Arithmetic expressions are written according to the following rules:
- You can not omit the multiplication sign between the factors and put two signs of operations side by side.
- The indices of array elements are written in square (school AY, Pascal) or round (Basic) brackets.
- Variables are used Latin letters.
- Operations are performed in order of precedence : first, the computation of functions, then the exponentiation, then the multiplication and division, and last of all, addition and subtraction.
- Operations of one seniority are performed from left to right . However, in school AA there is one exception to this rule: erection operations are performed from right to left. Thus, the expression 2 ** (3 ** 2) in the school AJ is calculated as 2 ** (3 ** 2) = 512. In the QBasic language, the similar expression 2 ^ 3 ^ 2 is calculated as (2 ^ 3) ^ 2 = 64 And in the Pascal language the operation of raising to a power is not provided at all, in Pascal x ^ y is written as exp (y * ln (x)), and x ^ y ^ z as exp (exp (z * ln (y)) * ln (x)).
Examples of writing arithmetic expressions
| Math notation | Record in school algorithmic language |
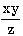 | x * y / z |
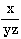 | x / (y * z) or x / y / z |
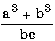 | (a ** 3 + b ** 3) / (b * c) |
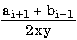 | (a [i + 1] + b [i-1]) / (2 * x * y) |
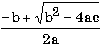 | (-b + sqrt (b * b - 4 * a * c)) / (2 * a) |
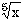 (x <0) (x <0) | sign (x) * abs (x) ** (1/5) |
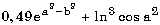 | 0.49 * exp (a * a - b * b) + ln (cos (a * a)) ** 3 |
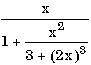 | x / (1 + x * x / (3 + (2 * x) ** 3)) |
Typical errors in writing expressions:
5x + 1
a + sin x
((a + b) / c ** 3 | Missed multiplication sign between 5 and x
The x argument of the sin x function is not enclosed in brackets
Not enough closing brackets |
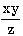

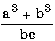
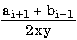
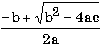
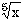 (x <0)
(x <0) 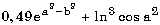
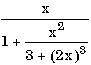
Comments
To leave a comment
Programming Languages and Methods / Translation Theory
Terms: Programming Languages and Methods / Translation Theory