Lecture
Currently, subscriber sets in electronic PBXs are largely unified and run on microelectronic elements (except relay and transformer circuits). The full list of functions for a set made on the basis of electronic circuits is usually denoted by the abbreviation BORSCHT:
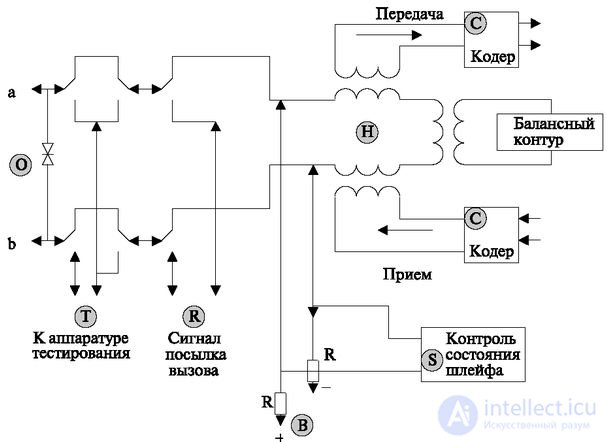
The scheme of such a set is shown in Fig. 2.19. The terminal’s power supply (for example, microphone and logical part) is supplied from a stationary battery of 60 V with a grounded positive pole (function B). (function S).
The protection functions against hazardous voltages (O) are performed at two points of the subscriber loop: at the station's cross-connect and in the subscriber set.
The first protects against short-term overvoltages (for example, from lightning voltage falling on the line). Therefore, the protection devices in the cross-country got the name of "thunderbolts". They work "for breakdown", i.e., under the influence of overvoltage, they short circuit the entrance of the station and, when the pulse disappears, they restore the normal circuit again.
In the subscriber set, the protection works on the principle of a fuse, i.e., as the current or voltage increases, the protection insert “burns out” and terminates the subscriber loop. In electronic stations, one of the main problems of protection is that the speed of protective devices must be greater than the speed of the main circuits. In other words, protection should work before the work of the main circuits is disturbed. In this regard, high requirements are placed on the performance characteristics of protective circuits.
The reaction time for impulses with very stringent requirements for the duration of the leading edges and the blocking time of the main circuits is stipulated.
The R function provides a ring-back signal. The magnitude of the voltage of this signal is 90V. The parameters of this signal and possible options for its implementation were considered in the first section. The most common current signal of alternating current frequency of 25 Hz. To prevent the relay contacts from burning out, its switching off and on is synchronized with the moments when the signal is zero.
Encoding and decoding (Function C). It takes place with the help of a coder and a decoder, made in the form of one device (codec).
The implementation of the functions of the differential system (function H). The function is implemented using transformer circuits. The principle of its work was shown in the book [7] (see. Fig. 6.1). The balance circuit, built on resistors and capacitors, can be programmatically adjustable and tune to a specific line.
Test subscriber lines (function T). The control parameters of the subscriber line by using the contacts of two relays. They allow you to connect test equipment to the subscriber line or in the direction of the station.
Test equipment (total per group or per station) allows monitoring the parameters of the subscriber line or conducting testing of the station from the subscriber side, connecting the subscriber, simulating the load, etc.
The subscriber bundle is one of the most popular devices of the station; therefore, much work is being done on its micro-miniaturization. Chipsets that implement its functions are abbreviated as SLIC (Subscriber Line Interface Circuit).
Comments
To leave a comment
Telecommunication Services and Devices
Terms: Telecommunication Services and Devices