Lecture
You can use floating-point arithmetic commands to perform the following operations on two 32-bit floating-point IEEE numbers:
IEEE 32-bit floating point numbers are of type REAL. Using floating point arithmetic, you can perform the following operations with a single 32 – bit IEEE floating point number:
The state of signal 1 at the enable input (EN) activates the command Addition of floating-point numbers. This command adds inputs IN1 and IN2. The result can be queried at the output OUT. If the result is outside the acceptable range for floating-point numbers (overflow or underflow), then the OV and OS bits of the status word are 1, and ENO is 0. For information on evaluating these indicators in the status word, see section 7.6.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
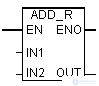 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN1 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | First term | |
| IN2 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Second term | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Amount |
Example and bits of the word of the state of addition of floating-point numbers
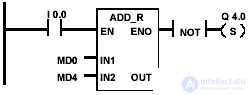 | The state of signal 1 at input I 0.0 activates the ADD_R block. The result of the addition of MD0 + MD4 is placed in the double word of memory MD10. If the result falls outside the permissible range for real numbers or the state of the signal at input I 0.0 is 0, then the output Q 4.0 is set. |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | x | x | x | x | x | one | x | x |
This command is identical to the previous one, the difference is that the command subtracts the input IN2 from IN1. Information on evaluating these indicators in the status word can be found in section 7.6.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
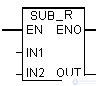 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN1 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Minuend | |
| IN2 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Subtrahend | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Difference |
Example and bits of the state word of the subtraction of floating-point numbers
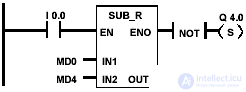 | The state of signal 1 at input I 0.0 activates the SUB_R block. The result of the subtraction MD0 - MD4 is placed in the memory double word MD10. If the result falls outside the permissible range for real numbers or the state of the signal at input I 0.0 is 0, then the output Q 4.0 is set. |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | x | x | x | x | x | one | x | x |
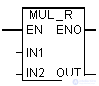
The multiply floating-point command multiplies the input IN1 by IN2. In all other respects, the command is identical to the previous one. Information on evaluating these indicators in the status word can be found in section 7.6.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN1 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | First factor | |
| IN2 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Second factor | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Composition |
Example and bits of the floating point multiplication state word
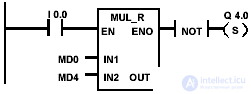 | The state of signal 1 at input I 0.0 activates the MUL_R block. The result of the multiplication MD0 x MD4 is placed in the memory double word MD10. If the result is outside the acceptable range for integers or the state of the signal at input I 0.0 is 0, then the output Q 4.0 is set. |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | x | x | x | x | x | one | x | x |
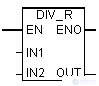
This command divides IN1 input to IN2. In all other respects, the command is identical to the previous one. Information on evaluating these indicators in the status word can be found in section 7.6.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN1 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Dividend | |
| IN2 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Divider | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Private |
Example and bits of the floating point division state word
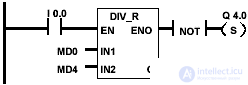 | The state of signal 1 at input I 0.0 activates the DIV_R block. The result of dividing MD0 by MD4 is placed in the double word of memory MD10. If the result falls outside the permissible range for real numbers or the state of the signal at input I 0.0 is 0, then the output Q 4.0 is set. |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | x | x | x | x | x | one | x | x |
Mathematical operations affect the following bits of the status word:
A dash (-) in the bit column of the table means that the corresponding bit is not affected by the result of the operation.
The state signal of the status word bits for floating point results that are within the allowable range of values
| The valid range for the result of the operation on floating-point numbers (32 bits) | Status word bits | |||
| CC1 | CC0 | Ov | OS | |
| +0, -0 (zero) | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| –3.402823E + 38 <result <–1.175494E – 38 (a negative number) | 0 | one | 0 | - |
| + 1.175494E-38 <result <3.402823E + 38 (positive number) | one | 0 | 0 | - |
The status signal of the status word bits for floating point results that are outside the allowable range of values
| Invalid range for floating-point operation result (32 bits) | Status word bits | |||
| CC1 | CC0 | Ov | OS | |
| –1.175494E – 38 <result <–1.401298E – 45 (negative number) loss of significance | 0 | 0 | one | one |
| + 1.401298E – 45 <result <+ 1.175494E – 38 (positive number) loss of significance | 0 | 0 | one | one |
| Result <–3.402823E + 38 (negative number) overflow | 0 | one | one | one |
| result> 3.402823E + 38 (positive number) overflow | one | 0 | one | one |
| Result <–3.402823E + 38 or result> + 3.402823E + 38 not a floating point number | one | one | one | one |
Using the command Generate absolute value of a floating-point number, you can get the absolute value of a floating-point number.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
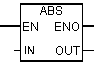 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Input: Real Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Output: the absolute value of a real number |
Example and bits of the floating-point absolute value state word
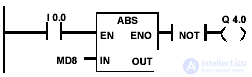 | If I 0.0 = 1, then the absolute value of MD8 is output to MD12. MD8 = +6.234 x 10-3 results in MD12 = 6.234 x 10-3. Output Q 4.0 is "1" if no conversion is performed (ENO = EN = 0). |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | - | - | - | - | 0 | x | x | one |
With the help of the Square command for a floating-point number, you can square a floating-point number. Using the command Square root of a floating point number, you can extract the square root of a floating point number. This command outputs a positive result if the operand is greater than “0”. The only exception: the square root of - 0 is –0. Information on evaluating these indicators in the status word can be found in section 7.6.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
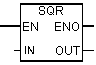 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Square number |
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
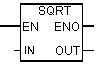 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Square root number |
Example and bits of the word of the formation of a square or square root
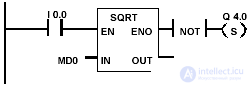 | The SQRT block is activated when I 0.0 = 1. The result of the SQRT (MD0) is stored in the memory double word MD10. If MD0 <0, or if the result is outside the acceptable range for floating-point numbers, or the state of the signal at input I 0.0 = 0, then the output Q 4.0 is set. |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | x | x | x | x | 0 | x | x | one |
With this command you can form the natural logarithm of a floating point number.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | The natural logarithm of a number |
Example and bits of the state word of the formation of the natural logarithm
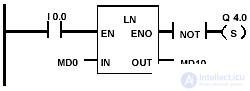 | The LN block is activated when I 0.0 = 1. The result of LN (MD0) is stored in the memory double word MD10. If MD0 <0, or if the result is out of range for floating-point numbers, or if the state output Q 4.0 is set. |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | x | x | x | x | 0 | x | x | one |
Using the Formation of the exponential value of a floating-point number command, you can form the exponential value of a floating-point number with base e (= 2.71828 ...).
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Exponent number |
Example and bits of the word of the state of formation of an exponential value
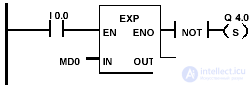 | The EXP block is activated when I 0.0 = 1. EXP (MD0) is stored in the memory double word MD10. If MD0 <0, or if the result is outside the acceptable range for floating-point numbers, or if the signal state I 0.0 = 0, the output Q 4.0 is set. |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | x | x | x | x | 0 | x | x | one |
With the following commands you can form trigonometric functions of angles represented as floating point numbers (32 bits, IEEE).
| Team | Explanation |
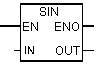
| Sin | To form the sine of the angle given in radians. |
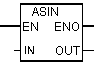
| ASIN | Form arcsine floating point numbers. The result is an angle given in radians. This value is in the following range: -¶ / 2 = <arcsine = <+ ¶ / 2, where ¶ = 3.14 ... |
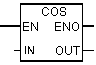
| Cos | To form the cosine of a floating-point number representing the angle given in radians. |
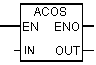
| ACOS | Form arc cosine floating point numbers. The result is an angle given in radians. This value is in the following range: 0 = <arc cosine = <+ ¶, where ¶ = 3.14 ... |
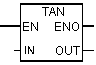
| TAN | To form the tangent of a floating-point number representing the angle specified in radians. |
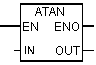
| ATAN | To form the arctangent of a floating point number. The result is an angle given in radians. This value is in the following range: -¶ / 2 = <arctangent = <+ ¶ / 2, where¶ = 3.14 ... |
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Sine number |
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Arcsine numbers |
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Cosine number |
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Arccosine number |
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Tangent of number |
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
 | En | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive entry |
| ENO | Bool | I, Q, M, D, L | Permissive exit | |
| IN | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Number | |
| Out | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Arctangent of number |
Example and bits of the word of the state of trigonometric functions
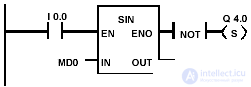 | The SIN block is activated when I 0.0 = 1. The result of the SIN (MD0) is stored in the Dual Word of the MD10 memory. If the result is outside the allowable range for floating-point numbers or I 0.0 = 0, then the output Q 4.0 is set. |
| Status word bits | |||||||||
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC | |
| Record | x | x | x | x | x | 0 | x | x | one |
Comments
To leave a comment
Industrial programming. programming of controllers
Terms: Industrial programming. programming of controllers