Integer Comparison
Comparing integers performs a comparison operation on 16-bit fixed-point numbers. You can use this command as an ordinary contact. This command compares the inputs IN1 and IN2 according to the type of comparison that you select in the browser. The following table lists the valid comparisons.
If the comparison is true, then the result of the logical operation (RLO) of this
function is 1. Otherwise, it is 0. Negative exit
no comparison as this result can be obtained
using the appropriate inverse comparison function.
| Comparison Types for Integers |
| Comparison Type | Characters in the title at the top of the block |
IN1 is equal to IN2. | = = |
IN1 is not equal to IN2. | <> |
IN1 is greater than IN2. | > |
IN1 is less than IN2. | < |
IN1 is greater than or equal to IN2. | > = |
IN1 is less than or equal to IN2. | <= |
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
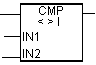 | IN1 | Int | I, Q, M, D, L | First value to compare |
| IN2 | Int | I, Q, M, D, L | Second value compared |
Example and bits of integer comparison status word
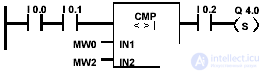 | Output Q 4.0 is set if the following conditions are true: 1 is equal to the state of the signal at inputs I 0.0 and I 0.1, and MW0 <> MW2, and equal to 1 the state of signal at input I 0.2 |
| Status word bits |
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC |
| Record | - | x | x | 0 | - | x | one | x | one |
Example and bits of integer comparison status word
Comparing double integers
The Comparing double integers command performs a comparison operation on 32-bit fixed-point numbers. In all other respects, she is no different from the previous team. the type of comparison you choose in the browser. The table above lists valid comparisons.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
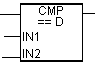 | IN1 | Dint | I, Q, M, D, L | First value to compare |
| IN2 | Dint | I, Q, M, D, L | Second value compared |
Example and bits of the word of the comparison of double integers
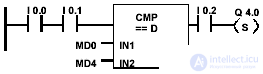 | Output Q 4.0 is set if the following conditions are: Equals 1 signal state at inputs I 0.0 and I 0.1 and MD0 = MD4 And equals 1 signal state at input I 0.2 |
| Status word bits |
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC |
| Record | - | x | x | 0 | - | x | one | x | one |
Example and bits of the word of the comparison of double integers
Floating point comparison
The command Comparing floating-point numbers starts the comparison operation. In all other respects, she is no different from the previous team. the type of comparison you choose in the browser. The table above lists valid comparisons.
| LAD block | Options | Data type | Memory area | Description |
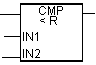 | IN1 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | First value to compare |
| IN2 | REAL | I, Q, M, D, L | Second value compared |
Example and bits of the floating-point comparison state word
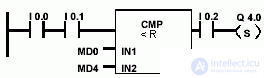 | Output Q 4.0 is set if the following conditions are met: Equals 1 signal state at inputs I 0.0 and I 0.1 and MD0 = MD4 And is equal to 1 signal state at input I 0.2 |
| Status word bits |
| BR | CC 1 | CC 0 | Ov | OS | OR | Sta | Rlo | FC |
| Record | - | x | x | x | x | x | one | x | one |
Example and bits of the floating-point comparison state word






Comments
To leave a comment
Industrial programming. programming of controllers
Terms: Industrial programming. programming of controllers