Dedicated Server) - virtual servers with physical, constant allocation of memory resources, disk space and CPU core. To support VDS operation, servers with hardware virtualization support and KVM, XEN, VMWare and other technologies are used. With this technology, physical elements of servers are emulated, which in most cases allows installing any x86-compatible OS (up to OS / 2 or QNX-specific) and making any system modifications of the operating system in a guest machine and even changing BIOS settings. This technology we use for our SSD VDS. The advantages of hardware virtualization are obvious - a fixed allocation of resources when you start a virtual machine, data security, endless configuration options.
Thus, that VDS, that VPS are “virtual” solutions, when there are several virtual ones on one physical machine. That is, these are slightly different, but related solutions, where the resources of one server are divided between virtual machines of several users.
But the dedicated server (dedicated server, DS, dead server, dedic) is a real computer with a power supply, case, cooling system and other necessary elements installed in a rack and included in the switch. This is not a “virtual”, but a physical, tangible device, where the user gets all the available resources for indivisible use - bandwidth of the bus, memory, disk and so on. In our data centers we use modern dedicated servers optimized for round-the-clock work with a heavy load.
ps You can give an analogy about the above more simple, non-technical language. Hosting is a room in a student dormitory, where everyone uses all the facilities within the framework of strict rules. VPS is a communal apartment, where every tenant has his own private room, but the kitchen remains shared. VDS can be imagined as an apartment building - everyone has enough space, but there are neighbors behind a common wall. A dedicated server is a comfortable, spacious cottage with a private garden and barbecue.
Another type of web hosting is colocation.
Colocation, colocation (from fr. Colocation - co-habitation, English collocation - location nearby, in turn from lat. Collocatio (n-) - put together [2] ) is a service consisting in that the provider places the equipment of the client on its territory (usually in a data center), connects it to electricity, provides maintenance and connection to communication channels with high bandwidth. Sometimes this equipment does not belong to the client, but is rented to them from the same provider, in this case the service is called “dedicated server rental”.
Such an arrangement allows saving on the organization of the communication channel from the provider to the client - the last mile. Most often, colocation is provided by servers designed to maintain websites and other network services with a large volume of traffic, as well as equipment that requires reliable access from many points, for example, VPN hubs, IP-telephony gateways.
Usually, in addition to proper placement of equipment and connection to a communication channel, this service also includes:
Other related services (for example, data backup, information protection) are usually provided by the operator for a fee.
Some tend to classify collocation as a subtype of hosting, while others consider it an independent service.
To remotely manage your own resources on the Internet, there are two types of access to hosting:
An FTP client is special software that simplifies user access to FTP servers. All data received from the server using an FTP client is displayed as a list of files and folders, just like the display of local resources on a computer.
The role of such a tool can be played by a file manager, a browser, or a standalone FTP client. It’s difficult to say exactly what is best for a particular user, since it all depends on tasks and preferences.
If you are too lazy to spend time studying new software, then you can restrict yourself to the usual file manager (of course, provided that FTP support is implemented in it), in which all operations with files and folders on remote servers are performed exactly the same as on local computer. However, the ability of file managers to work with FTP servers is limited by the minimum necessary, although it is quite enough to download files from the server and upload them to the server, as well as to remotely rename and delete files / folders and edit text files.
The functionality of standalone FTP clients is usually much broader - they provide for downloading / uploading files in a more secure mode (due to the support of the corresponding protocols, various encryption options, etc.) and with much faster speed. The latter is achieved due to the multithreading of downloading and file compression on the fly. In addition, the process of downloading / uploading files to FTP clients is more convenient, since they often implement one or the other option of quick access to frequently visited FTP servers, it is possible to connect to several servers at the same time, work on schedule can be provided, etc. .
Regardless of how you communicate with the FTP server: using an FTP client, a browser or a file manager, you will need to log in. For authorization on the FTP server, you must enter a username and password.

SmartFTP Client is an advanced multilingual FTP client. Presented in two editions: Home and Professional. Home users are designed for Home edition, it has basic functionality. SmartFTP Client Home provides secure connections to FTP servers with support for 128-bit TLS / SSL encryption and allows you to view their contents with regard to filtering (including in the form of thumbnails). It can work with several servers (or several connections to one server) at the same time, is able to recover interrupted download processes and can work on a schedule. This FTP client can load data into several streams (this option is disabled by default and enabled through the properties of the downloaded file) and ensures their compression during transmission, which saves time and traffic. It also provides remote editing of data on FTP servers and their synchronization between local and remote directories. Data transfer between servers (FXP) is allowed.
The demo version of the program (there is a Russian-language localization) is fully functional and operational for 30 days, the cost of the commercial version of Home is $ 36.95.

FileZilla is a multi-platform open-source FTP client with enough functionality for many home users. The program has an advanced level of security (support for the SSL (Explicit / Implicit) and SSH2 protocols, ability to work through a firewall, GSS authentication and data encryption using Kerberos) and stable operation. FileZilla provides viewing of the contents of FTP servers (at a given moment it can work with only one server), can download data into several streams and supports swapping. Allows you to create folders on FTP servers, remotely change the names of files and folders, delete and modify deleted files.
The program (there is a Russian-language localization) can be downloaded and used completely free of charge.
File managers are indispensable for performing various operations with disks, folders and files. However, in addition to their direct assignment, they can often be used to work with FTP servers due to the presence of built-in FTP clients.
The built-in FTP clients of file managers support only the main types of FTP servers (Unix, Windows NT, VMS and PC / TCP, partly OS9 and AS-400). If they cannot be used to access the server prompt (that is, the list of server directories is not displayed in the corresponding window), you will need to contact one of the external FTP clients discussed above.

The main purpose of Total Commander file manager is convenient work with disks, files and folders. And support for working with FTP servers is just one of the additional features of this application. The built-in Total Commander FTP client allows you to download files to your computer and upload them to an FTP server, as well as transfer files between FTP servers directly (FXP). And thanks to the support of the SSL / TLS protocol, such copying of files can be done in protected mode.
The demo version of the program (there is a Russian-language localization) is fully functional and operational for 30 days, the cost of the commercial version is $ 38.
Warning: connecting to ftp through a browser is not recommended, as in any browser there are a lot of holes through which intruders enter the site. If ftp access comes from the browser, then you should install an antivirus and, if possible, a firewall on your computer.
To connect to an ftp-server through a browser, you need to specify: login, password and IP-address. The hoster sends these data to the mail after activating the account (the purchase of the hosting services). The listed data must be entered in the browser’s command line and the connection to the site will occur.
It looks like this: ftp: // your_login: your_password @ ip_address Example of this address: ftp: // example: 5356@12.133.911.20If the entered data is correct and the connection to the server is established, the root folder of the site will open in the browser, which will display the list of site files.
Here is an example of the root folder of a specific site after connecting to an ftp server via a browser:
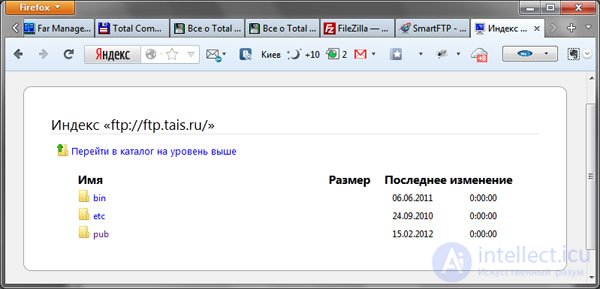
Usually, site files are stored in the www or public_html folder.
Basic FTP options
host (or un)
port (21 by default)
FTP operating modes - active passive (several ports or 2 ports are used)
coding (mappings)
password
To access a dedicated server, SHH protocol or IP KVM, KVM technology is used.
PuTTY is a client program for working with network protocols SSH, Telnet, SCP, SFTP, for connecting via a COM port and ZModem, a utility for generating RSA and DSA digital SSH keys.
The most popular ways to use PuTTY are remote administration of Linux, connection to virtual servers VDS / VPS using SSH protocol, setting up network routers via a serial port, connection to remote Telnet terminals.
PuTTY works on both Windows and Linux. And in the list of third-party modifications, you will find the SSH client version for Mac OS X, iPhone, Android, Windows Mobile, Symbian.
PuTTY is a free open source application, contains the implementation of the network protocols SSH, Telnet, Rlogin, and is distributed under the Open Source MIT license. The original version of PuTTY is written and maintained by Simon Tatham. The Russian version is developed by the site PuTTY.ORG.RU.
Screenshots of the Russian version of PuTTY:
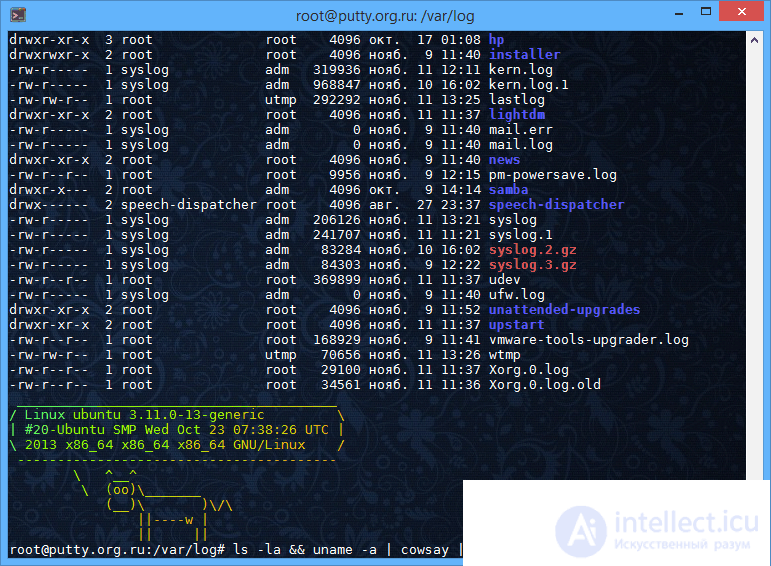
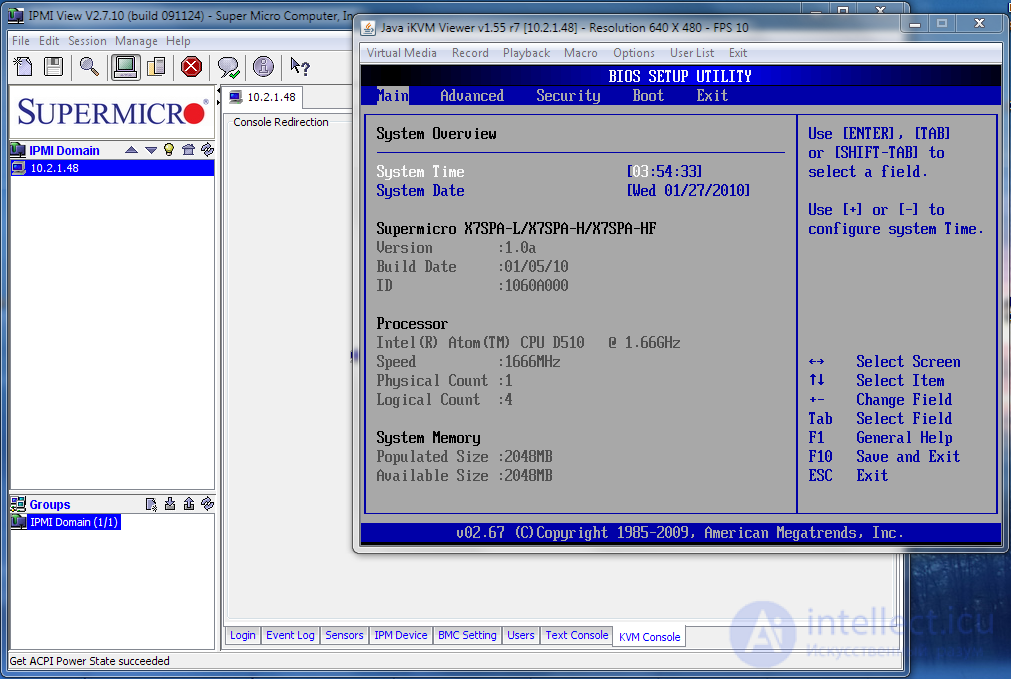
KVM (keyboard + mouse + video) is a device that allows you to access a remote dedicated server on the Internet, even if your server is turned off or you cannot access the server for other reasons. IP KVM эмулирует клавиатуру, монитор и мышь устройства, а также виртуальный носитель (виртуальный диск в .iso или другие форматы и т.д.) доступные через сеть. Таким образом, обычный веб - браузер с Java плагином или Flash плагином (или утилитой) подключается к KVM и может полностью управлять, перезагружать, включать и выключать сервер, настроить сервер даже на уровне BIOS.
С помощью KVM вы можете отслеживать сообщения консоли сервера на экране или подключиться на сервер с помощью консоли , как если бы вы физически были на сервере. Кроме того , вы можете удаленно подключить виртуальные носители (например , компакт- диск или DVD в виде образа .iso или других форматах) и удаленно установить любую операционную систему, загрузить и запустить Live CD / Rescue CD для восстановления ОС, или копировать файлы. На сервере это виртуальное устройство выглядит как обычный, внешний CD / DVD - диск , подключенный через USB. Для обеспечения постоянного доступа у устройства, часто, нестолько блоков питания( включая для горячей замены) и дополнительный аккумулятор. Дополнительая сетевая карта имеет автономное питание даже при выключенном компьютере, и собственный BIOS. Таким образом сервер имеет 2 независимых сетевых интерфесов, один из который включен всегда.
IP KVM позволяет контролировать и настроить сервер через сеть(локальную или глобальную) таким же образом, как если бы у вас был физический доступ к серверу.
Comments
To leave a comment
Fundamentals of Internet and Web Technologies
Terms: Fundamentals of Internet and Web Technologies