Lecture
Example N 1
In PDK are given vectors 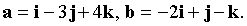 Find the unit vector x perpendicular to the vectors a, b .
Find the unit vector x perpendicular to the vectors a, b .
Decision.
The vector c = a × b is perpendicular to the vectors a, b .
As the desired vector x you can take the vector 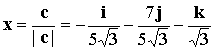 or vector
or vector 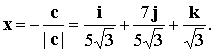
Vectors 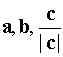 form the right three vectors, and
form the right three vectors, and 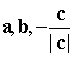 - left.
- left.
Answer:or
Example N 2
To find 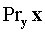 if it is known that
if it is known that 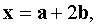
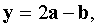
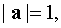
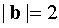 The angle φ between the vectors a, b is φ / 6.
The angle φ between the vectors a, b is φ / 6.
Decision.
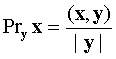 . Using the properties of the scalar product, we find
. Using the properties of the scalar product, we find
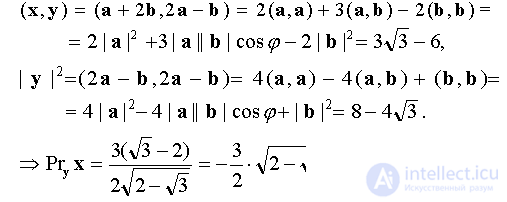
Answer:
Example N 3
Vectors are specified in PDK 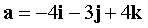 ,
, 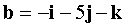 ,
, 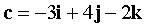 ,
, 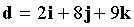 . Prove that the vectors a, b, c form a basis, and find the expansion of the vector d in the basis of a, b, c .
. Prove that the vectors a, b, c form a basis, and find the expansion of the vector d in the basis of a, b, c .
Decision.
Find the determinant composed of the coordinates of the vectors a, b, c :
Because Δ ≠ 0, then a, b, c is a basis. Now we find the expansion of the vector d in the basis of a, b, c . It is necessary to find the numbers α 1 , α 2 , α 3 such that a α 1 + b α 2 + c α 3 = d . In expanded form, this equality is a linear system of algebraic equations with unknowns α 1 , α 2 , α 3 :
According to Kramer’s formulas we find:
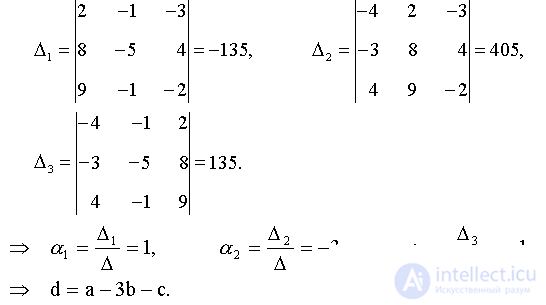
Answer:
Example N 4
Vectors are specified in PDAC 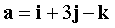 ,
, 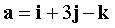 ,
, 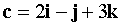 . Find a vector x such that its scalar product with vectors a, b, c equals - 12, 6, - 8, respectively.
. Find a vector x such that its scalar product with vectors a, b, c equals - 12, 6, - 8, respectively.
Decision.
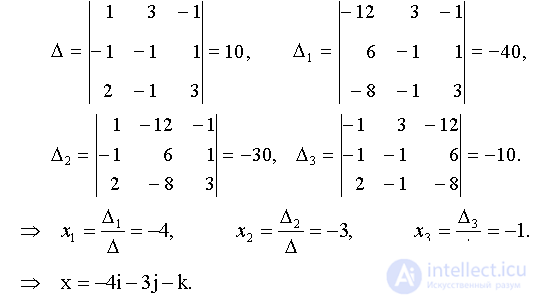
Let be 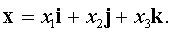 From the condition of the problem we get
From the condition of the problem we get
It is necessary to solve a system of linear algebraic equations with unknowns x 1 , x 2 , x 3 . According to Kramer’s formulas we find
Answer:
Example N 5
Vectors are specified in PDAC 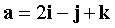 ,
, 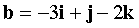 . Find the area of the parallelogram built on the vectors x, y where the vector x is perpendicular to the vectors a, b , and x = 3 , and the vector
. Find the area of the parallelogram built on the vectors x, y where the vector x is perpendicular to the vectors a, b , and x = 3 , and the vector
y = a + b .
Decision.
The vector c = a × b is perpendicular to the vectors a, b
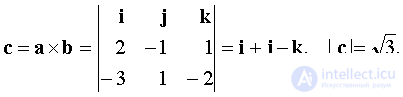
The vector x must be collinear to the vector c . Since the condition of the problem is x = 3 , then 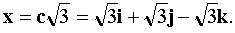 Find
Find 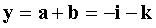 ,
,
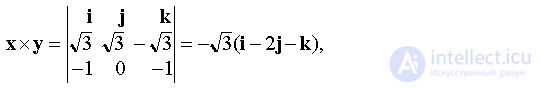
area parallelogram built on vectors x, y .
Answer:
Example N 6
Vectors are specified in PDAC 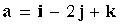 ,
, 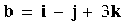 and points
and points 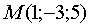 ,
, 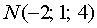 . Find the volume of a parallelepiped constructed on vectors
. Find the volume of a parallelepiped constructed on vectors 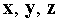 Where
Where 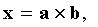
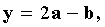
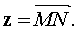
Decision.
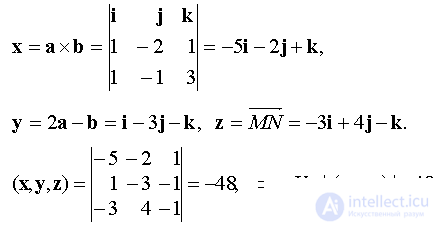 - volume of parallelepiped built on vectors
- volume of parallelepiped built on vectors 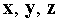 .
.
Answer:
Example N 7
At what value of x will the vectors a, b, c be coplanar if
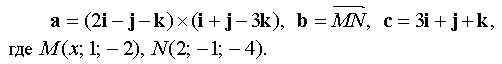
Decision.
Vectors a, b, c will be coplanar if ( a, b, c ) = 0 .
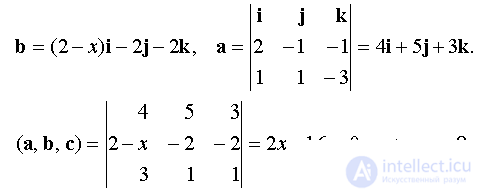
Answer: x = 8.
Example N 8
In the triangle with vertices K (-5; 4), L (1; -4), M (-9; 1) find:
a) the equation of a straight line containing the height dropped from the vertex L ;
b) the length of the height lowered from the vertex L ;
c) the point N , symmetric to the point L , with respect to the straight line passing through the points K, M ;
d) the equation of a line containing the bisector of the angle L.
Decision.
a) the normal vector of a straight line (Lh) containing height is a vector 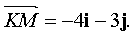 Find the equation of the line
Find the equation of the line
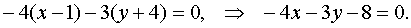
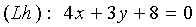 - the equation of a straight line containing the height lowered from the top;
- the equation of a straight line containing the height lowered from the top;
b) the length of the height dropped from the vertex L is equal to the distance ρ from the point L to the straight line (K, M) passing through the points K, M.
Find the equation of this line. Because 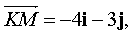 that
that 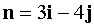 is the normal vector of this line. Find the general equation of the line (K, M) :
is the normal vector of this line. Find the general equation of the line (K, M) :
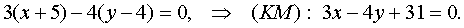
The normal equation of the line (K, M) is
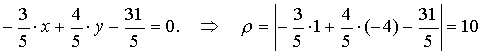 - height length;
- height length;
c) to find the point N you need to determine the point of intersection  direct (Lh), (KM) i.e. it is necessary to solve a system of linear equations
direct (Lh), (KM) i.e. it is necessary to solve a system of linear equations
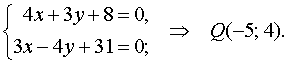
Now we find the point N (x; y): 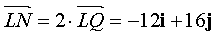 .
.
d) vector 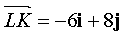 is a straight line vector (LK) , and vector
is a straight line vector (LK) , and vector 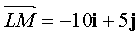 - direct (LM) . Let be
- direct (LM) . Let be 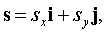 where s x , s y - unknown vector of a line (Ll) containing the bisector of the angle L. Vector s forms with vectors
where s x , s y - unknown vector of a line (Ll) containing the bisector of the angle L. Vector s forms with vectors 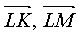 equal angles. Consequently,
equal angles. Consequently, 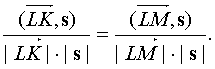 Because
Because
Answer: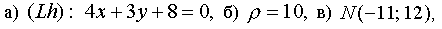
Comments
To leave a comment
Linear Algebra and Analytical Geometry
Terms: Linear Algebra and Analytical Geometry