Lecture
To organize the interaction of devices in a network, the International Organization for Standardization or simply ISO (International Organization for Standardization) approved a model describing the integration of computers into a network.
The model was named OSI (Open System Interconnection), which translated into Russian means - the interaction of open systems.
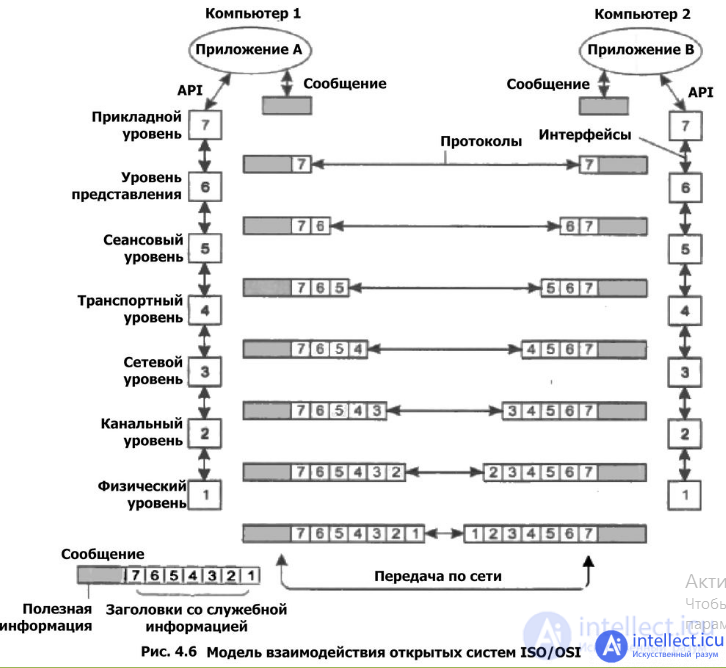
The OSI model is based on seven hierarchically arranged levels, over which all the functions required for the transfer of information are distributed. The number seven was not chosen by chance, since a smaller number did not give special advantages, and the number of levels more than seven, due to the occurrence of vertical costs, led to unnecessary consumption of system resources.
When developing the ISO / OSI standard, we did not think about the concept of real time and did not predict the heyday of field buses. The site https://intellect.icu says about it. But, despite this fact, only later, it was accepted that the OSI model is quite suitable for describing the functioning and industrial networks of the field level.
The lower level of the OSI model, the physical one, is the transmitting one; it describes the mechanical and physical parameters necessary for data transmission. The next layer, the data link layer, manages the interaction of networks at the physical layer and controls the occurrence of errors. At the network level, routing is built, or in other words, a path is chosen. For example, in the telephone network, at the network level, a route is selected depending on the dialed phone number, thereby correct switching of subscribers occurs. The transport layer controls information flow and controls the correct order of data packets. The next, fifth in order, session level serves to organize the simultaneous exchange of data between different subscribers. At this level, the participants of the session are identified, and if the session is interrupted, it is resynchronized. The representative layer, or as it is also called the presentation layer, coordinates the language of symbols transmitted in data packets, and is also responsible for encrypting and decrypting information. And finally, the seventh, application layer can be called a kind of interface to the outside world. It represents a set of custom communication services. You should be familiar with the application layer protocols, for example: HTTP, FTP, POP3, SMTP and many others.
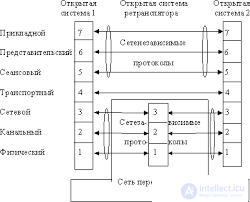
Also, in this article it will be appropriate to mention the differences between concepts such as interface and data transfer protocol.
Comments
To leave a comment
Fundamentals of Internet and Web Technologies
Terms: Fundamentals of Internet and Web Technologies