Lecture
Это окончание невероятной информации про организационное развитие.
...
"critical mass" of employees contributing to these changes, while the value of the "critical mass" is 1 / (7 ± 2) of the total number of employees in the organization.
11 Limitations of the proposed approaches:
- A description mainly of recommendations that do not imply technology implementation;
- Orientation mainly on the head, referring to the managerial level of influence;
- Presentation of generalized rules of work on the support of the organization, in an insufficient degree taking into account the specifics of innovative activity.
The basis of the procedure and tools of practical work, along with theoretical principles, are the following practical areas of work;
- justification of the selection of personnel for participation in innovation, the creation of an information system;
- preliminary and subsequent organizational diagnostics at the personal and group levels, the characteristics of innovation, but designated areas;
- the use of special gaming technologies aimed at designing, detailing and accepting the future (changes) or changing the current situation;
- the use of training technologies aimed at the formation of certain skills and abilities for the development of innovative abilities, the formation of readiness for perception and participation in innovation.
The empirical complex model of managing innovations in an organization has the main characteristics:
1. An integrated approach that arises from the complexity of innovations and their types; the complex nature of resistances and their causes, which are at different levels of research and the diversity of organizational tasks and goals.
2. Work at the group level. Most of the organizational innovations we are considering in the field of management, organizational structure, social policy affect groups within the organization’s collective. The impact at the group level is determined by the designated provisions of social psychology: the desire to change people must be based on the group dynamics. In this regard, a small group can
considered in three qualities: environment, object, agent of change. Based on the quality of the agent of change, through a small group it is more effective to influence the organization as a whole. A group can be used as an innovative core - a group conductor of change.
3. Focus on prevention.
4. Modularity and dynamism.
The main modules of the model :
Diagnostic primary module - a mandatory module at the personal, group and organizational levels. The diagnostic module GPT most capacious and includes certain blocks. Blocks of the diagnostic module can be used in the complex, or separately, depending on the organizational situation.
There are basic blocks of the diagnostic module.
1. Objective data about the organization ("passport data"):
- type of ownership:
- specific activities and directions;
- time of existence, reorganization;
- personnel: quantitative composition, age composition, sex composition, education;
- organization structure (including divisions, hierarchy of subordination, personnel);
- existing training programs;
- ongoing innovations.
Methods - survey, interview, document analysis.
2. Specificity of innovation, a request to a consulting psychologist:
- formulation of the problem, the basis of its statement;
- who and how set the task;
- how big is the task;
- how unique the task is;
- highlighting the specifics of innovation;
- typology of innovation: globality, depth, focus, relevance, utility.
Methods - questioning, interview.
3. Innovative organization environment (readiness):
- mission and purpose of the organization;
- development strategy, immediate and distant prospects;
- openness to change;
- norms and traditions;
- staff motivation mechanisms;
- pathology of the organization.
Methods - diagnostic structured interview, expert assessment, reflection (7C scheme, basic organization values, organization dysfunctions, managerial errors), projective methodology - organization metaphor; SWOT analysis.
4. The presence of position in the organization, group distribution:
- who will help and hinder innovation;
- the attitude of different categories of workers to innovation;
- the main goals of the innovation participants;
- who is interested in what outcome of the situation and why;
- what key figures do in innovation;
- Whom do the intrusive changes concern.
Method - positional analysis, sociometry.
5. Abilities, skills and abilities required for innovation:
- what skills and abilities are necessary for the successful work of each category of specialists (subjects of innovation);
- what skills need to be developed.
Methods - expert assessment, assessment center, structured observation.
Based on the results of the application of the diagnostic primary module, the defining modules are arranged according to their relevance.
Formative Module 1: Innovation Workshop. It is one of the main modules of GPT. It is carried out at the group level (subjects of innovation take part), influences at the personal, group, organizational level.
The main tasks of the module:
- familiarization of the subjects of innovation with the fact of innovation and specificity;
- development or correction of aspects of innovation;
- assignment of innovation at the personal and group levels;
- division of responsibility for innovation.
Methods - An innovative workshop may include diagnostic methods.
Following the results of the use of the module, subsequent training modules are formed.
Forming module 2: cycle of training programs. The module consists of a number of training programs aimed at the formation of knowledge, qualities, skills and abilities necessary for the adoption and maintenance of innovation. It is carried out at the group level. Influences personal, group and organizational levels. The focus of programs is presented in Table. 3.4.
Table 3.4
Forming module tutorials
|
Direction |
Innovative effects |
Impact level |
Methods |
|
Team building |
Loyalty, a sense of solidarity, mutual trust, common destiny, the creation of emotional relationships, group norms and group processes, the distribution of roles, a favorable climate, etc. |
Group |
Socio-psychological training |
|
Goal setting and time management |
Planning, building short- and long-term goals, setting priorities, social stability, timeliness |
Personality, Organizational |
Socio-psychological training |
|
Self-regulation, stress management |
Elaboration of the root causes of resistance, psychological security, thinking nozivism, emotional stability, reflection |
Personal |
Socio-psychological training |
|
Motivation and self motivation |
Ability to motivate oneself and others, changing and shaping attitudes |
Personality, group, organizational |
Seminar - training |
|
Creativity |
Expanding the scope of perception of reality, initiative, development of intelligence |
Personality, Organizational |
Seminar - training |
|
Professionally important qualities |
Formation and development of the necessary for a particular innovation qualities, skills and abilities in the context of professional duties. For example, effective sales |
Personality, group, organizational |
Socio-psychological training |
|
Other tutorials |
|||
The result of the application of the module is the formation of innovative readiness at the personal, group and organizational levels, which is a criterion for effectively preventing resistance to innovations.
Diagnostic final module - evaluation of the effectiveness of the previous modules: the formation of innovative readiness at the personal, group, organizational levels, innovation parameters, organizational situation. A module may contain blocks similar to a diagnostic primary module. A special role is played by expert assessment, psychodiagnostic personal procedures.
The use of the model in organizational practice should be commensurate with such indicators of innovation as:
– жизненный цикл или стадия нововведения. Предупреждение нововведения возможно на стадиях зарождения и освоения нововведения;
– направление и вид нововведения. Социальная и личностная значимость нововведения регулирует включенность и качество психологических реакций субъектов;
– масштаб или объем нововведения. Данный показатель также влияет на качество психологических реакций;
– рациональность или "полезность" нововведения с организационной позиции.
Данный показатель определяет необходимость внедрения намеченного изменения.
В этом случае влияние модульной психотехнологии соотносится с развитием инновационного поведения субъектов нововведения следующим образом: исходное поведение – инновационная готовность – принятие нововведения (не возникают сопротивления) и формирование инновационной готовности па личностном, групповом и организационном уровнях.
Согласованность развития во времени организационной ситуации, нововведения, инновационного поведения субъектов нововведения и сопровождение инновационной деятельности с целью предупреждения сопротивлений представлено на рис. 3.7.
Необходимость перестройки и изменений организационной культуры нередко сопровождается сопротивлением. Под сопротивлением понимается многогранное явление, вызывающее отсрочки, непредвиденные расходы и нестабильность процесса стратегических изменений. Сопротивление является проявлением иррационального поведения организации, отказа принять новые черты реальности. Человек сопротивляется изменениям, когда он не чувствует себя в безопасности. Это происходит, например, когда:
– руководитель не выступает в организации символом уверенности в целесообразности изменений;
– для работников повышена степень риска деятельности;
– наблюдается несоответствие новых трудовых ролей квалификационному базису работников;
– появляется требование новых стилей поведения.
Эти и ряд более частных причин продуцируют массовое
сопротивление новациям. Эта массовость в направлении единой цели служит хорошим гарантом прочности социальной позиции отдельной личности, т.е. защитой.
Психологическая защита как форма социального противостояния фрустрирующим обстоятельствам выполняет две функции: во-первых, сплачивает группу в направлении единой цели (защиты) и, во-вторых, более четко фиксирует организационную структуру, интенсифицирует процессы
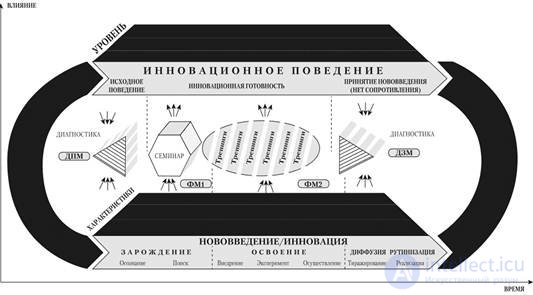
Рис. 3.7. Комплексный подход к предупреждению сопротивлений
адаптации и внутренней интеграции. Наиболее ярко защита проявляется в сопротивлении новациям, что провоцирует у персонала организации страх и тревогу. Причем эти реакции направлены против достаточно мощных внесистемных организационных влияний.
Установлено, что для людей принимающих и не принимающих новации, характерны различные структуры психологических и личностных качеств. Основными конструктами, включенные в метасистему психологической защиты при сопротивлении, являются: рефлексия, ригидность, тревожность, склонность к риску. Различия между защитными структурами работников принимающих и не принимающих новации носят не количественный, а качественный характер. Системообразующие качества в структуре защиты лиц, не принимающих новации, – ригидность и тревожность, которые находятся в прямой зависимости друг с другом.
Сопротивление в разной степени проявляется всегда в ответ на любые изменения, поскольку они связаны с некоторым временным снижением доходов (или желаемых результатов). В процессе реформирования организации часто имеют место следующие явления:
– отсрочка начала изменений;
– отсрочка внедрения и увеличение расходов относительно запланированных;
– саботаж изменений с маскировкой более важными делами.
Если результаты изменений отстают от ожидаемых, то в организации появляются попытки отнести их за счет ранее существовавшей базы и деятельности. Управляющие сопротивляются изменениям, когда их позиции в системе организационной власти оказываются в опасности.
Степень сопротивления определяется следующими факторами:
– степенью несоответствия структуры власти будущим изменениям;
– последствиями изменений для организации в целом и руководителя в частности;
– длительностью периода внедрения изменений;
– силой и содержанием организационной культуры;
– угрозой потери авторитета, престижа, власти управляющих;
– преданностью работников организации.
Для того чтобы снизить сопротивление и обеспечить одобрение изменений необходимо создание специфических условий. Совокупность этих условий называется "стартовой площадкой" и включает следующие шаги:
– диагностика стратегических задач;
– анализ моделей поведения с точки зрения ожидаемого сопротивления;
– изменение норм организационной культуры и критериев оценки как основы для проведения необходимых изменений;
– стратегический контроль за перспективой;
– вознаграждение стратегической деятельности и рискованных решений;
– вовлечение в инновационную деятельность всех управляющих.
Осуществление инновационной деятельности должно контролироваться на протяжении всего процесса изменений. Это необходимое условие для преодоления сопротивления на начальной стадии процесса. Предложения по контролю в ходе создания "стартовой площадки" включают:
– высвобождение времени у руководителей для реализации новой стратегии;
– выявление и вовлечение в процесс изменений всех сторонников новой стратегии;
– четкое планирование проводимых изменений с определением сроков появления результатов;
– осуществление комплексных мероприятий по снижению сопротивления системы.
Практически любые организационные изменения могут вызвать сопротивление со стороны отдельных членов организации, конкретных руководителей и "малых групп". Необходимо проводить специальную целенаправленную работу по преодолению сопротивления организационным новациям и эта деятельность должна быть встроена в общую стратегию изменений.
Часть 1 3. ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT
Часть 2 Управление инновациями в организации - 3. ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT
Часть 3 - 3. ORGANIZATIONAL DEVELOPMENT
Comments
To leave a comment
Organizational psychology
Terms: Organizational psychology