Lecture
CD-R became the very first among recordable optical media. They had the ability to record only once. The data was saved when the laser heated the working layer, causing its chemical reaction (at t? = 250? C). At this moment dark spots are formed at the places of heating. This is where the concept of “burn out” came from. On DVD-R discs, “burn through” happens in a similar way.
 A bit different situation with CDs , DVDs and Blu-ray discs with rewriting function. On their surface does not form such dark points, because the working layer is not a dye, but a special alloy that is heated by a laser to 600? C. Then, the surface areas of the disk that fall under the laser beam become darker and have reflective properties.
A bit different situation with CDs , DVDs and Blu-ray discs with rewriting function. On their surface does not form such dark points, because the working layer is not a dye, but a special alloy that is heated by a laser to 600? C. Then, the surface areas of the disk that fall under the laser beam become darker and have reflective properties.
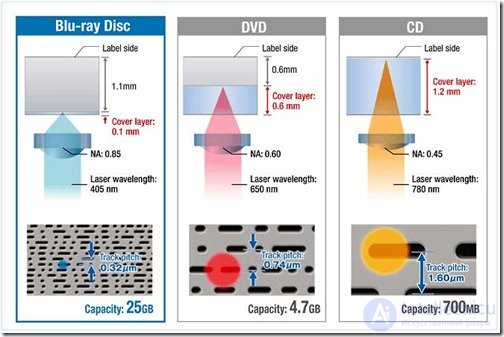
At the moment, in addition to CDs, which can be considered the pioneers in a series of optical media, there are such discs as DVD and Blu-ray. These types of disks differ from each other. For example, capacity. Blu-ray disc holds data up to 25 GB, DVD - up to 5 GB, and CD - up to 700 MB in total. The next difference is the way data is read and written to Blu-ray drives. A blue laser is responsible for this process, the wavelength of which is one and a half times less than that of a red laser CD or DVD drive. That is why on the surface of Blu-ray discs, equal in size to other types of discs, you can record information many times larger.
The above three types of laser discs can also be classified according to their formats:
1. CD-R, CD-RW discs are the same in volume (up to 700; sometimes 800MB, but such discs are not readable by all devices). They differ only in that CD-R is a one-time recordable disc, and CD-RW is reusable.
2. DVD-R, DVD + R format discs, as well as DVD-RW discs differ only in the ability to repeatedly rewrite DVD-RW discs, and the rest of the parameters are the same. 4.7 GB - the volume of a standard DVD and 1.4 GB - the volume of a DVD with a diameter of 8 cm.
3. DVD-R DL, DVD + R DL - dual-layer discs that can hold 8.5GB information.
4. BD-R Formats - Blu-ray single-layer discs, 25 GB in size and BD-R DL - Dual-layer Blu-ray discs, 2 times larger.
5. Formats BD-RE, BD-RE DL Blu-ray discs - rewritable, up to 1000 times.
 Disks with “+” and “-” signs are a relic of formatted disputes. Initially it was thought that “+” (for example, DVD + R) was the leader in the computer industry, and “-” (DVD-R) was a quality standard for consumer electronics. Now almost all the equipment easily recognizes disks of both formats. None of them has clear advantages over each other. Materials for their production are also identical.
Disks with “+” and “-” signs are a relic of formatted disputes. Initially it was thought that “+” (for example, DVD + R) was the leader in the computer industry, and “-” (DVD-R) was a quality standard for consumer electronics. Now almost all the equipment easily recognizes disks of both formats. None of them has clear advantages over each other. Materials for their production are also identical.
The disc itself, which is used at home to record information, is no different in size from discs produced industrially. The structure of all optical media is multilayered.
 Now a drop of scientific theory. All optical media have a spiral track running from the very center to the edge of the disk. It is along this path that the laser beam records information. The spots formed during the “burning” by the laser beam are called “pitas”. The areas of the surface that remain intact are called land. According to the language of the binary system, 0 is “pit”, and 1 is “land”. When a disc starts to play, the laser reads all the information from it.
Now a drop of scientific theory. All optical media have a spiral track running from the very center to the edge of the disk. It is along this path that the laser beam records information. The spots formed during the “burning” by the laser beam are called “pitas”. The areas of the surface that remain intact are called land. According to the language of the binary system, 0 is “pit”, and 1 is “land”. When a disc starts to play, the laser reads all the information from it.
Pitas and Lands have different reflectivity, therefore, the drive easily distinguishes between all the dark and light areas of the disk. And this is the very sequence of ones and zeros inherent in all physical files. Gradually, it became possible to increase focusing accuracy due to the development of technologies that have reduced its wavelength from a laser beam. Now on the same area of the disk as before, you can place a much larger amount of information, because the distance between the laser and the working layer is directly dependent on the wavelength. Shorter wave - shorter distance.
Stage 1. Recognition of media type. We loaded the disc and wait for the recorder to give information about the appropriate recording speed and the most optimal laser beam power.
Stage 2 The program that controls the recording, makes a request to the recorder about the type of media used, the amount of free space and speed with which to burn the disc.
Stage 3 We specify all the necessary data requested by the program, and compile a list of files that require writing to disk.
4 stage. The program transmits the recorder all the data and monitors the entire process of "burning".
Stage 5 The recorder sets the power of the laser beam and starts the recording process.
Even for carriers of the same format, the recording quality can be completely different. To ensure the quality of the recording is high, you should pay attention to the speed specified in the recording. There is a “golden rule” - fewer errors at lower speeds and vice versa. A significant role is played by the recorder itself, namely, its model.
 A disk on which some information has appeared, it is desirable to sign right there, in order to avoid confusion. This can be done in different ways:
A disk on which some information has appeared, it is desirable to sign right there, in order to avoid confusion. This can be done in different ways:
On the labels of new discs, you can see the term indicating how much data can be stored on this carrier. Sometimes this figure corresponds to 30 years. In reality, such a term is almost impossible. During its existence, the disk can be subjected to various impacts and damage. If it was recorded at home, its shelf life is reduced even more. Only perfect storage conditions will keep all data on disks safe and sound.
CD-DA (Compact Disc - Digital Audio), were developed by Sony and Philips in 1982. The wavelength of the laser in the air - 780 nm. Diameter 120 mm (information zone from approximately 50 mm to 116 mm) or 80 mm. Thickness 1.2 mm. Weight - from 14 g to 33 g (DVD - from 13 to 20 g). The chain of grooves (pits) is arranged in a spiral as in a record, but in a direction from the center (in fact, CD is a sequential access device with an accelerated rewind). The interval between the turns is 1.6 μm, the pit width is 0.5 μm, the depth is 0.125 μm (1/4 of the wavelength of the laser beam in polycarbonate), the minimum length is 0.83 μm. The volume is 74 minutes of sound (44.1 kHz, 16 bits, PCM, big-endian) or 650 MB of data (333000 sectors of 2048 bytes), for 80 mm - 21 minutes (185 MB). The sampling rate was chosen to make copying to DAT (48 kHz) difficult. There are modifications in 80 minutes (700 MB), 90 minutes (791 MB) and 99 minutes (870 MB). A constant linear speed of moving the carrier relative to the head (1.25 m / s) is provided, respectively, the rotational speed changes when reading different parts of the disk (from 500 rpm to 200 rpm), which increases the access time (it is necessary to accelerate and slow down the rotation of the disk) . The nominal (1x) data transfer rate is 150 KB / s (176400 bytes / s of audio or raw data, 4.3 Mbps of “physical” data).
|
Standards |
|
Carrier |
CD может иметь bar code (вертикальные штрихи), прожженный лазером в BCA (burst cutting area, внутреннее кольцо перед lead-in), используемый для серийного номера, но мне не встречались устройства, которые умеют его читать. DVD может иметь BCA только на односторонних дисках. Для повышения надежности используются коды EDC и ECC.
SID (Source Identification Code) для DVD Audio. Состоит из двух частей: Mastering Code (строка "IFPI" и 4-символьный код, выжигается лазером на штампе) и Mould Code (строка "IFPI" и 4-символьный код, гравируется на форме), которые отпечатываются на противоположных сторонах подложки на внутреннем кольце (до BCA). Должны читаться невооруженным глазом. В этом же кольце могжет быть напечатана и другая информация, требуемая местными законами.
Не рекомендуется наклеивать что-либо на поверхность диска (нарушите балансировку, а скорость вращения 5000 об/мин; к тому же некоторые виды клея растворяют защитный лак; а эти гадкие воздушные пузыри?) или надписывать его (промнете защитный слой или чернила его растворят, графитовая пыль тоже не подарок). Единственным безопасным методом маркировки является печать на специальном принтере. Кстати, простейший способ уничтожить информацию на CD - это содрать присохшую наклейку. Мыть можно теплой водой с мылом (никаких органических растворителей, спирта и прочей химии).
Торговая марка, под которой продаются заготовки, не всегда (точнее, почти всегда не) соответствуют их реальному изготовителю. Даже по ATIP вы можете узнать лишь изготовителя матрицы, но не конкретный завод, использующий эту матрицу. Примеры ATIP дисков различных типов, размеров и скоростей записи. Большой обзор CD-R заготовок, продающихся на московском рынке, можно найти на IXBT.
|
Формат данных CD |
Поверхность диска разделена на области:
Двоичный нуль представляется в виде отсутствия изменений в отражающей способности поверхности диска (длина участка определяет число нулевых бит), единица - в виде изменения отражающей способности на рассматриваемом участке.
Каждый байт данных (8 бит) кодируется 14-битным символом на носителе (кодировка EFM). Символы отделяются 3-битными промежутками, выбираемыми так, чтобы на носителе не было более 10 нулей подряд.
Из 24 байтов данных (192 бита) формируется кадр (F1-frame), 588 битов носителя, не считая промежутков:
При декодировании могут использоваться различные стратегии обнаружения и исправления групповых ошибок (вероятность обнаружения против надежности коррекции).
Последовательность из 98 кадров образует сектор (2352 информационных байта). Кадры в секторе перемешаны, чтобы уменьшить влияние дефектов носителя. Адресация сектора произошла от аудиодисков и записывается в формате A-Time - mm:ss:ff (минуты:секунды:доли, доля в секунде от 0 до 74). Отсчет начинается с начала программной области, т.е. адреса секторов вводной области отрицательные. Биты субканалов собираются в 98-битные слова для каждого субканала (из них 2 бита - синхронизация). Используются субканалы:
На самом деле все еще "интереснее", т.к. в дополнение к секторам определяются секции того же полезного размера, но с несовпадающими границами, причем часть адресов является адресами секторов, а другая - адресами секций. Но об этом лучше сразу забыть ;)
A sequence of sectors of the same format is combined into a track (track) from 300 sectors (4 seconds. See subchannel P) to the entire disk. A disc can have up to 99 tracks (numbers from 1 to 99). A track may contain service areas:
The introductory digital domain must end with post-gap. The first digital track should start from the second part of the pre-view. The last digital track should end with post-gap. Output digital domain does not contain pre-view.
CD-DA. Each sector contains 588 signal samples (PCM, 2 channels, 16 bits). Samples are spread across the sector to reduce the impact of data dropout.
CD-ROM Mode 0: not available.
CD-ROM Mode 1: synchronization, block address, 2048 bytes of user data, EDC (CRC-32), ECC (276 bytes, two sums: P and Q - not to be confused with subchannels!), 8 bytes of zeros.
CD-ROM Mode 2: synchronization, block address, 2336 bytes of user data without additional protection.
CD-ROM XA Mode 1 is the same as CD-ROM Mode 1.
CD-ROM XA Mode 2 Form 1: synchronization, block address, CD-I subtitle (8 bytes, defines the type and format of user data - audio, video, data), 2048 bytes of user data, EDC (CRC-32), ECC ( 276 bytes, two sums: P and Q - not to be confused with subchannels!).
CD-ROM XA Mode 2 Form 2: synchronization, block address, subtitle CD-I (8 bytes), 2324 bytes of user data, EDC (CRC-32).
CD Text (text - author, title - is recorded in the subchannels RW).
CD-Graphics. RW subchannels are used to record graphics.
CD-R and CD-RW. When the disc is closed (finalizing, fixating), the output area is recorded immediately after the program area, after which the input area containing the TOC is recorded. If the disc was not recorded at one time, then the TOC is formed from PMA. The laser can not turn on and off instantly, so the data "burned" during the transition process can not be read (because of this there is a problem of emptying the buffer). Unused spaces are left at the joints. Recording methods:
Multisession (multisession) record. The lead-out area of the second session is recorded after the lead-out area of the first session, then the data area, etc. The size of the exit zone for the second and subsequent sessions is reduced to 2,250 sectors (0.5 minutes, 4 MB). A session is called closed if its data area is framed by an input and output area. Unclosed sessions can only be read by recording devices (access to PAM is required). The pointer in the session TOC to the output area may contain either the address of the output area of the session (closed disk), or the address of the input area of the next session. Recording is limited by disk space, space in PMA and the number of tracks (tracks are numbered all over the disk from 01 to 99). A session can be independent (TOC indicates only tracks within a session) or related (TOC contains addresses of tracks from previous sessions). Sessions can also be linked at the file system level. The session mechanism allows you to "change" a CD-R by writing a new session.
CD-RW erasure: full and fast (TOC only). If the disk is so damaged that it is impossible to perform erasing, then you can try to erase it with ultraviolet light (or sunlight).
It is rumored that some devices record on each disk the Recorder Unique Identifier (RID): the device manufacturer's identifier, model number and serial number (as I remember, typewriters were recorded in the USSR;).
|
Write over 650 MB of data to disk (overburn) |
There are two methods: purchase of a blank marked up (pregroove) for a more standard volume due to closer spiral turns or use of lead-out for these areas and some space behind it. You can use both methods at once. CD-R blanks come in 80 minutes (700 MB), 90 minutes (791 MB) and 99 minutes (870 MB), CD-RW blanks have been encountered (so far?) Only 700 MB. Both methods violate the standard. Either the recording device or the reading device may not be able to work with a closer spiral (see the table of compatibility of recording devices and supported write speeds). For example, my Plextor PX-W1610TA has to set the write speed for 700 MB of CD-RW blanks to 8x (and this does not always help). Lack of space for a lead-out can lead to abnormal termination of the recording (in this case, the TOC will not be written and the disk will be unreadable - write it in DAO mode and the TOC will always be, the -dao switch in cdrecord), the program will fail to start recording (use the -ignsize switch in cdrecord) or the inability to read the resulting disk (especially in older devices, nothing will help here). Another problem is caused by the method of addressing blocks on a disk (the address is written in the format MM: SS: FF relative to the beginning of the data region): first, 2 decimal digits are allocated to the number of minutes, which immediately limits the amount to 99 minutes, second, blocks Lead-in addresses are negative numbers for which addresses are reserved starting at 80:00:00. That is why in the ATIP even the 99-minute blanks are imprinted length 79:59:74. And what the recording device, program or reader will do when it encounters two blocks with the same address is unknown. In general, if your data is dear to you - do not be greedy, write down this 700 MB for 2 blanks.
|
DVD-ROM data format |
The disk information area is divided into an input zone (lead-in zone), a data zone (data zone), and a lead zone (lead-out zone). On a double-layered disk with opposite spirals (OTP), each side contains only one information zone on both layers. An intermediate zone (middle zone) is used to move the beam from layer to layer. Sectors are addressed sequentially throughout the information zone (LBA). No tracks, pauses, gaps, subchannels and A-time addressing. Uniform data format: farewell modes and forms.
The structure of the introductory zone:
Binary zero is represented as no change in the reflectivity of the disk surface (the length of the section determines the number of zero bits), the unit - in the form of changes in the reflectivity in the area under consideration.
The physical sector contains 4836 bytes. Of these, 104 bytes of synchronization and 4732 bytes of channel data.
For DVD, in contrast to CD, the encoding is 8-bit bytes of the recording frame with 16-bit channel symbols without RLL (2.10) spaces (the encoding itself provides no more than 10 consecutive zeros, but knowledge of the subsequent character is sometimes required to decode a byte).
Bytes of 16 frames are mixed similarly to CD to reduce the impact of local carrier defects. Each such “large” block (ECC block) contains 4832 bytes of ECC and 33024 (2064 * 16) bytes of the data frame.
The data frame DVD-ROM, DVD-RAM, DVD-R, DVD-RW (Data Frame) consists of:
Thus, the storage of 2048 bytes of user data consumes 4836 bytes of the physical sector (mixed and spread). This is significantly better than approximately 8415 bytes in the case of a CD-ROM.
NBCA is a narrow ring to the introductory zone on which the code is marked with vertical bars (and what is written there?).
|
DVD-RAM data format |
DVD-RAM contains both printed (embossed) and rewritable data. The first 5 zones of the lead-in zone are printed: the initialization zone, the reference code, the first buffer zone, the control data and the second buffer. In the remaining zones, the spiral is formed by an etched groove (groove), and the recording is made both in the grooves (groove track, groove sector), and between them (land track, land sector). The spiral is divided into virtual tracks (360 ° rotation). In the introductory zone, in addition to the 5 zones defined by the DVD-ROM standard, there is a junction zone (gap between printed and rewritable regions, empty space without sectors), protection zone 1, disk testing area, disk testing area, protection area 2, reserve zone, DMA 1 (defective block management area), DMA 2. Address 0x030000 has not the first sector of the data zone, but the first sector of the first protection zone. The lead-out zone consists of a DMA 3, DMA 4 zone, a protection zone 1, a zone for testing a disk, a zone for testing a disk drive, a protection zone 2, a reserve zone. The first sector of the data zone has the address 0x031000. Each track of the introductory zone consists of 18 sectors. The rewritable region is divided into 24 subzones divided by guard zones. The subzone is framed by protective zones and has an area of spare blocks. LSN (Logical Sector Number) addressing is entered, so all sectors with user data have consecutive numbers starting from 0. Within each subzones, the tracks consist of the same number of sectors (from 17 to 40), but these sectors contain 2697 bytes (data format the physical sector of the DVD-ROM is framed with any additional information, and the title is imprinted during manufacture). The helix itself has a sinus-like shape, with the zero phase located on the border between the sector header and the rest of it (now I understand why DVD-RAM blanks are so expensive;). The contents of all DMA zones are identical and contain information about the formatting of the disk, the primary list of defects (detected during formatting) and the secondary list of defects (detected during operation).
|
DVD-R data format |
The DVD-R before the lead-in zone contains the R-Information zone, which is divided into the PCA (Power Calibration Area, 7088 sectors, 256 for the disc manufacturer) and RMA (Recording Management Area) familiar with the CD-R.
The lead-out zone follows the data zone, but cannot begin earlier than some boundary. Recording mode - CLV. In incremental mode, 3 methods of linking old and new pieces can be used (who chooses?):
The size of the initialization zone (in Lead-In) is determined rigidly and it is divided into the initialization zone itself (45,664 sectors of zeros), buffer zone 0 (512 sectors of zeros) and the information zone about the physical format, which consists of 3,072 sectors containing 192 repetitions of 16 sectors (in fact, the same information as in the control data zone, but not filled by the manufacturer of the blank):
The boundary zones are designed to prevent ordinary DVD-ROM devices from reading data from still unrecorded parts. Each takes from 12 MB to 92 MB depending on the location.
The control data zone is embossed or pre-recorded, therefore framed by binding to the previous and subsequent information. The buffer zone 2 has been renamed to the zone of additional boundary (it contains one more variant of information about the physical format).
A control spiral track is squeezed out on a DVD-R, which also contains data (blocks are numbered down) - Unrecorded Zone (almost undead;):
The data zone can be divided into subzones (RZone, 2102), which can be open (no more than 2) and closed (completed). The unused and unreserved part is called the invisible RZone.
RMA format
|
DVD-RW data format |
The data structure is very similar to the DVD-R structure. Recording mode - CLV.
The control data zone and buffer zone 1 are extruded or prerecorded. The control data zone does not consist of 192 identical copies, but only of 176, followed by 16 servo control units (not defined in the standard).
The extruded control path (Unrecorded Zone) additionally contains suggested OPC values and strategies for erasing. In the PCA, for the disk manufacturer, 16 sectors are allocated around 256.
The format of information on each recording session (RMD) is different for different recording modes (DAO, incremental recording, limited rewriting) and contains data on the disk status (empty, complementary recording, DAO, closed after the complementary recording, minimally cleared, a failure occurs formatting, empty and write-protected, DAO and write-protected, complementary recording and write-protected, closed after complementary recording and write-protected, minimally cleared and write-protected, various limited rewriting modes), copy of information from the embossed track, OPC information for 4 devices (similar to DVD-R, but supplemented with information about erasing), number of changes, number of erasures, RMD bitmap defectiveness bitmap, type of erasing now and current position, type of formatting happening now and current position, addresses and status of input and output boundaries (up to 16 pieces), the number and boundaries of RZone (up to 16 pieces), bitmaps of defectiveness of blocks.
Types of erasure
Formatting types (everything is filled with zeros, except for the input zone, output zone, input boundary, output boundary)
States of limited area:
Каждая заготовка DVD-RW 1.1B имеет уникальный (64 бит) идентификатор (механизм защиты CPRM). Содержимое диска может шифроваться (C2) по ключу, генерируемому из этого идентификатора, поэтому простое копирование даст нечитаемые данные (фильмы).
|
Формат данных DVD+RW |
Режим записи - CLD (Constant Linear Density), устройство может реализовать CAV. Скорость записи - до 4x. Формат фрейма данных и его кодирование совпадает с DVD-ROM. Выбранный метод записи позволяет произвольно записывать и перезаписывать ECC блоки (32 КБ).
Информационная зона делится на вводную зону, зону (пользовательских) данных (2295104 сектора) и выводную зону. Все их можно перезаписывать, чистая болванка не содержит ничего. Первый сектор зоны данных имеет адрес (PSN) 0x30000. Логический адрес (LSN) этого сектора равен 0.
Запись идёт по выдавленной канавке. Канавка имеет форму спирали, на которой с помощью небольших отклонений записана информация об адресах блоков, которые должны быть размещены в данном месте (ADIP - Address-in-Pregroove). На 1 ECC блок приходится 51 бит информации, записанной в ADIP (из них 22 бита - физический адрес). Дополнительно во вводной зоне ADIP содержит информацию о физическом формате (256 байт, копируется в управляющую зону при инициализации):
Вводная зона состоит из
Выводная зона состоит из
Полное форматирование означает заполнение всей информационной зоны (информацией или нулями). Диск считается частично форматированным, если заполнена вводная зона, кроме начальной зоны. При этом внутрення зона идентификации диска должна содержать Formatting DCB (FDCB). Форматирование может происходить до записи на диск (необязательная проверка зоны данных), в фоновом режиме одновременно с записью, последовательная запись без форматирования (в конце записанной области создаётся временная выводная зона; может быть перезаписана при следующем сеансе записи; минимальный размер записи довольно велик).
DCB используются для обмена информацией между устройствами типа +RW. Для чтения полностью отформатированных или записанных дисков в DVD-ROM они не нужны. Обеспечиавют возможность защиты от форматирования, перезаписи и чтения управляющей информации. Каждый DCB должен содержать уникальный идентификатор последнего записавшего его устройства (изготовитель, модель, серийный номер). Пока определены 2 типа DCB
продолжение следует...
Часть 1 optical discs CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-ROM, DVD-R, DVD-RAM, DVD-RW, DVD + RW, DVD + R,
Часть 2 - optical discs CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-ROM, DVD-R, DVD-RAM, DVD-RW,
Comments
To leave a comment
Electromechanical devices of electronic devices
Terms: Electromechanical devices of electronic devices