Lecture
A rectangular Cartesian coordinate system (PDK) consists of a fixed point O (the center of the coordinate system ) and three intersecting in it, mutually perpendicular direction lines O x , O y , O z ( axes of the coordinate system ). Directions are chosen so that the straight lines form the right three vectors.
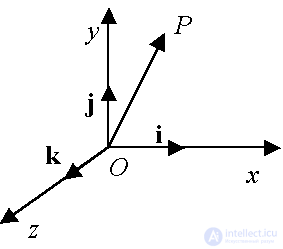
Fig. 2
The unit vectors defining the directions of the axes O x , O y , O z are denoted by the letters i, j, k and form an orthonormal basis (Fig. 2).
Vector 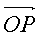 called the radius vector of a point
called the radius vector of a point 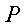 . Vector coordinates
. Vector coordinates 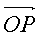 relative to the base i, j, k are coordinates of the point
relative to the base i, j, k are coordinates of the point 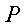 i.e. if a
i.e. if a 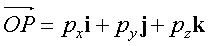 (
( 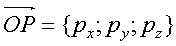 ), then
), then 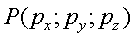 - point with coordinates p x , p y , p z .
- point with coordinates p x , p y , p z .
Because 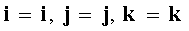 then
then 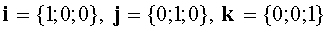 .
.
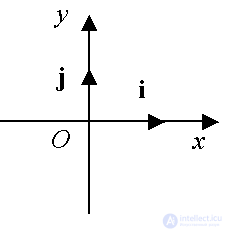
Fig. 3
If vectors are viewed on a plane, then the PDK consists of two perpendicular axes O x , O y with the guide orta i, j ( i = {1; 0}, j = {0; 1}) (Fig. 3).
Comments
To leave a comment
Linear Algebra and Analytical Geometry
Terms: Linear Algebra and Analytical Geometry