Open (unsolved) math problems - problems that were considered by mathematicians, but still not solved. Often they have the form of hypotheses that are supposedly correct, but need to be proved.
In the scientific world, the practice of compiling well-known scientists or organizations for lists of open problems that are currently relevant is popular. In particular, well-known lists of math problems are:
- Gilbert's problems
- Landau problems
- Millennium problems
- Smale problems
Over time, published problems from such a list can be resolved and, thus, lose the status of open. For example, some of the problems of Hilbert, which he presented in 1900, have now been solved in one way or another.
Number theory
Main article: Open problems in number theory
- The problem of Goldbach. Can each even number greater than 2 be presented as a sum of two primes?
- Waring's problem. Hardy function
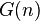 - least
- least 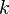 such that the equation
such that the equation 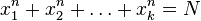 solvable at
solvable at 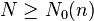 . Values of this function are known only for
. Values of this function are known only for  equal to 2 and 4.
equal to 2 and 4.
- Is the set of twin numbers infinite?
- Biel's hypothesis. Is it true that if
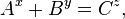 Where
Where  - natural and
- natural and  then
then  have a common prime divider?
have a common prime divider?
- Collatz's hypothesis (hypothesis 3n + 1).
- Erdёs hypothesis. Is it true that if the sum of the reciprocals for some set of natural numbers diverges, then in this set one can find arbitrarily long arithmetic progressions?
- Van der Waerden numbers ( English ). For what is the smallest N for any partition of the set
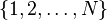 into two subsets at least one of them will contain an arithmetic progression of length 7? [one]
into two subsets at least one of them will contain an arithmetic progression of length 7? [one]
Geometry
- In the problem of moving the sofa, the maximalness of the best lower bound (Herver's constant) is not proved.
- Is it possible to find 4 points on any closed Jordan curve on the plane, which are the vertices of some square? [2] [3]
- Does such a constant exist
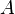 that any set of points on a plane having an area
that any set of points on a plane having an area 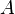 Does it necessarily contain vertices of at least one triangle of area 1? [four]
Does it necessarily contain vertices of at least one triangle of area 1? [four]
- Is there a dense set of points on a plane whose distance between every two points is rational? [five]
- Is there a triangle with integer sides, medians and area? [6] [7]
- Is there a point in the unit square, the distance from which to each of the 4 vertices is rational? [7] [8]
- The challenge of 9 circles. Are there 9 circles, such that every two intersect, and the center of each circle lies outside the other circles? (The execution time of the verification algorithm is too long).
- Does any convex polyhedron have a development without self-intersections? [9]
- Positive real numbers are given.
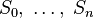 . What is the largest and smallest volume that a polyhedron can have, whose faces are equal to these numbers?
. What is the largest and smallest volume that a polyhedron can have, whose faces are equal to these numbers?
- How many times can the volume of a nonconvex polyhedron exceed the volume of a convex polyhedron composed of the same faces? [ten]
- At what minimum
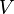 any convex body of a unit volume can be placed inside any triangular pyramid of volume
any convex body of a unit volume can be placed inside any triangular pyramid of volume 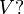 [eleven]
[eleven]
- What is the chromatic number
 -dimensional Euclidean space? This task is not solved even for the plane. In other words, it is not known what minimum number of colors is needed so that they can color the plane so that no two points at a unit distance from each other are painted in the same color (Nelson – Erdшаos – Hadwiger problem).
-dimensional Euclidean space? This task is not solved even for the plane. In other words, it is not known what minimum number of colors is needed so that they can color the plane so that no two points at a unit distance from each other are painted in the same color (Nelson – Erdшаos – Hadwiger problem).
- Thomson's task. How to place
 equal charged points on the sphere so that the potential energy of the system (that is, the sum of pairwise inverse distances between the points) is minimal (the problem is strictly solved only for
equal charged points on the sphere so that the potential energy of the system (that is, the sum of pairwise inverse distances between the points) is minimal (the problem is strictly solved only for 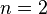 3, 4, 6 and 12). [12] How many equilibrium states (local extremes) exist for a system of
3, 4, 6 and 12). [12] How many equilibrium states (local extremes) exist for a system of  points?
points?
- How to place
 points on a sphere so that the smallest of the pairwise distances between them is maximum? [13]
points on a sphere so that the smallest of the pairwise distances between them is maximum? [13]
- For each pair of natural numbers (n, k), find the smallest real number d (n, k) such that any set of unit diameter in the n-dimensional Euclidean space can be divided into k subsets with diameter not greater than d (n, k). The problem is solved only in a few special cases. [14] [15]
- What is the area of the Mandelbrot set? There is a score of 1,506 591 77 ± 0,000 000 08. [16]
- A task with a happy ending. At what minimum
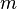 among any
among any 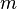 points on the plane, no 3 of which lie on one line, there are vertices of some convex
points on the plane, no 3 of which lie on one line, there are vertices of some convex  the corner? The solution is known only for
the corner? The solution is known only for 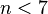 . Result for
. Result for 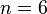 (which turned out to be 17) obtained in 2006 using computer analysis.
(which turned out to be 17) obtained in 2006 using computer analysis.
- What is the smallest number of tiles that can contain a lot of tiles Wang ( English ), which can tile the plane only non-periodically? The smallest known result is 13.
- Is there a point in any polygonal room with mirrored walls, when placed in which the light source the whole room will be lit? [17]
- Is it possible to place 8 points on a plane so that no 3 of them lie on one straight line, no 4 of them lie on one circle and the distance between any 2 points is an integer? The solution for 7 points was found in 2007. [18] [19] [20]
- What is the largest possible volume of a convex hull of a spatial curve of length 1?
- Bonniesen's hypothesis - Fennel. What three-dimensional body of constant width has the smallest volume? [21] [22] [23]
Packaging tasks
- What is the largest number of non-intersecting circles of unit radius that can be placed on a sphere of radius
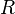 ? [24]
? [24]
- What is the side of the smallest square in which you can pack 2 unit circles, one of which is allowed to cut along the chord into 2 segments? [25]
- What is the least dense rigid package of identical circles on the plane? [25]
Multidimensional spaces
- What is the contact number in Euclidean spaces with the dimension
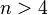 ? This task is solved only for
? This task is solved only for 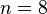 (240) and
(240) and 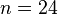 (196,560). [26] [27]
(196,560). [26] [27]
- The task of packing the balls in
 dimensional euclidean space for
dimensional euclidean space for 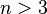 . For three-dimensional space, this problem was solved in 1998: it was proved that Kepler's hypothesis is true. However, the existing evidence is extremely large and difficult to verify. [28]
. For three-dimensional space, this problem was solved in 1998: it was proved that Kepler's hypothesis is true. However, the existing evidence is extremely large and difficult to verify. [28]
- Keller's conjecture. Is it possible to fill a 7-dimensional space with equal 7-dimensional hypercubes so that no two hypercubes have a whole common 6-dimensional hyperface? (It is known that for spaces of dimension less than 7 the answer is negative, and more than 7 is positive) [29]
Mechanics
- For each movement of four points in space, one can choose such a (possibly non-inertial) reference frame so that in it the trajectories of all four points turn out to be flat convex curves? [five]
- Is it true that with a sufficiently large number of moving points with entangled trajectories (trajectories are called linked if there is no homeomorphism of the space in which they fall inside disjoint convex sets) in any frame of reference will trajectories of at least two points be linked?
Algebra
- The inverse theorem of Galois theory. For any finite group
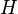 there is a field of algebraic numbers
there is a field of algebraic numbers 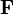 such that
such that 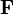 is an extension of the field of rational numbers
is an extension of the field of rational numbers 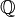 and
and 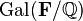 isomorphic
isomorphic 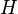 . [ source not specified 618 days ]
. [ source not specified 618 days ]
- Any finitely given group, each element of which has a finite order, is finite. For a finitely generated group (weaker condition) this is not true. [thirty]
- Is there a simple group that is not transfinitely super-simple? [31]
- Is the ring of periods a field?
- Problem O. Yu. Schmidt Do there exist non-quasicyclic groups, all proper subgroups (subgroups different from the singular and the whole group) which are finite? [32]
- Problem L.S. Pontryagin Let
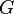 - effective transitive bicompact group of space transformations
- effective transitive bicompact group of space transformations 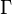 , homeomorphic
, homeomorphic  - dimensional sphere. Is there such a homeomorphic mapping of space
- dimensional sphere. Is there such a homeomorphic mapping of space 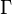 on a single sphere
on a single sphere 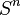 Euclidean
Euclidean 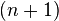 - dimensional space in which the group
- dimensional space in which the group 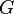 goes into a certain group of sphere movements
goes into a certain group of sphere movements 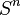 ? [33] .
? [33] .
- Algebraic systems Are there any conditions for which, if there are, non-trivial varieties of groupoids, rings and lattices that are accessible on the classes of all groupoids, all rings or lattices? [34] .
- Algebraic systems Whether and to what conditions there exist, in the case of existence, non-trivial varieties and quasivariety of semigroups with several distinguished elements, rings and lattices, accessible on the class of all such semigroups [34] .
- Do operations exist in a multitude of groups that are distinct from the operations of direct and free multiplication and possess their basic properties? [35]
- Will there be a set of all non-isomorphic abelian groups of given cardinality
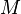 to have power
to have power 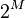 ? [36]
? [36]
- Problem A. I. Maltsev Does there exist a countable group such that every countable group is isomorphic to one of its subgroups? [37]
Kourovskaya notebook
It is a world-famous collection of several thousand unsolved problems in the field of group theory. It has been published since 1965 at intervals of 2-4 years. Available in Russian and English. [38] [39]
Dniester notebook
It is a collection of several hundred unsolved problems in the theory of rings and modules. [40]
Sverdlovsk notebook
It is a collection of unsolved problems in the theory of semigroups. [41]
Analysis
- Riemann's hypothesis. Do all non-trivial zeros of the zeta function lie on a line
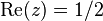 ?
?
- What is the Mills constant? The existing methods of calculation are based on the still unproved Riemann hypothesis.
- Until now, nothing is known about the normality of such numbers as
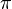 and
and  ; it is not even known which of the numbers 0-9 are found in the decimal representation of the number
; it is not even known which of the numbers 0-9 are found in the decimal representation of the number 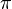 an infinite number of times.
an infinite number of times.
- Is every irrational algebraic number normal?
- Does it
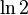 normal number? [42]
normal number? [42]
- Not a single number is known for which it would be proved that the geometric mean of the terms of its decomposition into a continuous fraction tends to the Khinchin constant ( English ), although it was proved that almost all real numbers have this property. It is assumed that this property should have the numbers
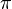 , Euler's constant - Mascheroni, Khinchin constant itself and many other mathematical constants.
, Euler's constant - Mascheroni, Khinchin constant itself and many other mathematical constants.
- Do the ranks meet
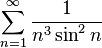 and
and 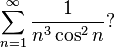 [43]
[43]
Irrationality issues
- The measure of irrationality is not known for any of the following numbers: Euler's constant — Mascheroni, Catalan's constant, Bruna's constant, Mills's constant, Khinchin's constant, numbers
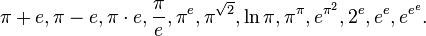 None of them even knows whether it is a rational number, an algebraic irrational or a transcendental number [44] [45] [46] [47] [48] [49] [50] .
None of them even knows whether it is a rational number, an algebraic irrational or a transcendental number [44] [45] [46] [47] [48] [49] [50] .
- It is unknown whether
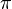 and
and  algebraically independent.
algebraically independent.
- It is unknown whether
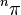 or
or 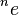 integers with any positive whole
integers with any positive whole  (see tetration). It is not even known whether
(see tetration). It is not even known whether 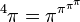 whole.
whole.
- Unknown whether
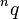 be whole if
be whole if  Is a positive integer, and
Is a positive integer, and 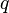 - positive rational, but not integer (in particular cases
- positive rational, but not integer (in particular cases 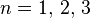 the answer is negative) [51] .
the answer is negative) [51] .
- It is not known whether the positive root of the equation
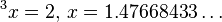 an algebraic or transcendental number (although it is known that it is irrational).
an algebraic or transcendental number (although it is known that it is irrational).
- It is not known whether the positive root of the equation
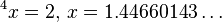 rational, algebraic irrational or transcendental number. A similar problem for tetrating any greater height is also open.
rational, algebraic irrational or transcendental number. A similar problem for tetrating any greater height is also open.
- The exact measure of irrationality for each of the following irrational numbers is unknown:
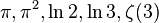 [52] .
[52] .
- It is unknown whether the first number of Skyuza
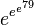 integer
integer
- Are the Riemann Zeta Functions Transcendental?
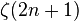 for all natural
for all natural  ?
?
- Are the gamma functions transcendental?
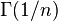 for all wholes
for all wholes 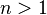 ?
?
- Are the Feigenbaum Constants Transcendental?
- Is the pell constant transcendental? [53]
- Is every infinite non-periodic fraction with bounded members transcendental?
Combinatorics
- The existence of a Hadamard matrix of a multiple of 4.
- The existence of a finite projective plane of natural order which is not a power of a prime number.
- Unknown number of unlocked horse routes.
- Erdёs hypothesis - Renyi . If a
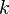 - fixed integer
- fixed integer 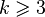 then
then 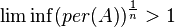 for
for 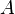 of
of 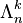 . Here
. Here 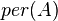 - matrix permanent
- matrix permanent 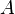 ,
, 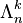 - a lot of all
- a lot of all 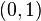 - order matrices
- order matrices  c
c 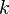 units in each row and each column [54] .
units in each row and each column [54] .
Graph theory
- The Hacquist Katssettstyt hypothesis is a directed graph with n vertices, each vertex of which contains at least m edges, has a closed contour no longer than
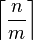 . [55]
. [55]
- Гипотеза Хадвигера — каждый n -хроматический граф стягиваем к полному графу
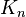 .
.
- Гипотеза Улама :
- а) всякий граф с более чем двумя вершинами однозначно определяется набором графов, где каждый граф из набора получен удалением одной из вершин исходного графа;
- б) всякий граф с более чем тремя вершинами однозначно определяется множеством графов, где каждый граф из множества получен удалением одной из вершин исходного графа.
- Гипотеза Харари (слабая форма гипотезы Улама) — если граф имеет более трёх рёбер, то его можно однозначно восстановить по подграфам, полученным удалением единственного ребра.
- В любом графе, не содержащем мостов (ребер, удаление которых увеличивает число компонент связности графа), можно выбрать множество простых циклов, такое, что каждое ребро принадлежит ровно двум из них.
- В любом кубическом графе можно выбрать 6 1-факторов так, чтобы каждое ребро принадлежало ровно двум из них.
Теория узлов
- Существует ли нетривиальный узел, полином Джонса которого является таким же, как и у тривиального узла?
- Чему равно количество простых узлов ( англ. ) с n двойными точками ( англ. ) для n > 16? Является ли эта последовательность строго возрастающей? [56] Значения для n < 17 даёт последовательность A002863 в OEIS.
Теория алгоритмов
Вопросы алгоритмической разрешимости
- Аналог 10-й проблемы Гильберта для уравнений степени 3: существует ли алгоритм, позволяющий по любому диофантовому уравнению степени 3 определить, имеет ли оно решения?
- Аналог 10-й проблемы Гильберта для уравнений в рациональных числах. Как узнать по произвольному диофантову уравнению, разрешимо ли оно в рациональных (не обязательно целых) числах и можно ли это узнать вообще (то есть возможен ли соответствующий алгоритм)? [57] [58] [59]
- Алгоритмическая разрешимость проблемы умирающей матрицы для матриц порядка 2. Существует ли алгоритм, позволяющий для данного конечного множества квадратных матриц
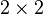 определить, существует ли произведение всех или некоторых из этих матриц (возможно, с повторениями) в каком-либо порядке, дающее нулевую матрицу. [60]
определить, существует ли произведение всех или некоторых из этих матриц (возможно, с повторениями) в каком-либо порядке, дающее нулевую матрицу. [60]
- Расширение класса выражений, для которых известен алгоритм, определяющий, равно ли выражение нулю (Проблема констант ( англ. )). Для каких классов выражений эта задача алгоритмически неразрешима?
- Существует ли алгоритм, позволяющий узнать по целочисленной матрице, существует ли степень, имеющая нуль в правом верхнем углу? [59]
Теория сложности вычислений
- P = NP?
- Является ли задача изоморфизма графов NP-полной? [61]
- Принадлежит ли задача нахождения простого множителя натурального числа к классу P?
- Принадлежит ли задача распознавания тривиального узла ( англ. ) к классу P?
- Определить точную нижнюю границу сложности алгоритма умножения целых чисел. Из известных алгоритмов наименьшую сложность имеет алгоритм Мартина Фюрера, выполняющийся за
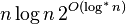 where
where 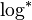 — итерированный логарифм ( англ. ).
— итерированный логарифм ( англ. ).
- Определить точную нижнюю границу сложности алгоритма умножения матриц. Из известных алгоритмов наименьшую сложность имеет алгоритм Копперсмита — Винограда, работающий за
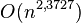 (однако с непрактично большим коэффициентом).
(однако с непрактично большим коэффициентом).
Другие проблемы теории алгоритмов
- Проблема «усердного бобра» ( англ. ) [62] . Сколько ходов может продержаться (незацикливающаяся) машина Тьюринга с
 состояниями и алфавитом
состояниями и алфавитом 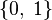 на заполненной нулями ленте? Известно, что нет алгоритма (а значит, и рекурсивно аксиоматизируемой формальной теории), который может решить этот вопрос для всех
на заполненной нулями ленте? Известно, что нет алгоритма (а значит, и рекурсивно аксиоматизируемой формальной теории), который может решить этот вопрос для всех  , и пока известны только значения для
, и пока известны только значения для 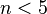 . [63]
. [63]
- Существует ли алгоритм, распознающий для любых двух трёхмерных многообразий, заданных своими триангуляциями, гомеоморфны ли они? [59]
- Существует ли алгоритм, распознающий по произвольной позиции игры "Жизнь", "вымрет" ли она (станут ли в итоге все клетки пустыми)? [59]
- Существует ли теорема о полноте для решетки Мучника? [59]
- Существует ли алгоритм, определяющий разрешимость и арифметичность множества реализуемых и множества неопровержимых пропозициональных формул? [59]
- Существуют ли в обычных алгебраических системах алгебраически корректные массовые проблемы различной сложности? [59]
- Существует ли алгебраическая система, для которой равномерная эквивалентность отличается от программной или программная от проблемной? [59]
Аксиоматическая теория множеств
- В настоящее время наиболее распространённой аксиоматической теорией множеств является ZFC — теория Цермело — Френкеля с аксиомой выбора. Вопрос о непротиворечивости этой теории (а тем более — о существовании модели для неё) остаётся нерешённым.
- Проблема Скулема. Рассмотрим множество
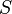 функций одного натурального переменного
функций одного натурального переменного  , построенных из термов
, построенных из термов 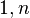 и замкнутых относительно сложения,умножения и возведения в степень. Для функций
и замкнутых относительно сложения,умножения и возведения в степень. Для функций 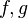 из этого множества будем писать
из этого множества будем писать 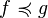 , if a
, if a 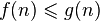 выполняется для всех достаточно больших
выполняется для всех достаточно больших  . Известно, что отношение
. Известно, что отношение 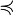 вполне упорядочивает множество
вполне упорядочивает множество 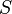 . Какой ординал соответствует этому упорядочению? (Известно, что он не меньше чем
. Какой ординал соответствует этому упорядочению? (Известно, что он не меньше чем 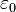 и не больше чем первый критический ординал
и не больше чем первый критический ординал 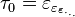 ) [64] [65] Аналогичные вопросы возникают при добавлении в множество разрешённых операторов дополненная тетрации,пентации и гипероператоров более высоких порядков (проблема Скулема, дополненная только тетрацией, была решена в 2010 году). [66] [67]
) [64] [65] Аналогичные вопросы возникают при добавлении в множество разрешённых операторов дополненная тетрации,пентации и гипероператоров более высоких порядков (проблема Скулема, дополненная только тетрацией, была решена в 2010 году). [66] [67]
- Существует ли линейно упорядоченное множество с порядковым типом ( англ. ) α, удовлетворяющим условиям α ≠ α 2 и α = α 3 ? [68]
- В теории множеств Цермело-Френкеля без аксиомы выбора неизвестно, существуют ли регулярные кардиналы
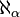 , большие
, большие 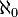 [69] .
[69] .
- Проблема сингулярных кардиналов. Для каких функций
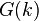 существует модель Цермело-Френкеля, в которой
существует модель Цермело-Френкеля, в которой 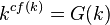 для всех кардиналов
для всех кардиналов 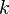 [70] .
[70] .
- Верно ли, что если непротиворечива система аксиом Цермело-Френкеля вместе с аксиомой выбора, то непротиворечива система аксиом Цермело-Френкеля, принцип зависимого выбора и каждое множество действительных чисел есть измеримое по Лебегу множество? [71]
- Whether the assumption of the existence of such cardinal numbers would lead to a contradiction
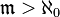 such that the Cartesian product of m-compact spaces is always m-compact. It is also unknown whether the smallest of these numbers would coincide with the smallest measurable number or not [72] .
such that the Cartesian product of m-compact spaces is always m-compact. It is also unknown whether the smallest of these numbers would coincide with the smallest measurable number or not [72] .
Evidence Theory
- What is the shortest insoluble statement in Peano arithmetic? [73] The unsolvable statement of the theory is a statement that can neither be proved nor refuted in the given theory. The proofs of Godel's theorems demonstrate how such statements can be constructed, but the resulting assertions turn out to be of a very considerable size, being written in the formal language of arithmetic.
Computational Mathematics
- Determine the maximum level of approximation
 Runge – Kutta method method (one-stage = Euler method =
Runge – Kutta method method (one-stage = Euler method = 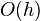 , two-stage = modified Euler method =
, two-stage = modified Euler method = 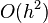 , four-stage = classical Runge – Kutta method =
, four-stage = classical Runge – Kutta method = 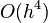 , five-stage = Felberg method ( English ) = also
, five-stage = Felberg method ( English ) = also 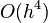 ).
).
Differential equations
- The exact solution of the van der Pol equation is unknown (it is the van der Pol oscillator): [74] [75]
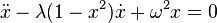
- Unknown exact solution of the Duffing equation [76]
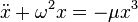
- Unknown exact solution of the Mathieu equation [77]
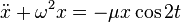
- Ablowitz-Ramani-Segura hypothesis All ordinary differential equations derived from fully integrable partial differential equations have the Painlevé property (the position of any algebraic, logarithmic or essential singularity of solutions of the equation does not depend on the initial conditions, only the position of the poles depends on arbitrary integration constants) [78] .
- Does the Liouville-integrable Hamiltonian system have an equivalent formulation using the Lax pair, and if so, how to construct it? [79]
Probability theory
- Necessary and sufficient conditions for the membership of an infinitely divisible law of the distribution of a random variable in the one-dimensional and multidimensional cases to the class of laws that do not have indecomposable components are unknown. [80]
Equations of mathematical physics
- There is no rigorous mathematical justification for the method of continual integration in quantum field theory [81] .
- Continual integrals can be calculated only for the case of Gaussian quadratures. In the general case, the method for calculating continual integrals is unknown [82] .
- The exact solution of the Schrödinger equation for many-electron atoms is not known [83] .
- In quantum mechanics, when solving the problem of the scattering of two beams on one obstacle, the scattering cross section is infinitely large [84]
- Navier – Stokes equations
- There are hundreds of unsolved problems in hydrodynamics [85] .
- There is no complete theory explaining the origin and evolution of the Earth’s magnetic field [86] .
Game theory
- There is no general mathematical theory of games conducted on the space of functions (since the power of the set of real functions significantly exceeds the power of the continuum) [87] .
- There is no general mathematical theory of pseudo-games (conflict situations that are not games) [87] .
- There is no general mathematical theory of non-cooperative games.
 persons for
persons for 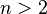 [87] .
[87] .
- Formulations
 unresolved problems in game theory are in the book [88] .
unresolved problems in game theory are in the book [88] .
- The problem of constructing algorithms for learning how to solve games is not solved when the elements of the payment matrix are not constant, but are random variables, or are unknown (a blind game) [89] .
Group Representation Theory
- Langlands hypothesis. Any irreducible representation of a real semisimple Lie group
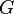 included in the discrete part of the decomposition of a regular representation is realized in the space
included in the discrete part of the decomposition of a regular representation is realized in the space 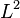 - cohomology of a suitable beam on space
- cohomology of a suitable beam on space 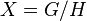 where
where 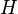 - compact Cartan subgroup in
- compact Cartan subgroup in 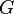 [90] .
[90] .
General topology
- Dowker task. Determine whether every normal Hausdorff space is countably paracompact [91] .
- List of
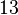 There are unsolved problems in set-theoretic topology in [92] .
There are unsolved problems in set-theoretic topology in [92] .
- The power of sets complementary to A-sets is unknown, even in the one-dimensional case [93] .
Linear algebra
- Banach hypothesis. Every separable Banach space has a countable basis [94] .
Theory of random processes
- The task of determining the distribution law
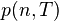 the number of emissions of a random process in the general case does not have a complete and compact solution [95] .
the number of emissions of a random process in the general case does not have a complete and compact solution [95] .
- The problem of determining the law of distribution of the absolute maxima of a random process is solved only for Markov processes. For other processes, the exact solution is unknown [96] .
Functional analysis
- List of
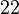 The unsolved problems of the theory of operators in a Banach space are in the book [97] .
The unsolved problems of the theory of operators in a Banach space are in the book [97] .
Theory of Dynamic Systems
- It is not known whether a system of two or more rigid billiard balls is a K-flow in non-singular interactions [98] .
Riemannian geometry
- Hopf Problem Does a Differentiable Variety Exist?
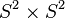 Riemannian metric of positive curvature? [99] .
Riemannian metric of positive curvature? [99] .
Operations research
- There is no combinatorial method for solving integer linear programming problems with a polynomial (as opposed to exponential) estimate of laboriousness? [100] .
- There is no general theory of algorithmic optimization methods that allows acceleration of convergence and the choice of an iteration step in the general case of multi-step algorithms [101] .
- The conditions of convergence are almost unknown in the region for multi-step adaptation and learning algorithms [102] .
- Unknown rules for determining the moment of establishment of stationarity of the adaptation and learning algorithm [102] .
- Estimates of the dependence of the accuracy of the approximation on the number of functions and the estimation of the learning time for recognition algorithms [103] are unknown.
- Unknown general methods for obtaining unbiased estimates for a given criterion of optimality in identification problems [104] .
- Unknown general rules for the selection of a system of functions in filtering problems [105] .
- The relationship between the rate of change of external influences and the duration of the filter adaptation process has not been studied [105] .
- Unknown ways to use a priori information about the distribution of random variables to build adaptive filters [105] .
- The method of applying the adaptive approach in accelerated reliability tests [106] is unknown.
- There is no general theory of network planning using the adaptive approach with insufficient a priori information [107] .
Algebraic geometry
- List of
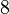 unresolved problems of algebraic geometry are in the book [108] .
unresolved problems of algebraic geometry are in the book [108] .
Known issues recently resolved
- The problem of four colors
- Fermat's Great Theorem
- Poincare conjecture
- Road Coloring Hypothesis [109]
- Van der Waerden's hypothesis about the permanent
- Takeuti hypothesis
- Bieberbach hypothesis
- Problem serra
see also
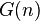 - least
- least 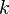 such that the equation
such that the equation 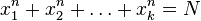 solvable at
solvable at 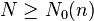 . Values of this function are known only for
. Values of this function are known only for  equal to 2 and 4.
equal to 2 and 4.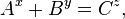 Where
Where 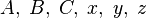 - natural and
- natural and 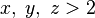 then
then 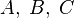 have a common prime divider?
have a common prime divider?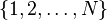 into two subsets at least one of them will contain an arithmetic progression of length 7? [one]
into two subsets at least one of them will contain an arithmetic progression of length 7? [one]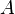 that any set of points on a plane having an area
that any set of points on a plane having an area 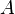 Does it necessarily contain vertices of at least one triangle of area 1? [four]
Does it necessarily contain vertices of at least one triangle of area 1? [four]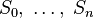 . What is the largest and smallest volume that a polyhedron can have, whose faces are equal to these numbers?
. What is the largest and smallest volume that a polyhedron can have, whose faces are equal to these numbers?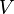 any convex body of a unit volume can be placed inside any triangular pyramid of volume
any convex body of a unit volume can be placed inside any triangular pyramid of volume 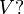 [eleven]
[eleven] -dimensional Euclidean space? This task is not solved even for the plane. In other words, it is not known what minimum number of colors is needed so that they can color the plane so that no two points at a unit distance from each other are painted in the same color (Nelson – Erdшаos – Hadwiger problem).
-dimensional Euclidean space? This task is not solved even for the plane. In other words, it is not known what minimum number of colors is needed so that they can color the plane so that no two points at a unit distance from each other are painted in the same color (Nelson – Erdшаos – Hadwiger problem). equal charged points on the sphere so that the potential energy of the system (that is, the sum of pairwise inverse distances between the points) is minimal (the problem is strictly solved only for
equal charged points on the sphere so that the potential energy of the system (that is, the sum of pairwise inverse distances between the points) is minimal (the problem is strictly solved only for 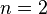 3, 4, 6 and 12). [12] How many equilibrium states (local extremes) exist for a system of
3, 4, 6 and 12). [12] How many equilibrium states (local extremes) exist for a system of  points?
points? points on a sphere so that the smallest of the pairwise distances between them is maximum? [13]
points on a sphere so that the smallest of the pairwise distances between them is maximum? [13]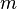 among any
among any 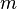 points on the plane, no 3 of which lie on one line, there are vertices of some convex
points on the plane, no 3 of which lie on one line, there are vertices of some convex  the corner? The solution is known only for
the corner? The solution is known only for 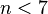 . Result for
. Result for 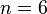 (which turned out to be 17) obtained in 2006 using computer analysis.
(which turned out to be 17) obtained in 2006 using computer analysis.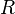 ? [24]
? [24]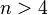 ? This task is solved only for
? This task is solved only for 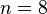 (240) and
(240) and 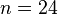 (196,560). [26] [27]
(196,560). [26] [27] dimensional euclidean space for
dimensional euclidean space for 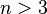 . For three-dimensional space, this problem was solved in 1998: it was proved that Kepler's hypothesis is true. However, the existing evidence is extremely large and difficult to verify. [28]
. For three-dimensional space, this problem was solved in 1998: it was proved that Kepler's hypothesis is true. However, the existing evidence is extremely large and difficult to verify. [28]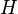 there is a field of algebraic numbers
there is a field of algebraic numbers 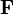 such that
such that 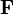 is an extension of the field of rational numbers
is an extension of the field of rational numbers 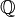 and
and 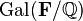 isomorphic
isomorphic 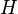 . [ source not specified 618 days ]
. [ source not specified 618 days ]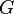 - effective transitive bicompact group of space transformations
- effective transitive bicompact group of space transformations 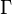 , homeomorphic
, homeomorphic  - dimensional sphere. Is there such a homeomorphic mapping of space
- dimensional sphere. Is there such a homeomorphic mapping of space 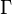 on a single sphere
on a single sphere 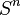 Euclidean
Euclidean 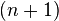 - dimensional space in which the group
- dimensional space in which the group 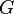 goes into a certain group of sphere movements
goes into a certain group of sphere movements 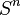 ? [33] .
? [33] .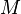 to have power
to have power 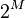 ? [36]
? [36]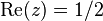 ?
?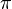 and
and  ; it is not even known which of the numbers 0-9 are found in the decimal representation of the number
; it is not even known which of the numbers 0-9 are found in the decimal representation of the number 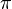 an infinite number of times.
an infinite number of times.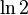 normal number? [42]
normal number? [42]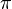 , Euler's constant - Mascheroni, Khinchin constant itself and many other mathematical constants.
, Euler's constant - Mascheroni, Khinchin constant itself and many other mathematical constants.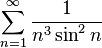 and
and 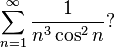 [43]
[43]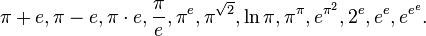 None of them even knows whether it is a rational number, an algebraic irrational or a transcendental number [44] [45] [46] [47] [48] [49] [50] .
None of them even knows whether it is a rational number, an algebraic irrational or a transcendental number [44] [45] [46] [47] [48] [49] [50] .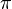 and
and  algebraically independent.
algebraically independent.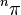 or
or 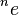 integers with any positive whole
integers with any positive whole  (see tetration). It is not even known whether
(see tetration). It is not even known whether 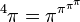 whole.
whole.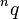 be whole if
be whole if  Is a positive integer, and
Is a positive integer, and 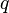 - positive rational, but not integer (in particular cases
- positive rational, but not integer (in particular cases 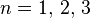 the answer is negative) [51] .
the answer is negative) [51] .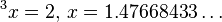 an algebraic or transcendental number (although it is known that it is irrational).
an algebraic or transcendental number (although it is known that it is irrational).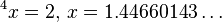 rational, algebraic irrational or transcendental number. A similar problem for tetrating any greater height is also open.
rational, algebraic irrational or transcendental number. A similar problem for tetrating any greater height is also open.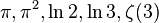 [52] .
[52] .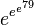 integer
integer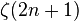 for all natural
for all natural  ?
?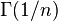 for all wholes
for all wholes 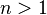 ?
?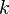 - fixed integer
- fixed integer 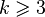 then
then 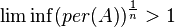 for
for 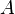 of
of 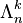 . Here
. Here 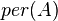 - matrix permanent
- matrix permanent 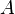 ,
, 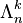 - a lot of all
- a lot of all 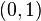 - order matrices
- order matrices  c
c 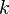 units in each row and each column [54] .
units in each row and each column [54] .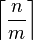 . [55]
. [55]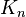 .
. определить, существует ли произведение всех или некоторых из этих матриц (возможно, с повторениями) в каком-либо порядке, дающее нулевую матрицу. [60]
определить, существует ли произведение всех или некоторых из этих матриц (возможно, с повторениями) в каком-либо порядке, дающее нулевую матрицу. [60]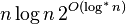 where
where 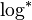 — итерированный логарифм ( англ. ).
— итерированный логарифм ( англ. ).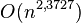 (однако с непрактично большим коэффициентом).
(однако с непрактично большим коэффициентом). состояниями и алфавитом
состояниями и алфавитом 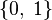 на заполненной нулями ленте? Известно, что нет алгоритма (а значит, и рекурсивно аксиоматизируемой формальной теории), который может решить этот вопрос для всех
на заполненной нулями ленте? Известно, что нет алгоритма (а значит, и рекурсивно аксиоматизируемой формальной теории), который может решить этот вопрос для всех  , и пока известны только значения для
, и пока известны только значения для 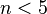 . [63]
. [63]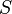 функций одного натурального переменного
функций одного натурального переменного  , построенных из термов
, построенных из термов 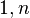 и замкнутых относительно сложения,умножения и возведения в степень. Для функций
и замкнутых относительно сложения,умножения и возведения в степень. Для функций 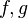 из этого множества будем писать
из этого множества будем писать 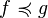 , if a
, if a 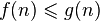 выполняется для всех достаточно больших
выполняется для всех достаточно больших  . Известно, что отношение
. Известно, что отношение 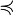 вполне упорядочивает множество
вполне упорядочивает множество 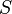 . Какой ординал соответствует этому упорядочению? (Известно, что он не меньше чем
. Какой ординал соответствует этому упорядочению? (Известно, что он не меньше чем 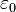 и не больше чем первый критический ординал
и не больше чем первый критический ординал 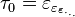 ) [64] [65] Аналогичные вопросы возникают при добавлении в множество разрешённых операторов дополненная тетрации,пентации и гипероператоров более высоких порядков (проблема Скулема, дополненная только тетрацией, была решена в 2010 году). [66] [67]
) [64] [65] Аналогичные вопросы возникают при добавлении в множество разрешённых операторов дополненная тетрации,пентации и гипероператоров более высоких порядков (проблема Скулема, дополненная только тетрацией, была решена в 2010 году). [66] [67]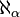 , большие
, большие 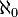 [69] .
[69] .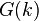 существует модель Цермело-Френкеля, в которой
существует модель Цермело-Френкеля, в которой 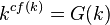 для всех кардиналов
для всех кардиналов 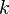 [70] .
[70] .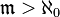 such that the Cartesian product of m-compact spaces is always m-compact. It is also unknown whether the smallest of these numbers would coincide with the smallest measurable number or not [72] .
such that the Cartesian product of m-compact spaces is always m-compact. It is also unknown whether the smallest of these numbers would coincide with the smallest measurable number or not [72] . Runge – Kutta method method (one-stage = Euler method =
Runge – Kutta method method (one-stage = Euler method = 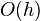 , two-stage = modified Euler method =
, two-stage = modified Euler method = 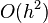 , four-stage = classical Runge – Kutta method =
, four-stage = classical Runge – Kutta method = 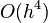 , five-stage = Felberg method ( English ) = also
, five-stage = Felberg method ( English ) = also 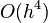 ).
).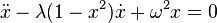
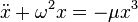
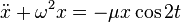
 persons for
persons for 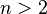 [87] .
[87] . unresolved problems in game theory are in the book [88] .
unresolved problems in game theory are in the book [88] .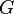 included in the discrete part of the decomposition of a regular representation is realized in the space
included in the discrete part of the decomposition of a regular representation is realized in the space 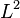 - cohomology of a suitable beam on space
- cohomology of a suitable beam on space 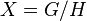 where
where 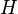 - compact Cartan subgroup in
- compact Cartan subgroup in 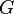 [90] .
[90] . There are unsolved problems in set-theoretic topology in [92] .
There are unsolved problems in set-theoretic topology in [92] . the number of emissions of a random process in the general case does not have a complete and compact solution [95] .
the number of emissions of a random process in the general case does not have a complete and compact solution [95] . The unsolved problems of the theory of operators in a Banach space are in the book [97] .
The unsolved problems of the theory of operators in a Banach space are in the book [97] .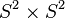 Riemannian metric of positive curvature? [99] .
Riemannian metric of positive curvature? [99] . unresolved problems of algebraic geometry are in the book [108] .
unresolved problems of algebraic geometry are in the book [108] .
Comments
To leave a comment
introduction to math. the basics
Terms: introduction to math. the basics