Lecture
Next, we move on to a more accurate determination of the diameter of our satellite dish , and learn how to deal with the satellite coverage area map.
On the previous pages of this section, some dimensions of the diameter of the satellite dish were explained. For example, for reception in the Ku-band , one diameter, and for reception in the C- band, another. This is due to the properties of the passage of an electromagnetic radio signal, at a certain frequency.
Also, on the first pages of this section, I indicated the height of geostationary satellites from the very surface of the earth. This distance, as you may recall, is approximately 36,000 (thirty-six thousand) kilometers. To overcome such a long distance, the satellite signal, of course, must have its own specific radiation power .
Each geostationary satellite is a kind of a narrowly focused transmitter. Each of them has a certain radiation power of the signal, and its own direction of this radiation, that is, where the beam of this signal is directed.
For the principle of directional propagation of a satellite signal over the surface of the earth, one can take the same principle of operation for a familiar hand flashlight. Rather, the principle of lighting them a certain part of the surface of the earth ( Fig. 1 ).
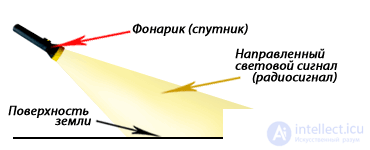
Fig. 1 Comparison of satellite signal propagation over the surface of the earth, with the principle of the action of a flashlight.
A flashlight, like a satellite, has its own specific signal strength (only here we mean the light signal), and a certain direction of emission of this signal relative to the surface of the earth. All of you probably more than once used such a flashlight in the evening. For example, walking along the path, and illuminating the very surface of the earth. And as you remember, not the whole path was lit by such a flashlight, but only a certain part of it. The beam, with its light beam, as if brightly illuminating only some place of the path, and the further the beam of the flashlight went, the less illuminated this path.
The same happens with the satellite signal. On one section of the earth's surface, the radiation power is at its maximum, and as one moves away from the satellite, this power gradually falls.
Now, what we have is ... The diameter of the satellite dish mirror is directly dependent on both the power of the signal received from the satellite and the distance of the antenna from this satellite. That is, the greater the signal power , the smaller the diameter of the satellite antenna required. And vice versa. The smaller the signal power , the larger the diameter of the satellite dish .
And here, begs such a question. But where do we get to ordinary users, to know what power, and in what direction, the signal comes from a particular satellite? That is, where do we get these parameters from?
These parameters are determined by a special satellite coverage map, and are usually provided by the satellite provider itself.
(provider - provider) is an organization that provides services of a satellite service. For example, television, radio channels, or services associated with satellite Internet.
Where do we get these cards? If you read these pages, it means that you have access to the Internet. Therefore, respectively, satellite coverage maps, it is easier and more convenient for you to take on the site of the satellite providers themselves.
Having connected to the Internet, go to any Internet search engine, for example, Yandex or Google, and enter something like the words " satellite coverage map XXXXXXX " (where "XXXXXXX" is the name of the satellite), and in any case you will definitely find some useful links.
If you are going to become a user of satellite Internet, you can take a coverage map directly from the site of the company that provides this service. As a rule, such companies provide services of several providers. For example, at the time of this writing, RusLink provided six satellite Internet providers: skyDSL, PlanetSky, SpaceGate, SatGate, SpectrumSat and OpenSky.
Also, satellite coverage maps can be found on other websites of a similar theme. For example, www.telesputnik.ru or www.lyngsat.com. To tune a satellite dish to a particular satellite, I used the site www.lyngsat.com more than once. Below, I have indicated the procedure in more detail:
For example, go to Google search engine, and enter such a query " Express AM 22 satellite coverage map ". That is, for the satellite Express AM 22 53.0 ° E. Here we choose something simpler from the heap of links. For example, a coverage map from the site of the company Union Sat.
Now, let's look at the map of the desired satellite offered to us ( Fig. 2 ).
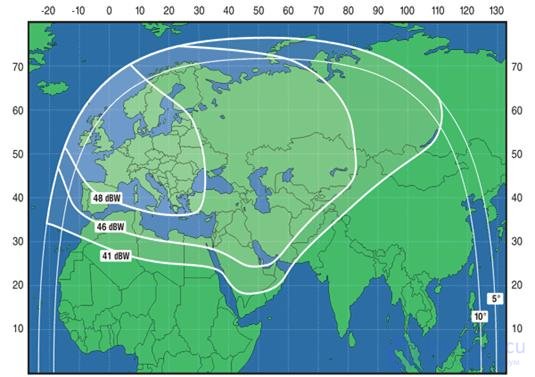
Fig. 2 Satellite coverage map Express AM 22 53.0 ° E.
As you can see, on this map, there are three selected zones. Their number may be more, maybe less, it depends on the data submitted by the provider. They are called zones of confident reception . It turns out that the map itself is, as it were, divided into three areas (they can also be called “petals”, “rays”, etc.). Each region has its own specific signal strength, which is received by this satellite. Such power is calculated in dBW (decibel-watt).
dBW (decibel-watt) - in order, again, not to bother you with this parameter, without this large amount of information, we will not consider in detail. Just take it as a unit of measurement of the satellite signal power , which is necessary for further calculation of the diameter of your satellite dish .
At the border of each zone, there are values of the signal power, which, already reached the earth's surface (Fig. 3). In our example, they are 48 dBW , 46 dBW and 41 dBW .
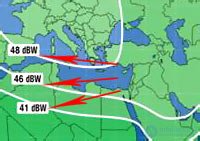
Fig. 3 Signal strengths on the ground.
You probably already noticed, these values are gradually decreasing. That is, as I explained above, the further the satellite dish is from the satellite itself, the lower the signal power will be. Or, to put it differently, the larger the coverage area, the lower the power of the emitted signal at its edges.
Now, let us recall a simple example of the propagation of a light beam from a flashlight, which I compared with a directional beam of a satellite signal ( Fig. 4 ).
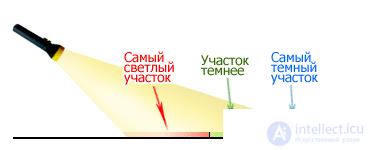
Fig. 4 The spread of the light beam from a flashlight.
As on the coverage map (shown in Fig. 2 ), I also divided the illuminated surface into three areas. As you can see, everything is simple. At each edge of the area (petal), its specific “light power” is emitted.
Now, let's determine how the diameter of the satellite dish , you can confidently take a particular satellite signal power. For this, we need to convert the dBW parameter to the desired antenna diameter. But in order to do this, it is necessary in our calculations to use a rather abstruse formula, where not all values will be understood by the beginner. Therefore, we will use the table of ready-made dBW ratios - the diameter of the satellite dish taken from the same site www.unionsat.ru, or rather, from the same page where the satellite coverage map is located.
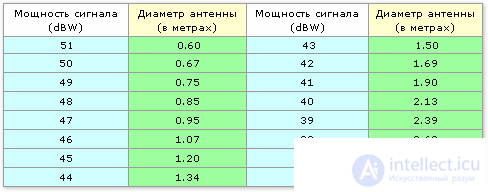
From this table, it is quite clearly seen that the smaller the signal power, the larger the diameter, a satellite dish is required for reliable reception of a signal from this satellite.
Now, by determining in which of the coverage areas your settlement is located, you can easily calculate the size of the antenna you need (which are recommended by this satellite provider).
In order to make it easier to understand satellite coverage maps, without any calculations, on some sites, instead of the dBW parameter (dBW), the diameter of the satellite dish is immediately indicated, in meters. For example, as on the coverage map taken from the RusLink website ( Fig. 5 ).
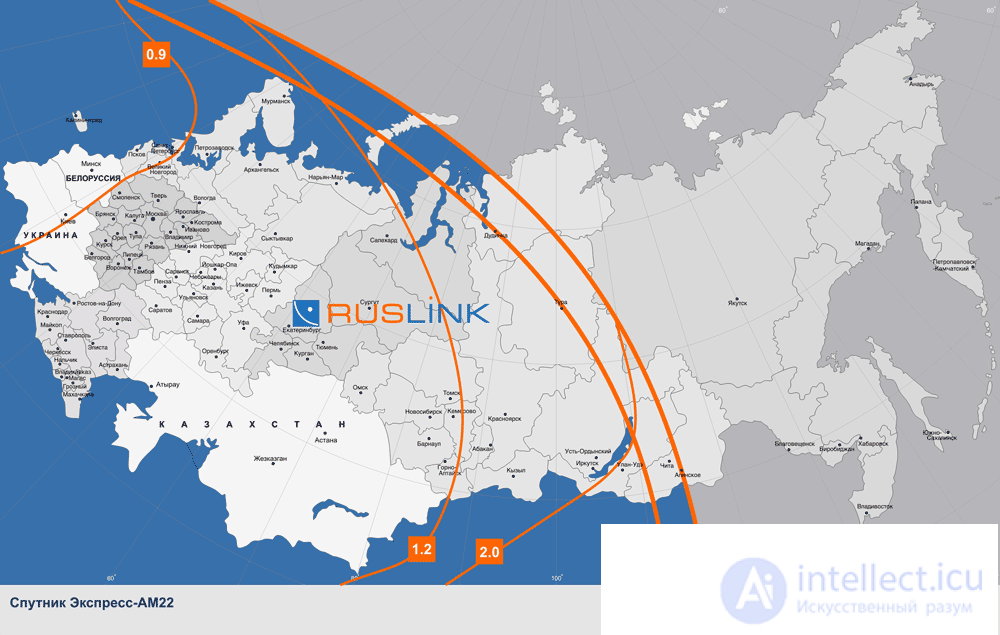
Fig. 5 Satellite coverage map Express AM 22 53.0 ° E.
Satellite coverage maps can be given for both individual and several transponders. It can also be given for the Ku or C bands.
Unfortunately, the satellite provider itself cannot foresee all the nuances associated with the end users, that is, us. Therefore, to determine, so to speak, a more confident value of the diameter of our satellite dish , let's follow the signal transmission order from the satellite to the satellite receiver itself.
Comments
To leave a comment
The television. Theory. Satellite
Terms: The television. Theory. Satellite