Lecture
We tried in some way to systematize the approach to the choice of the antenna, the result was the scheme, which is shown below. The selection includes two stages. At the first stage, the minimum necessary requirements for the antenna are determined. This is a “purely technical” stage, it does not imply a choice: if these requirements are not met, you will not be able to receive the necessary programs with the desired quality. The second stage is “gustatory”. Depending on the available money or personal preferences, you can choose one or another antenna, but only from those that meet the minimum necessary requirements. 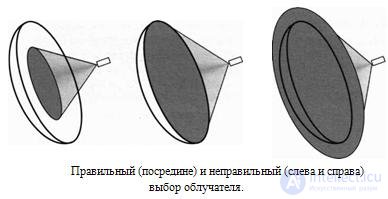
The initial data for the first stage are your geographic location and the set of satellite channels that you would like to watch. The selection of satellite channels for viewing is in itself a difficult task for a beginner. Tables of TV channels that can be received in Russia can be viewed in the Tele-Sputnik reference book. Satellite television". In addition, the most accurate, daily updated data on satellite channels can be found on the Internet. The most well-known and reliably working pages are the Lyngemark Satellite Chart www.lyngsat.com and Satellite Control Center www.satcodx.com projects. The second site supports many languages, including Russian. The first site exists only in the English version, but it is more convenient: channel tables are more visually compact, in addition, an additional reference service is supported. For example, it is possible, knowing the name of the channel and the country, to determine which satellite (s) the channel is broadcasting (lyngsat-address.com). There is also a not very accurate, but very convenient online calculator of azimuths and elevation angles of Lync SatTracker satellites. Sometimes it is difficult for the user to evaluate certain satellite channels, since he has never seen them before and does not know anything or anything about them. In this case, let's say another option is to choose not specific channels, but a satellite (s) on which the most channels, for example, in a certain language. One way or another, one or more satellites are selected for reception.
The satellite visibility and the required antenna diameter are determined by the selected satellite and the geographical location of the receiving point. If you know for sure that the desired satellite is actually being received in your city by an antenna of a certain size, the question is closed. Most often the way it is, because the requests from users are usually the same, and the same satellites are the most popular. Nevertheless, it is possible that you need an “exotic” satellite that no one in your region has yet received, or this satellite has just begun work, or you are still the first and only satellite TV enthusiast a hundred miles around. Then you have to make some calculations.
Satellite visibility is determined easily and unambiguously. To do this, you need to calculate the polar coordinates of the satellite in your area - the azimuth and elevation. Previously, formulas or nomograms were used for calculations, it is quite difficult. Now this is not necessary, you can easily find many calculator programs on the Internet. A simple and visual calculator can be downloaded for free from the page http://chishma.ru/download/satellite-antenna-alignment.html . After downloading and installing the program, you need to start the calculator with the Antenna Alignment button (antenna setting) and enter the initial data: geographical longitude (Longitude) and latitude (Latitude) of your city and satellite orbital position (Satellite Position). If the elevation angle (Elevation) is negative (Below horizon), the satellite is below the horizon, and its reception in your city is impossible. You can use online calculators, for example, the SatTracker calculator at www.lyngsat. com. Once logged in, you must select the SatTracker service for the desired region (Europe, Asia, America, Atlantic) and select the desired satellite from the table. A map appears in which you need to poke the mouse as accurately as possible to indicate your position. The latitude and longitude of the selected point are displayed side by side, so you can adjust your position so that the coordinates are as close as possible to the actual ones. The azimuth and satellite elevation are calculated automatically. In this regard, the domestic program sattv.exe is even more convenient. By entering the coordinates of the city or by selecting a city from the list, you can click the Polar Suspension button, and the program will display the positions of the two extreme satellites of the visible part of the geostationary orbit — the most western and the most eastern one. Now, if you go having bought a tour to St. Petersburg for a new year to your friends, and they have stopped showing a TV with a satellite receiver, you can set up a plate for them just as if you were in your hometown.
The diameter is determined by the equivalent isotroped radiated power (EIRP) of the satellite at the receiving point. Maps of satellite service areas can be found in the Tele-Satellite. Satellite television". To view the map on the Internet, you need to find the desired satellite on www.lyngsat.com, find the desired channel on the satellite and select the link in the Beam column (beam) opposite it. On the map you need to find the place where your city is located, and determine the EIRP for this place by isolines. Further several different methods of calculation are used. The simplified method is used if the eirp is quite large, and the diameter, respectively, is small. Its essence is very simple: according to the table, the diameter is selected depending on the eirp.
The method does not take into account the characteristics of other equipment, such as a converter, and other factors. For a more accurate calculation, you can use formulas or calculator programs, for example, those mentioned by SMWLink or sattv.exe. However, these calculations may give an incorrect result. The fact is that the eirp on maps is indicated for a “full transponder”, that is, for a signal with a 36 MHz bandwidth. Real digital television signals can occupy a smaller band, and in the 36 MHz band several signals can be placed, respectively, the power of the satellite transmitter (transponder) is divided between these signals. There are a number of parameters of the digital signal that also affect the minimum diameter of the antenna, but which are not taken into account in calculator programs. If we are talking about small diameters, within 1 -1.5 m, then the errors are not so terrible - anyway, the dimensions of the produced antennas have a number of typical values, and the result will still have to be rounded to the nearest size. In addition, the cost of such antennas is small and does not greatly depend on the diameter. Antennas more than 1.5 m are quite expensive, and with increasing diameter, the cost does not increase proportionally. Therefore, for large antennas, it is desirable to determine the size with maximum accuracy. More or less correct result is given by the “method of stock or shortage”. This method can be used if it is known that at a certain geographical point X the desired signal is received with a deliberately acceptable quality to an antenna with a diameter of Dx. It is necessary on the map of the satellite service area to find the EIRP for point X and the EIRP for your city. If the eirp is greater than eirp, then the antenna with a diameter D in your city will have a gain margin, if it is less, the gain will not be enough. The diameter of the antenna Do, necessary for reception in your city, is calculated by the formula:
Ao = Ah * 10 ^ (A / 20)
where A = eiru-eirp.
The size of the antenna almost uniquely determines its geometry. If the diameter is less than 1.5 meters, the antenna will be offset; if more than 2.5 m, it will be out-of-focus. Antennas from 1.5 to 2.5 m can be both offset and direct focus, but when choosing an offset antenna you should pay attention to the minimum angle of elevation. In high latitudes offset antennas of large sizes should not be used.
From the frequency range depends on the design of the antenna. To receive programs in the C band, you can use inexpensive mesh antennas (for example, LANS, KTI, Manhattan, Eagle) or prefabricated steel antennas of Chinese and Taiwanese production (SVEC, JONSA, HUATAI). If the antenna must operate in the Ki range, or in both bands, it must be solid and preferably integral. It is possible to use a national antenna for working in the Ki range only if it is a high quality antenna.
If you do not have enough television programs of one satellite, you can use a polar-mounted antenna, but this is not always the only possible solution. If there are few satellites of interest to you, and for receiving each of them a reasonably inexpensive antenna, it is often more advantageous to install several separate antennas. Using an inexpensive device - an antenna switch - you can easily connect up to 4 antennas to one receiver, and from 5 to 16 antennas using several switches. A popular system with two antennas for receiving NTV-Plus programs from the Eutelsat W4 satellite and the programs of European satellites Hot Bird in position 1 3 degrees east longitude. In some particular cases, it is possible to use one antenna with several converters for receiving two or even three satellites. For this, the satellites must be located in orbit close to each other. For example, it is possible to receive on one antenna TV channels of the Yamal, Express-BA and Express-AM1 1 satellites in positions 90, 80 and 96.5 degrees East. respectively.
At the second stage, the initial data are the minimum necessary requirements, defined earlier, and the amount of money that you have. If possible, it is better to install an antenna with a diameter larger than the minimum required. Gain margin is never superfluous, especially if in the future you decide to reconfigure the antenna to receive another satellite. If you can choose between a solid and a mesh antenna, it is better to buy a solid one, and from the whole and the national team it is better to choose a solid one. Such an antenna will work better and will last you longer.
Comments
To leave a comment
The television. Theory. Satellite
Terms: The television. Theory. Satellite