Lecture
Sensor - a measurement tool designed to generate a signal of measurement information in a form convenient for transmission, further transformation, processing and (or) storage, but not amenable to direct perception by the observer. Sensors made on the basis of electronic technology are called electronic sensors . A single sensor can be designed to measure (control) and convert one physical quantity or several physical quantities simultaneously.
The sensor includes sensitive and transducer elements. The main characteristics of electronic sensors are sensitivity and error.
Sensors are widely used in research, testing, quality control, telemetry, automated control systems and in other areas of activity and systems where measurement information is required.
Sensors are part of technical systems designed to measure, signal, regulate, control devices or processes. Sensors convert a monitored value (pressure, temperature, flow, concentration, frequency, speed, displacement, voltage, electric current, etc.) into a signal (electrical, optical, pneumatic) convenient for measuring, transmitting, converting, storing and recording information about the state of the measurement object.
Historically and logically, sensors are related to measurement techniques and measuring instruments, such as thermometers, flow meters, barometers, a horizon instrument, etc. The generic term sensor has strengthened in connection with the development of automatic control systems as an element of a generalized logical concept sensor - control device - the executive device is the control object. As a separate category of use of sensors in automatic systems for recording parameters, one can single out their use in systems of scientific research and experiments.
The following definitions are common:
These definitions correspond to the practice of using the term manufacturers of sensors. In the first case, the sensor is a small, usually monolithic device of electronic equipment, for example, a thermistor, photodiode, etc., which is used to create more complex electronic devices. In the second case, it is a device that is finished in its functionality and is connected via one of the known interfaces to the automatic control or recording system. For example, photodiodes in matrices (photo), etc. In the third and fourth definitions, emphasis is placed on the fact that the sensor is a structurally separate part of the measuring system that receives information, and therefore has self-sufficiency for this task and certain metrological characteristics.
Sensors are used in many sectors of the economy - mining and processing of minerals, industrial production, transport, communications, logistics, construction, agriculture, health care, science and other industries - being currently an integral part of technical devices.
Recently, in connection with the cheapening of electronic systems, sensors with complex signal processing, configuration and control options, and a standard control system interface are increasingly used. There is a definite tendency of expansive interpretation and transfer of this term to measuring instruments, which appeared much earlier than the mass use of sensors, as well as by analogy - to objects of a different nature, for example, biological ones.
Sensors in their purpose and technical implementation are close to the concept of “measuring instrument” (“measuring instrument”). However, the readings of the instruments are perceived by a person, as a rule, directly (through displays, boards, panels, light and sound signals, etc.), while the readings of the sensors require conversion to a form in which measuring information can be perceived by humans. Sensors can be part of the measuring device, providing a measurement of a physical quantity, the results of which are then converted for perception by the operator of the measuring device.
In automated control systems, sensors can act as initiating devices, driving equipment, valves, and software. Sensor readings in such systems, as a rule, are recorded on a memory device for monitoring, processing, analyzing and displaying on a display or printing device. Sensors are of great importance in robotics, where they act as receptors, through which robots and other automatic devices receive information from the outside world and their internal organs.
In everyday life, sensors are used in thermostats, switches, thermometers, barometers, smartphones, dishwashers, cookers, toasters, irons and other household appliances.
| Primary category | Secondary category | Sensor type |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial characteristics | Location The presence of the object Distance Orientation |
GPS sensor Magnetometer Object Presence Sensor Passive infrared sensor Object proximity sensor Linear position sensor Angle position sensor Tilt sensor Gyroscope Accelerometer Vibration sensor |
| Mechanical characteristics | Fluctuations Strength Human input |
Vibration sensor Force sensor Touch sensor Touch screen |
| Fluid characteristics | Liquid Gas / liquid Gas |
Liquid level sensor Flow rate sensor Pressure meter Gas concentration sensor Gas flow rate sensor |
| Radiation characteristics | Shine Heat Sound |
Photoresistor Photodiode Phototransistor Negative temperature coefficient thermistor Thermistor with a positive temperature coefficient Thermocouple Resistive Temperature Sensor Semiconductor temperature sensor Infrared temperature sensor Microphone |
| Electrical specifications | Current Voltage |
Current sensor (ampermatr) Voltage Sensor (Voltmeter) |
 |
a circle with a diameter of 10 mm depicts a sensor, as well as a secondary device and other devices installed in place; |
 |
a circle with a diameter of 10 mm with a diametral line denotes devices and devices mounted on the console or on the shield; |
 |
a circle with a diameter of 5 mm denotes an actuator; |
|
regulatory bodies in the form of valves, dampers, control valves are designated according to GOST, adopted in the TGV systems. It depicts, as an example, a control valve |
Letter designations of regulated and controlled values:
T is the temperature;
P is pressure;
F - consumption;
L - level;
Q - quality.
Next to the letter Q indicates the quality parameter. For example, 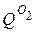 - a sensor, a secondary device that measures the dose of oxygen dissolved in water. The quality parameter is indicated at the top next to the letter. Other examples of quality parameter designation:
- a sensor, a secondary device that measures the dose of oxygen dissolved in water. The quality parameter is indicated at the top next to the letter. Other examples of quality parameter designation: 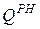 ,
, 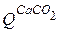 ,
, 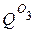 ,
, 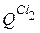 .
.
Letter symbols for instrument functions:
I - indications;
R - registration;
C - regulation;
A - alarm.
The letter designations of the sensors, secondary devices are recorded in the circle field in the upper sector, the lower sector is intended to indicate the ordinal numbering. The following are the full designations of sensors and secondary devices.
Legend of sensors, secondary devices
and additional conventions
Symbols of electrical sensors:
TE - temperature;
PE - pressure;
FE - consumption;
LE - level;
QE - quality.
Symbols of the indicating and recording devices:
TIR - temperature;
PIR - pressure;
FIR - consumption;
LIR - level;
QIR - quality.
Letter symbols of electrical secondary control devices:
TC - temperature;
PC - pressure;
FC - consumption;
LC - level;
QC - quality.
The letter designation may indicate all functions of the secondary device with indication of the parameter. The order of the letter designations of the functional characteristics of the device is taken in compliance with the sequence of designations: the first letter is a parameter, the remaining letters are in the order I, R, C, A. If there is no function in the device, then the order of the remaining letters is preserved.
Additional conventions:
NS is a block of relay contact equipment;
HS - device for manual switching on, switching off, switching;
Y is a computing device;
D / A - D / A converter;
A / D - analog-to-digital converter.
Designations of the type of energy used:
E is electrical energy;
P is the energy of compressed air;
G - hydraulic energy.
example
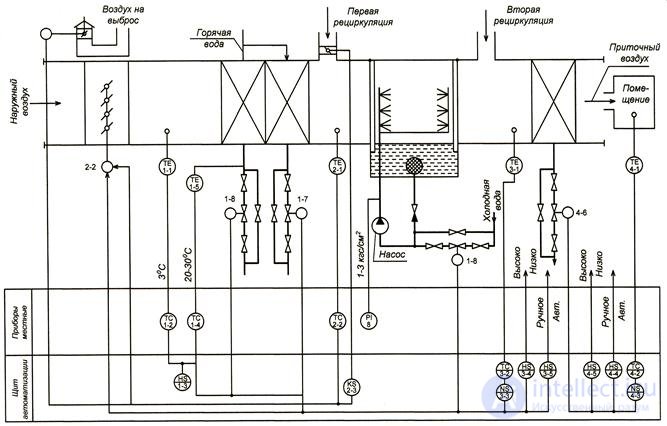
Fig. 2. Technological scheme of air conditioning automation with recirculation.
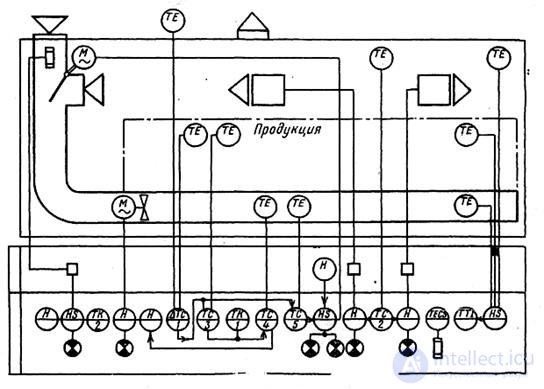 |
Fig. 3 Functional diagram of the automation of the heating and ventilation equipment of the vegetable store.
Comments
To leave a comment
Sensors
Terms: Sensors