Lecture
Satellite television - it's simple
After reading the title of this page, you probably thought: "... satellite TV - it's easy!? Oh, well ... this can not be ..." . And you will be absolutely right in this. Indeed, the structure of satellite broadcasting is complex, both in theory and in practice, it will not argue with this, neither the newcomer to this business, nor the professional one. But let's look at it, on the other hand ... from the side of a simple user , that is, you and me. Take, for example, any household electronic device, well ... TV, or VCR. By themselves, they are quite complex electronic-mechanical devices, and only people with good technical training can understand the schematics of their work. That's the way it is ... but, to the common man, precisely on whom this household equipment is designed, it is not necessary to have such deep knowledge, you just need to know how to use them. From this point of view, we will take a look at the theory of satellite television.
Nowadays, satellite television is becoming available to an increasing number of users. If earlier, only organizations could afford the installation of the corresponding equipment, now it is available to almost everyone who has more or less average income. Even if you do not have such equipment, then almost all of you can safely be called users of satellite television. Why? Someone may say, "... but I do not have a satellite dish , and therefore I do not use satellite technology ...", so it seems to be so, but ... Let's follow the whole common chain of transmission of a television signal from the manufacturer to the end user.
And so, for starters, a little history ...
When satellite communications were not yet developed as they are now, ground-based information transmission (transmission of a signal over radio waves) was carried out through the so-called PPC communications (PPC - Radio Relay Communications). On the ground, the receiving and transmitting radio relay stations were installed, which along the chain received and transmitted a radio signal in both directions (see Fig. 1 ). The distance between them, directly depended on the terrain, or, more precisely, the line of sight, and could be, for example, 60 km.
The principle of operation of the RRF was that a mast with two transceiver narrow - beam antennas was installed on the ground (the number of antennas depended on the branching of the RPC lines). One antenna, the first mast, in the transmission mode sent a signal to another same mast, and that, in turn, the receiving-transmitting antenna, which worked for this direction of the signal in the reception mode, received it, and then transmitted through the second antenna to the third mast ( Fig. 1 ). And so on, until the end user.
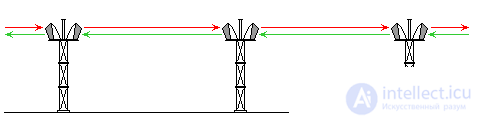
Fig. 1 Ground R adio P c o ligature (PPC).
The red arrows indicate the direction of the signal in one direction, green , in the other. On the " Photo 1 and 2 ", you can see two types of X-ray stations, with receiving and transmitting narrow - beam antennas.

Narrow-directional antenna - An antenna that transmits a radio signal in a specific direction.
In this case, for receiving and transmitting a radio signal, two antennas on different masts are directed at each other ( Fig. 2 ).
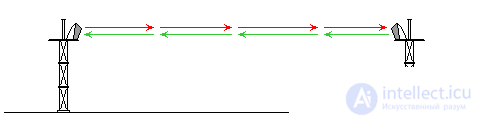
Fig. 2 Two antennas on different masts, directed at each other.
Telephony, television program transmission, and of course the Internet, were transmitted through such PPC communication lines. Television and radio signals, via radio-relay, went to the on-air transmitting station, which is colloquially called “Television tower”, or “Telecentre”. Which, in turn, over radio waves, from a large antenna, or more precisely, from the “antenna-feeder device”, transmitted a radio signal to the already familiar to us receiving television antennas ( Fig. 3 ). Such an antenna ("TV tower"), transmitted this radio signal, not only narrowly, but in a circle.
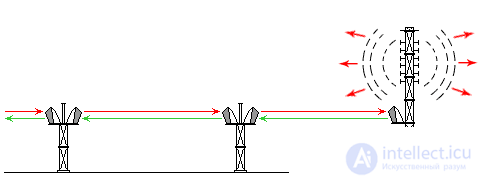
Fig. 3 PPC + TV tower.
Technical progress went forward, and television (including radio) was partially transmitted by another way. The radio signal from the television studio, through the transmitting satellite antenna (in common parlance "plate"), went to the satellite itself, and from there to the receiving satellite antenna of the telecentre, and then on through radio waves, to our television receivers ( Fig. 4 ).
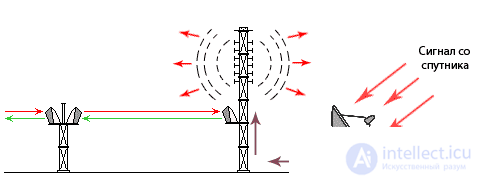
Fig. 4 PPC + Television tower + Satellite communication.
Below in the photo ( Photo 3 ), our first satellite Molniya-1 is depicted, which in 1965, figuratively speaking, threw the "space bridge" from Moscow to Vladivostok, through which television programs were transmitted in both directions, and also telephone exchange was carried out. -the telephone channels.
Photo 3 Space communications satellite Molniya-1.
Then a number of launches followed, and in space a system of Molniya-1 satellites, following one another with a time shift of several hours, was formed to ensure continuous communication.
Years passed ... Now the industry began to produce satellite equipment for end users (viewers), that is, for us. Now, it has become possible to practically not use terrestrial telecommunications, and to use satellite communications - a television studio - a satellite - a spectator ( Fig. 5 ). That's actually about this type of communication, in the future and will be discussed on the following pages.

Fig. 5 television studio  satellite
satellite  viewer.
viewer.
This concludes the history lesson, and move on to the concepts of the very foundations of satellite television ...
And so the overall signal sequence is television studio.  Satellite
Satellite  Viewer Or we will express more precisely the Provider (organization transmitting information)
Viewer Or we will express more precisely the Provider (organization transmitting information)  Satellite
Satellite  Consumer . Since we cannot control the provider (we watch the TV program and cannot change it), which means we, in principle, don't care how the signal goes to the satellite itself. Based on this, we will simplify our chain, mentally removing the provider, and we will succeed in such a one-way communication channel:
Consumer . Since we cannot control the provider (we watch the TV program and cannot change it), which means we, in principle, don't care how the signal goes to the satellite itself. Based on this, we will simplify our chain, mentally removing the provider, and we will succeed in such a one-way communication channel:
Satellite - Transmitting Satellite Antenna 
 satellite receiving antenna - viewer
satellite receiving antenna - viewer
The satellites from which we will receive the signal are in geostationary orbit, at a distance of about 36,000 (thirty-six thousand) kilometers from the earth. Since the satellite must constantly reside at the same point relative to our planet, it rotates around the earth perpendicular to its axis, in the same direction and at the same speed ( Fig. 1 ), that is, it is at the same time as the planet itself. Since the earth has a spherical shape, all coordinates are measured in degrees, and location is determined by longitude and latitude.
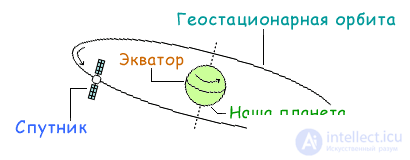
Fig. 1 Satellites in geostationary orbit
To make it easier to remember where the longitude is, and where the latitude is, let's take the familiar EQUATOR as a reference point. The latitude will be located parallel to this equator, and the longitude is perpendicular, that is, it will cross it.
For clarity, let's take, what be a satellite, for example Express AM 22 with coordinates of 53.0 ° E and figure out what values determine its coordinates.
The first is latitude , and as usual it is not indicated, since this value is constant and is always equal to 0 ° . Why? The fact is that the geostationary orbit is located strictly above the equator, which means that the latitude of all satellites is exactly the value of zero degrees , and the difference in location will be determined only by its longitude. And this means that the second value is longitude, and it is equal to - 53.0 ° .
The third value of E , or rather, an explanation, to the second, and indicates how long this satellite has, namely, east or west.
As a rule, in the definition of longitude, two Latin letters are used for abbreviations:
E - from the word East (in translation - EAST),
W - from the word West (in translation - the WEST).
In our case, the longitude will be east, that is, abbreviated E.
There is a little more ...
Based on the fact that the circle is 360 degrees, it is divided into two parts, 180 degrees each, and the zero degree of the geostationary orbit will pass through 0 ° latitude and 0 ° longitude, this is somewhere above the Strait of Guinea. West longitude will be located, to the west of Greenwich well and east, to the east of Greenwich ( Fig. 2 ).
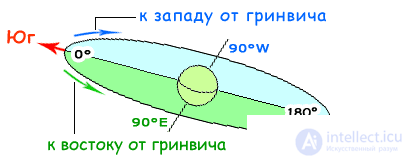
Fig. 2
Here, for example, two satellites, Express AM 22 53.0 ° E and Intelsat 707 53.0 ° W, have the same magnitude in degrees ( Fig. 3 ), and the difference in coordinates will be in which side of Greenwich the satellites are . In our case, Express AM 22 will be located east of Greenwich, east longitude, and Intelsat 707 west, west longitude.
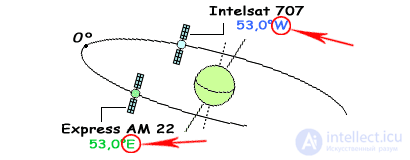
Fig. 3 Two satellites with the same numerical values.
From all this it follows that the satellite Express AM 22 has coordinates of 0 ° latitude and 53.0 ° east longitude.
Summarize:
Sometimes you will find that the coordinates of a particular satellite will be measured on the basis of the azimuth. In this case, the azimuth of the satellite is calculated directly from the place where your satellite dish is located .
Since we live in the northern hemisphere, all the satellites visible to us will be located in the southern side , and more precisely, in the south-east and south-west.
For any of us, from Earth, only part of the geostationary orbit is visible (in the form of an arc above the horizon). This determines the number of satellites from which the signal can be received, since the remaining satellites will disappear from us beyond the horizon.
The order of location and coordinates of well-known satellites can be found below from the table. Since the composition of the satellites periodically changes, or their names change, some data may no longer be accurate. For example, when setting up some satellite receivers (receivers), you may not find the name " ABS 1 " (75.0 ° E) in the satellite selection menu, and the old name " LMI 1 " will be present. For more accurate data, see the relevant literature, or on the Internet, for example, on the websites www.telesputnik.ru and www.lyngsat.com.
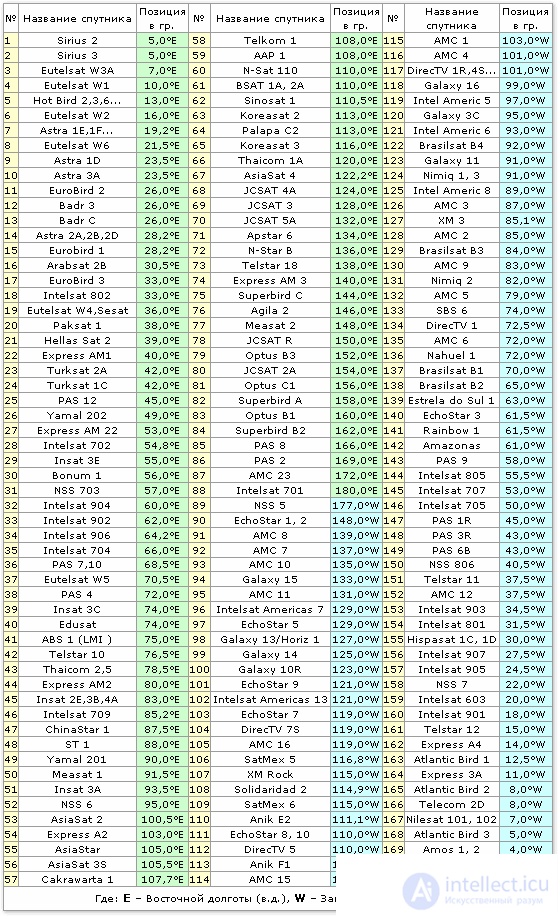 (table of satellites as of 2007–2008)
(table of satellites as of 2007–2008)
Now we know that the satellites do not fly somewhere overhead, but have their own specific orbit, and each has a specific location. And now you, without any difficulty, on a geographic map, you can walk through zero latitude (equator), and determine where any satellite you need is located.
But ... in order to properly configure the satellite antenna , it is not enough to know only the geostationary position of the satellite itself. You also need to have the coordinates of the settlement where you live. Here, as well as with the coordinates of the satellite, everything is calculated in degrees, and is determined by the latitude and longitude. Only the latitude there was a constant of 0 ° , and here it can take on different values and can be NORTH or SOUTH .
The latitude of the place: N - north, S - south.
Longitude of the place: E - east, W - west.
Here, I would like to clarify one point. Since you will be adjusting the satellite antenna manually, it is not necessary to know the exact coordinates. It is enough, for example, holding a compass in your hands, to know the direction in which the satellite you are looking for is located. But if, for ease of customization, you use any programs, then you need to enter accurate data. These data can be found in the topographic map of your area. For example, the geographical coordinates of Moscow will be as follows:
Moscow - 55.7 ° north latitude , and 37.6 ° east longitude
Of course, you will have to decide who will install the satellite equipment, you yourself, a friend, acquaintance, or a specialist from the service center. But in any case, you will have to choose a satellite (or satellites, if the antenna has a motor or a multifed) from which you receive the signal. But before you choose it, you must learn to understand the design of the satellite dish , its individual components and the principles of their work. Why?...
The fact is that the signal coming from the satellite transmitting antenna has a different configuration, which means that the receiving device of the satellite antenna , as well as its dimensions, are also different. That is, the equipment of the antenna and its cost, directly depends on what channels you will watch. And in order to understand the channel parameter table of the desired satellite (transponder table), you need to know what types of receiving devices a particular signal is received. Subsequently, you will know which TV shows, with a certain configuration of the antenna, you will be able to watch, and which simply will not be available. And most importantly, you can choose the configuration of the equipment, depending on your financial capabilities.
- the mirror, for the signal stream from the satellite, (in common parlance "plate") is intended to focus on the feed of the converter of a parallel beam of radio waves emitted by a particular satellite. In shape, antennas differ, on direct-focus and offset.
Converter - another name for LNB (Low Noise Blockconvertor) or LNA (Low Noisy Device) - is such a receiving device that is mounted in focus of the signal reflected from the satellite antenna . That is, an electromagnetic signal coming from the satellite is projected onto its illuminator. A converter converts this signal into an electrical one and transmits it to a receiver (receiver). Converters are for different ranges and for different configurations of signals, as well as for certain types of satellite dishes .
I want to explain a little at once. So that you better assimilate the material and do not clog the head, as long as it is unnecessary information, I will give only what you have to face. How to say so superficially, sufficient for the initial concept of the process of satellite reception.
Comments
To leave a comment
The television. Theory. Satellite
Terms: The television. Theory. Satellite