Lecture
Information security threats are various events, processes or actions that can lead to a violation of the state of the information system. Information security threats can be divided into two types: natural and artificial. Natural phenomena include natural phenomena that do not depend on humans, such as high or very low temperatures, tornadoes, earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, fires, etc. Man-made threats are created by humans and can be intentional or unintentional. Unintentional threats arise from carelessness, inattention, and ignorance. An example of such threats is the installation of programs that are not required for work and subsequently disrupt the operation of the system, which leads to loss of information. Intentional threats, unlike the previous ones, are created on purpose. These include attacks from both outside and inside the company. The result of the implementation of this type of threat is the loss of funds and intellectual property of the organization.
Depending on the different classification methods, all possible information security threats can be divided into the following main subgroups.
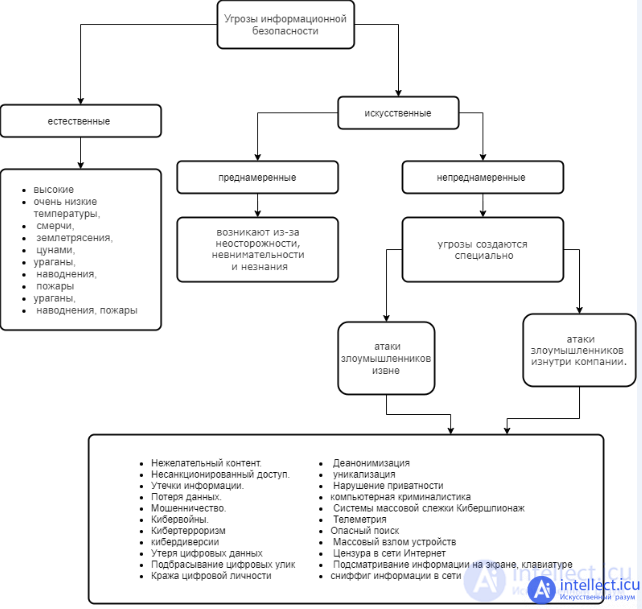
Inappropriate content is not only malicious code, potentially dangerous programs and spam (i.e., what is directly created to destroy or steal information), but also sites prohibited by law, as well as unwanted resources with information that does not correspond to the age of the consumer.
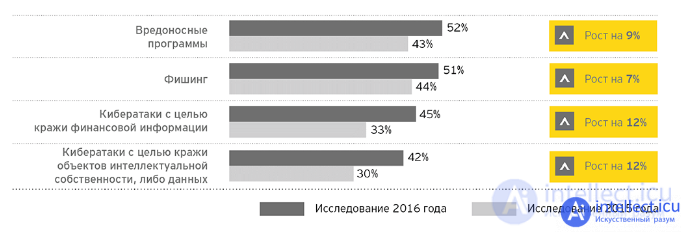
Source: EY International Information Security Survey “The Path to Cyber Resilience: Forecast, Resistance, Response”, 2016
Unauthorized access - viewing information by an employee who does not have permission to use it, by exceeding official authority. unauthorized access leads to information leakage. Depending on what the data is and where it is stored, leaks can be organized in different ways, namely through attacks on websites, hacking programs, intercepting data over the network, using unauthorized programs.
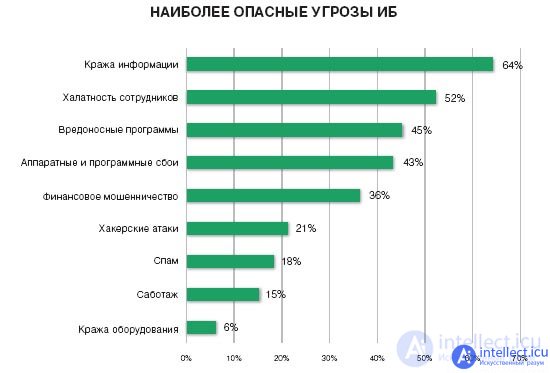
Information leaks can be classified as intentional or accidental. Accidental leaks are due to hardware, software and personnel errors. Intentional, in turn, organize deliberately in order to gain access to data, cause damage.
Data loss can be considered one of the main threats to information security. Violation of the integrity of information can be caused by equipment malfunction or deliberate actions of people, whether employees or intruders.
An equally dangerous threat is information technology fraud (“fraud”). Fraud includes not only credit card manipulation (“carding”) and hacking of an online bank, but also internal fraud. The goals of these economic crimes are to circumvent laws, security policies or regulations, and appropriation of property.
Every year, the terrorist threat is growing around the world, gradually moving into the virtual space. Today, no one is surprised by the possibility of attacks on automated process control systems (APCS) of various enterprises. But such attacks are not carried out without preliminary reconnaissance, for which cyber espionage is used to help collect the necessary data. There is also such a thing as "information war"; it differs from conventional war in that carefully prepared information is the weapon.
Cyber sabotage is secret, carefully prepared special measures of sabotage and reconnaissance groups (DRG) or individual scouts - saboteurs - to disable the most important objects of the information system or their elements by hacking, causing a refusal, defaming, as well as using other methods of influence, for achieving the goal.
Loss of digital data - can be software, hardware, physical. To protect against such situations, complex encryption of the hard disk, additional use of crypto-containers for especially valuable information, and of course a reliable system of regular automatic backup of valuable data, including places for secret storage of backups, are required. Passwords should be created taking into account these recommendations, if there is a risk that they could be snooped, an emergency data destruction system should be configured.
Tossing digital evidence
It often happens that law enforcement agencies, especially in developing countries, and cybercriminals plant digital evidence, and they can plant it to anyone, even to the highest ranking official.
How to protect yourself from digital evidence being planted?
Encrypt all your data All external media, hard drives, operating system must be securely encrypted, and information must be stored strictly in encrypted containers.
Theft of a digital identity is a crime in which a person's personal data is illegally used to obtain material benefits. The English term Identity theft appeared in 1964, its Russian translation is inaccurate, since the identity itself cannot be stolen.
What information is being stolen?
Photos, passport data, photocopies of documents, selfies with documents, copies of bank cards. You can find through the search a lot of offers to buy copies of passport data, maybe you will find your own among those sold.
Purposes of digital identity theft - Fraud and extortion, Getting bonuses and post-payment services, Registering fake accounts with your data, Obtaining a loan, Revenge, Damaging reputation , Corporate attacks.
Deanonymization is the process of establishing the identity of a user on the network or the true place of access to the network.
Establishing the identity of a user or a network exit point by IP address or mac-address is called passive deanonymization, when no attacks are used against the user. This is possible with a pear-to-pear connection to Skype. Viber and other voice messengers. Attacks on a user, for example through a website with malicious JavaScript, or phishing are active de-anonymization. It is important to understand that there is no direct connection between an IP address and any user. The IP address belongs to the network exit point. For example, if you connect to a Wi-Fi router, you get the IP address of this router. All other users connecting to this router will receive the same IP address. Checking the IP address can only indicate the ISP and the general location, by scanning, you can determine the model of the router. Internet service provider,who connected the Internet cable to this router, knows who it is registered for and where it is located, when requested from the competent authorities, he must issue this information. There is also an opportunity to analyze the provider's logs, router logs. An attacker can hack a Wi-Fi router and then start intercepting traffic in order to find clues in it to establish an identity, for example, social network accounts, or try to infect a computer through DNS spoofing or "gluing" packets.for example, social networking accounts, or trying to infect a computer through DNS spoofing or packet splicing.for example, social networking accounts, or trying to infect a computer through DNS spoofing or packet splicing.
Uniqueization - search and collection of unique browser identifiers to form a unique fingerprint, by which it will always be possible to recognize this browser regardless of the IP address and data provided by the user. Uniqueization, as a rule, does not carry the task of establishing the identity of the user, but only recognizing him in any situation. Examples - Canvas fingerprint, WebGL fingerprint, Front fingerprint, etc., as well as through the use of cookies, HWID is a unique fingerprint of "hardware",
Violation of privacy Many users confuse privacy and anonymity, believing that they are the same or similar concepts. In fact, anonymity is the ability to visit sites, perform any active actions on web resources, for example, leave messages, without the ability to associate your actions with your real person or the place of your access to the network. And privacy is the lack of access to information from persons for whom this information is not intended. For example, you are communicating in a messenger with your interlocutor, and Agent John is monitoring this. If he tries to establish the identity of the interlocutors - this is deanonymization, he encroaches on your anonymity. But if he reads your correspondence, this is already a violation of your privacy: he gets access to information, which is your secret with the interlocutor and is not intended for third parties. The most common violations of privacy are reading correspondence in instant messengers, viewing e-mail, and tapping phones. Unfortunately, intelligence agencies are much more likely to violate the privacy of ordinary network users than hackers and cybercriminals.
Tracking
Probably, each of you has come across a situation when you entered a word in the search, then, having closed the search, went to the site and you are shown ads related to recent search queries? This is tracking. The simplest example of tracking is targeted advertising in the Google advertising network.
Today, there are many implementations of user tracking, for example, tracking by MAC address. With an active Wi-Fi module, your mobile device or laptop constantly sends signals containing technical information, including the device's unique MAC address. The site https://intellect.icu says about it. Thanks to this feature, you can always find Wi-Fi networks nearby. The data sent by devices can be monitored, thereby tracking the movement of the owner. This system is used by trade networks and special services to track users.
There are also more advanced tracking technologies, for example, Cross-device tracking
Initially, the technology was supposed to add special sound beacons to advertisements on TV, which could perceive and process mobile devices, and then transmit to a single information processing center.
Forensic analysis
Forensic analysis is a set of technical solutions and techniques for extracting valuable information from digital devices. Forensic analysis is used, as a rule, by law enforcement agencies to search for information of interest for the investigation on the devices of suspects. But due to the fact that hardware and software are in the public domain, this tool can be obtained by any attacker. Forensic analysis can be performed on desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. Forensic experts are excellent at working with all popular operating systems: Windows, macOS, Linux-based operating systems, Android, BlackBerry and iOS. The difference between forensic analysis and simple physical access is the technology used.
Forensic analysis pays great attention to the device's RAM, where valuable artifacts, such as encryption keys, can be stored; in some cases, a DMA attack is used - gaining direct access to RAM, replacing the well-known cold boot attack. If anyone does not know, a cold boot attack is the same attack when RAM is frozen with liquid nitrogen, removed from the device, and then information is read from it. Modern fourth generation RAM (DDR4) and older are no longer affected by this vulnerability. If the cold boot attack is more of a story today, then the paging and hibernation files - areas on the hard disk where information from the RAM is stored - have not lost their relevance and can still tell a lot about the device owner.Computer forensics quite often uses data recovery on media, performed in special laboratories. Even deleting a file will not protect it from the threat of extraction by forensic analysis.
Modern techniques allow recovering deleted files quite effectively. Forensic software solutions skillfully find and extract images, videos, documents, messaging, social networks, information about the programs used, device backups stored in the cloud, website history - and that's bad news. The good news is that we will teach you how to effectively counter forensic analysis. We will encrypt media, set up a security policy, securely delete files, set up Panic Button, a program designed to protect against forensic analysis, work with hibernation and swap files, and check the device for vulnerabilities to DMA attacks.
Physical access to the information system
This threat involves gaining physical access to the device in order to steal information or perform any actions that can harm the owner. The most common attacks are direct theft of information, installation of malicious software, and connection of external media.
How to defend against such a threat? The first step is to add false characters to the password: this will protect you from those who like to spy on the password.
The consequences of physical access can be very different, they depend on the tasks pursued by the ill-wisher. It may be a father who wants to install cyber espionage software on his son's computer (the so-called hidden software for controlling children), as a result of the success of such an attack, the father learns what video his son prefers and what heresy he writes to girls instead of love letters.
Mass surveillance systems are not a new phenomenon in the world, and if in the past the main task was to intercept calls and telegrams, then in the digital age the collection of data on activity and communications on the Internet and cellular networks has become the main information collected.
In most cases, mass surveillance systems legally collect data through various communication channels. This is the collection and storage of calls, the coordinates of these calls, the so-called billing, and, of course, the collection and storage of Internet traffic. Users are aware of the collection of data, at least the existence of such systems is not a secret to the public.
Illegal data collection is also used, for example, the RAMPART-A project, which became known from the revelations of Edward Snowden. According to the published information, the US NSA concluded an agreement with a dozen countries in Western and Eastern Europe, Asia and Africa and collected information through fiber-optic cables passing through their territories.
Almost every country has its own system of mass collection of information: in Russia it is SORM, in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the USA and Great Britain - ECHELON, Frenchelon in France, the Golden Shield in China. another example is the social rating in china.
Most people assume that the intelligence services will not have enough space to store my data for many years.
Unfortunately, they have enough space to store information about every person on the planet for many years.
You will have to come to terms with the idea that encryption is only a temporary protection , but not a panacea. All your correspondence, calls, Internet traffic can eventually be decrypted even if today they are encrypted, but for now they can simply be collected and saved.
How do information leaks happen ?
There are two main ways. The first is the hack described earlier. They can hack the site's database, or they can, having penetrated the corporate infrastructure of the company, gain access to internal data. For example, hackers gain access to the hospital's corporate network and steal information about its patients, including their medical history. The second common leakage path is the so-called "leak", when data is leaked through people who have authorized access to it. One of the most notorious examples of this kind is the leak of the database of the Federal Drug Control Service of Russia (the Federal Drug Control Service).
Industrial cyber espionage - cyber espionage against companies, usually for the purpose of obtaining some valuable information. The Hacking Team is an Italian company that developed (and unfortunately is still developing to this day) cyber espionage tools and sold them to governments and law enforcement, in other words, developed tools to spy on you.
In addition to professional cyber espionage, there is also cyber espionage for the sake of pleasure aimed at individuals.
For implementation, hardware or software injection of malicious code is used to collect special information.
for this, programs can also be used, allegedly aimed at countering cyber espionage, such as antivirus and super protected messengers or other supposedly protective means.
Antiviruses themselves are becoming a tool for cyber espionage. I assume that you all know the history of Kaspersky and the NSA, I will tell you another case. DU Antivirus Security is a popular antivirus for Android, which, according to some reports, was installed by up to 50 million people, spied on users, and was caught by researchers from Check Point.
Cyber espionage software is often developed by law enforcement agencies as bait to catch intruders, or hackers to bait victims. So, at one time, a backdoor was discovered in Cobian RAT, which was actively distributed on underground forums and presented almost as an ideal program. The user downloaded a program for himself in order to infect victims, and at that moment he himself became a victim of the program. or the supposedly anonymous protonmail mail
Collecting data from your mobile device allows you to receive geo information even when gps navigation is turned off, data from tilt sensors can be interpreted even wherever you are - on the bed or in the toilet, or what mood prevails in you. what applications do you use and how do you have a list of contacts, relatives, friends, partners.
Cyber espionage and telemetry
Many experts, when distinguishing between cyber espionage and collecting telemetry, suggest focusing on the purpose of data collection. If the goal is to improve the operation of the application, understanding how users use it, then this is telemetry, if the goal is the users themselves, their data and activity, then this is cyber espionage. In my opinion, this is a controversial statement, although I cannot but agree on something. For example, if the browser collects information about all the sites visited by the user and sends it to the developer, it can hardly be called telemetry, since such information cannot in any way affect the improvement of the application, it is just collecting data, probably for their further sale. And the most annoying thing: if the software is closed source, then we do not know exactly what data the program is sending,as they are often sent encrypted. Yes, by tracing the requests, we can establish where they go and how often, but this information is clearly not enough.
Dangerous Search
The fact is that search engines can start indexing and caching private pages on websites. e.g. payment results, mailing or communication results
example
By sending free online SMS, people found SMS cache of the Yandex search engine. The Yandex cache contains dates, texts and numbers of SMS recipients. The cause of the problem was the sitemap of the Megafon operator's website, where there was no prohibition on indexing pages with information about the sent SMS, and the Yandex.Metrica tool. As planned, only the sender knew the page with the SMS, following the unique link, he could see information about the sent SMS and its status, but in the end he saw the entire Internet, and netizens were pleased to quote and discuss the most juicy SMS.
Leak of documents. "Vkontakte" at one time added the ability to upload documents. A really useful option that made it possible to share documents with interlocutors, only by default all documents were uploaded with the sharing option and their titles were indexed by the internal search of the social network. As a result, the search turned out to be photographs of bank cards, scans of passports, which the scammers were quick to use.
Ways to protect against dangerous search - when uploading a file, check if public access to it is open by sending SMS from the site, you will keep in mind the possibility of its leakage, creating a private chat in the messenger, think over options under which third parties can gain access to information stored in it.
Massive device hacking
break everything that can be hacked, even smart homes. There is only one requirement - the device must have Internet access . Computers, servers, mobile devices and routers are of particular interest to hackers, since they are easier to monetize, in other words, to make money from them.
Probably the most profitable way to monetize is encrypting device content and demanding a ransom. The victim's computer is hacked, the disks are encrypted, the encryption key is sent to the attackers' server, and the victim is given information on how to pay and then decrypt his data.
Sometimes the creators of ransomware simply trick victims: their programs can only encrypt without the ability to decrypt files. These are vipers masquerading as ransomware. An example of such a viper was the infamous Petya, which, after encrypting the data, demanded a ransom, having neither the ability to track who the payment came from, nor to decrypt the data. Petya is not a ransomware, it is a well-designed cyber weapon of mass destruction whose goal is to destroy and incapacitate. Sometimes the ransomware turns into a wiper due to an error, as was the case with the AVCrypt ransomware, where, due to a developer error, files were deleted without a trace.
Mining cryptocurrencies on hacked devices
This is probably one of the most harmless ways of monetization, in which a compromised device will simply mine cryptocurrency for attackers. For the victim, this will result in lower productivity, faster failure of device components due to constant high load and a noticeable increase in electricity bills. In some countries where cryptocurrency mining is prohibited, this can lead to legal problems.
DDoS through compromised devices
In simple terms, DDoS is the creation of a large number of requests to slow down or completely disable the final target. As a rule, the target is a server, but in fact, an attack can even be carried out on a Wi-Fi router by turning off the victim's Internet at the right time. At the command of the attacker, a compromised computer starts sending requests in bulk, and other victims do the same until the target of the attack runs out of resources to process them. In parallel, a real client, when trying to connect, for example, to make a purchase on the site, either waits for a long time to process his request, or cannot connect to the site at all. And, of course, the client will leave, most likely to the competitor of the target of the attack, the business will lose customers, and with them money
Spamming via jailbroken devices
Spam is a huge business infrastructure for illegal advertising. The services of spammers are mainly used by traders of illegal goods and goods of the so-called gray category, for example, underground pharmacology, or the creators of financial pyramids.
Concealment of committed crimes through hacked devices
Cybercriminals need to hide their true location, and for this they need tools: remote desktops, VPN, SSH and proxy. The victim's compromised computer can be used as a remote desktop, on which a program will be launched to commit criminal acts. For example, carders need remote tables to play poker with stolen money in order to cash it out.
Committing computer attacks through hacked devices
Computer attacks require scanning the network and, depending on the type of attack, guessing passwords or exploiting vulnerabilities. All this requires resources. Attackers need to rent servers, pay money, the servers will be blocked due to incoming complaints, require periodic maintenance ... But there is an alternative free option: the victim's computer can become a link in a chain of attackers and be used to further hack other devices. Most malware spreads in this way: a compromised computer infects other computers, and those in turn, others.
Displaying non-native or additional ads on jailbroken devices
This monetization method is usually used for hacked routers. On the compromised Wi-Fi router, the main DNS server is changed, and all requests to the sites go through the attacker's server, where ads are added to the victim. The easiest substitution option is to periodically redirect to an advertising landing page, and it doesn't matter which site is entered by the user. A more complex option involves replacing Google ad units and banners on existing sites.
Account theft through hacked devices
Theft can occur by changing the DNS server or through malicious software installed on the system. Stealing accounts is rarely an end in itself, usually hackers use it as an additional way to monetize. Accounts of banks and payment systems are of completely different interest; this is often the main target of many malicious companies. Stolen accounts are either cashed out by hackers on their own, or sold on shadow forums for a percentage of the balance.
Sometimes hackers do not steal an account, but use the substitution of details. For example, you copy a friend's bitcoin wallet where you want to send funds; The malware analyzes your clipboard and replaces the copied bitcoin wallet with the hacker's bitcoin wallet. Thus, by copying a friend's wallet, you end up sending money to the hackers and probably won't immediately understand how this happened.
Installing software on a compromised computer
This is a very simple method of monetization in which the attacker who hacked you sells to another attacker the installation of any program on your device. It could be a ransomware, a remote espionage warrior, a bitcoin miner, or any other program.
Choosing a password to access the device
Brute, or password guessing, is the most popular type of attack due to its simplicity. A fraudster only needs to install ready-made programs and launch an attack. This is mainly done by script kiddies - hackers who are not capable of anything more than using ready-made solutions.
To protect against it, the fail2ban system is installed or a similar - a specialized system for protecting against password guessing. After several attempts to guess the password, the attacker's IP address will be blocked for some time. With such a multi-layered protection, you can forget about the threat of brute-force login and password.
Exploiting vulnerabilities
May 2017 saw the largest massive attack on Windows computers in a decade. In Russia, computers of thousands of companies and organizations, including computers of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Megafon, were disabled. The consequences are the same everywhere: valuable information is encrypted, and to decrypt, you need to pay 300 USD to a bitcoin wallet. Typically, such infections occur through physical penetration, for example, a compromised USB flash drive or a letter with malware, but in this case, nothing like that happened. The computers were simply hacked, and the attack was dubbed WannaCry.
How to protect yourself?
Against password guessing There are the following protection methods against password guessing attacks: Changing the standard username and password to a secure combination.
Change of port SSH and RDP.
Blocking when trying to guess a password.
The main protection against exploitation of vulnerabilities is timely software updates.
In addition to the update, we will carry out a comprehensive configuration of device security. For example, we will close access from an external network to control a Wi-Fi router, disable RDP and SMB, SSH, configure a firewall, thereby blocking potentially dangerous attack paths.
Internet censorship
Speaking about Internet censorship, I would like to clarify right away that censorship itself is not a threat, and it is rather good than harm. ... For this, the state (at least some states) blocks dangerous resources.
But the abuse of censorship, when the government uses this tool to restrict freedoms and rights, is a real threat,
A complete shutdown of the Internet is a special case, such censorship cannot be circumvented by software. Restricting access to websites is a different matter, there are two main ways to implement blocking: by IP address and through DNS.
DNS blocking - are bypassed by simply replacing the DNS server, for example with Google's DNS servers, or using a VPN, which usually uses the DNS server specified in the VPN settings.
IP blocking - proxying Internet traffic. It can be an anonymizer, VPN, proxy, Tor, SSH, the main thing is that the server through which you access the network is in a different jurisdiction.
Ways to block applications
In the case of applications, such as instant messengers, everything happens in the same way. For the messenger to work, it must contact the control server, and at the connection stage , blocking occurs. Many modern applications protect themselves from port blocking. the application will start connecting through ports 80 or 443 or whatever.
Port blocking is sometimes performed. Every program that needs network access uses a port to connect to the network. If you block Internet traffic on these ports, the application will not be able to connect to the server. This is generally practiced at the company level.
In the case of mobile applications, there is another blocking method - through the App Store and Google Play. The application can be removed from the store and even forcibly blocked on users' devices.
How to deal with such censorship? To combat such censorship, you should switch to Android or jailbreak the device and install the application yourself.There
is also an alternative way to bypass the blocking in the app store - by changing the region in the settings
Censorship can also fight with the means of circumvention of restrictions: those used with VPN or proxy connections can be blocked ports,
Peeping information on the screen
By the threat of spying, I mean the ability of third parties to spy on the information on the victim's screen when she is using her smartphone or laptop. Those who like to work in public places such as cafes and restaurants are at a special risk group. or in countries with severe restrictions such as Russia, China, Iran and the USA
Mechanical anti-peeping solutions
The simplest solutions are protective films. They allow you to make out the image on the screen only when you are in front of it and hide the image from those looking at the screen at an angle
The most effective protection against back prying was the use of small mirrors, and soon nearly half of the employees had mirrors near the monitor to view the space behind their backs. In addition to the mirror, there is a much more elegant solution - the so-called self-adhesive mirror films, also called safe mirrors.
Anti-peeping software solutions
using software solutions for this task is unnecessary, oh
In 2017, Google introduced an application that, using a neural network, makes sure that no one spies on what is happening on the device screen.On the downside is the constant use of the front camera, which I strongly dislike. There are similar developments for the computer, for example, the PrivateEye program.
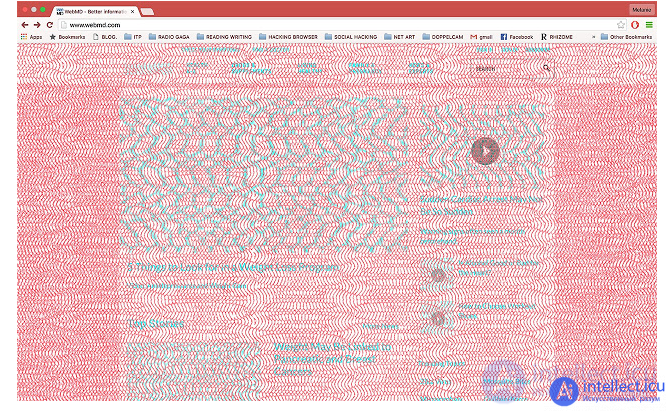
An interesting enough solution is Decodelia. This is an extension for Chrome, designed to protect against prying. For everyone who wants to see what site you have open in your browser, the image will look like this. To see the information on the screen, you must wear red glasses. An excellent solution, however, the need to wear glasses and the lack of protection for other programs, such as instant messengers, makes its use not very reasonable.
Violation of the information security regime can be caused both by the planned operations of intruders and by the inexperience of employees. The user must have at least some idea of information security, malicious software, so as not to harm the company and himself by his actions. Incidents such as loss or leakage of information can also be caused by targeted actions of company employees who are interested in making a profit in exchange for valuable data from the organization in which they work or have worked.
The main sources of threats are individual cybercriminals (“hackers”), cybercriminal groups and government intelligence agencies (cyber units), which use the entire arsenal of available cyber weapons listed and described above. To break through the protection and gain access to the necessary information, they use weaknesses and errors in the operation of software and web applications, flaws in firewall configurations and access rights settings, resort to eavesdropping on communication channels and the use of keyloggers.
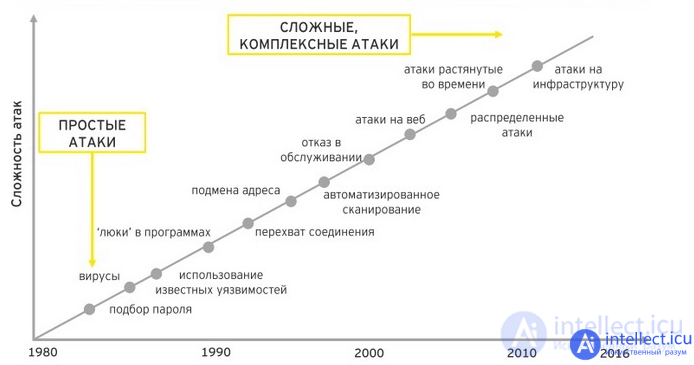
The way the attack is carried out depends on the type of information, its location, methods of access to it, and the level of protection. If the attack is based on the inexperience of the victim, it is possible, for example, to use spam mailings.
It is necessary to assess information security threats in a comprehensive manner, and the assessment methods will differ in each specific case. So, in order to exclude the loss of data due to equipment malfunction, you need to use high-quality components, carry out regular maintenance, and install voltage stabilizers. Next, you should install and regularly update the software (software). Special attention should be paid to security software, the databases of which must be updated daily.
Training the company's employees in the basic concepts of information security and the principles of operation of various malicious programs will help to avoid accidental data leaks, to prevent accidental installation of potentially dangerous software on a computer. Also, as a precaution against loss of information, you should make backups. In order to monitor the activities of employees in the workplace and be able to detect an intruder, DLP systems should be used.
To organize information security, specialized programs developed on the basis of modern technologies will help:
Comments
To leave a comment
Information security, Malicious, and information security
Terms: Information security, Malicious, and information security