Lecture
An emulator of an operating system (computer Science) is software and / or hardware operating in a certain operating system and hardware platform designed to execute programs made in another operating system or operating on a different hardware from the target, but allowing the same operations to be performed in the target environment, as in the simulated system.
Emulation and virtualization processes have a lot in common, but there are also noticeable operational differences.
If the client needs to work with an older operating system within the modern technical architecture, he will choose only the emulation option.
At the same time, all virtualized systems function independently of the basic equipment used.
The essence of emulation is that one system can technically mimic another.
An example is if the software structure works in system A, but not in system B, we create an emulation of the operation of system A inside the system B. As a result, the software quietly works to emulate system A.
This example can also be transferred to virtualization, which, in addition to system A., is divided into 2 more dedicated servers (B and C).
Both servers are independent technical containers with personalized access to software resources - RAM, CPU and storage - they can be freely rebooted independently of each other. Their "behavior" is completely identical to the behavior of real software.
Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages .
The figure below provides a visual representation of the architectural difference between virtual machines and containers:
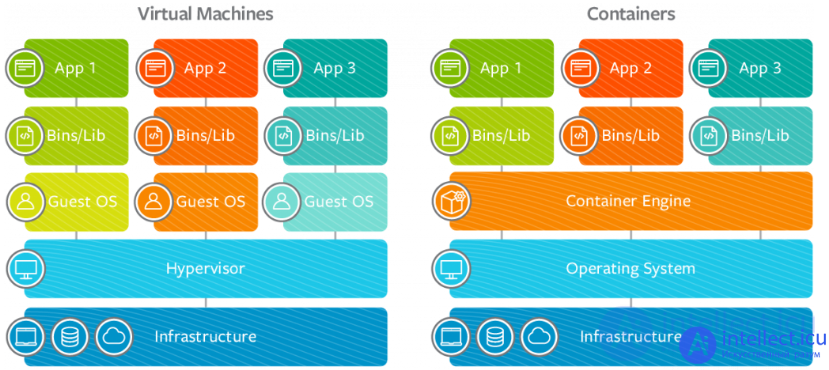
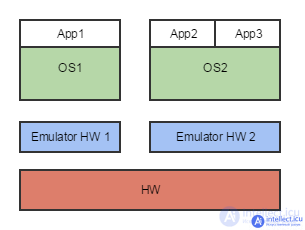
Figure 1. In computer virtualization, a hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM) provides isolation between each guest OS. In containers , the host operating system provides isolation between each container.
The difference in architecture offers the following key suggestions for IT staff and enterprises:
For DevOps-oriented organizations that focus on faster and more continuous release cycles for distributed microservice-based applications, containerization will continue to attract investment, especially in areas where virtualization has failed.
In relation to the above example, emulation acts as a special “placeholder” for hardware - the creation of a special technical environment that operates in hardware.
Emulation can have a special effect in such user scenarios:
Emulation processes are also useful when creating some software for several systems simultaneously. The process of writing program code can be performed on one machine, and the emulation process on several operating systems (everything functions simultaneously and without obvious failures).
The most important advantage of virtualization is that it interacts directly with hardware.
The most obvious advantages of this method of interacting with software components include:
By the way, between emulation and virtualization, you can calmly put an equal sign, since these processes help to thoroughly analyze the operation of any software.
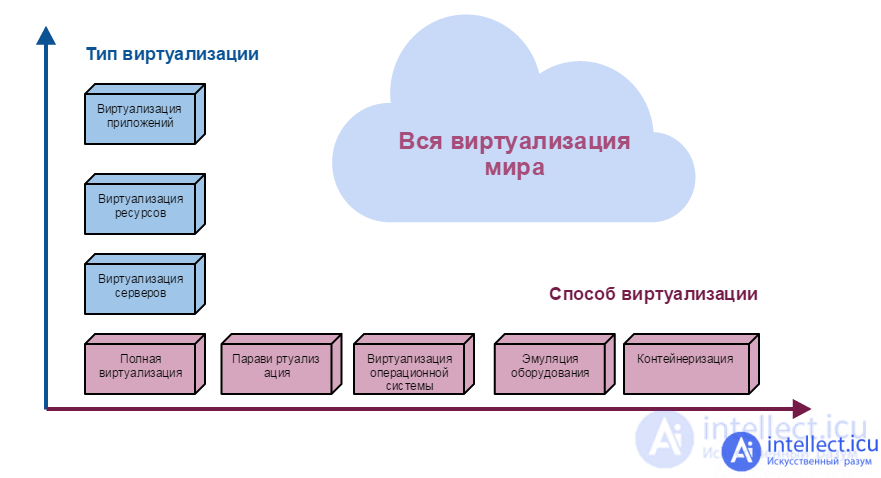
Server Virtualization
Usually, virtualization refers to the location of several virtual servers within the same physical
Resource virtualization
Resources are RAM, hard drives, processors . This is evidenced by the site https://intellect.icu. They can also be sliced and distributed in parts to different users.
Application Virtualization
Application virtualization is what we already know as PaaS and SaaS
The main virtualization methods are full virtualization and paravirtualization. The outline of both methods is very similar. There is a hypervisor and virtual machines with guest OSs. With full virtualization, no changes are made to the guest OS. Paravirtualization sets up optimized images for a particular hypervisor. This allows you to maximize the use of hardware resources and does not require any changes from applications. An example of a system that implements full virtualization is VMware, an example of paravirtualization is Xen and KVM.
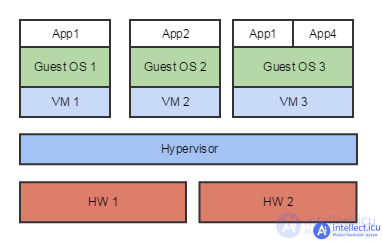
There are several ways to virtualize:
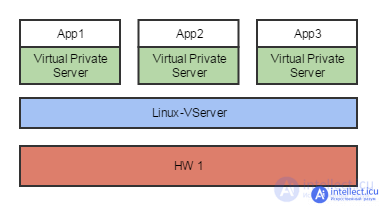
OS level virtualization
A feature is that there can be only one guest OS. An example of OS-level virtualization is Linux-VServer:
With this virtualization method, the VM fully emulates the operation of certain equipment. On the one hand, this makes it possible, for example, to emulate another type of processor on one processor. On the other hand, it is clear that this will slow down dozens of times. An example of an emulator is Bochs.
And for the sake of completeness, I will add library emulation. This is a way in which not all OS is emulated, but only part. For example, Wine on Linux is a library emulation for Windows applications.
It turns out that we can virtualize different systems using different methods. Those. we see that existing methods and types of virtualization can solve many problems. A logical question arises, when does it make sense to deploy a cloud platform?
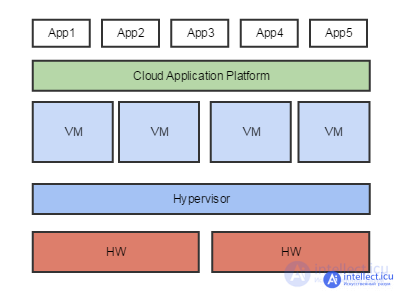
Cloud platforms are located above a set of virtual machines, completely isolate the application from both the hardware and the structure of the virtual environment. Cloud platforms are used for automatic and manual scale in / scale out, start / stop / configure VMs and applications. When does it make sense to stay in virtualization, and when to stay in the cloud? The concept is as follows: when there is a lot of everything - the cloud, a little - virtualization:
Next, we will talk about virtual machines and operational emulators, which can serve well when performing testing, and also dwell on their basic advantages and disadvantages.
VMWare Workstation is a very popular and easy-to-use virtual machine that is used on a professional basis.
Product Advantages:
Disadvantages:
A very common virtual machine with a decent set of useful technical functionality.
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
This product was originally positioned as a direct replacement for Microsoft Visual PC components.
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
A specialized product exclusively for Macs that can help you install Windows.
Advantage:
Disadvantages:
A special virtual machine that is used on Mac computers to interact with Windows operating components.
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
Specialized emulator for the Android operating system.
Product Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Modern emulator Android operating system.
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
Internet emulator for Android and iOS operating systems.
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
Specialized emulator for the Android operating system.
Benefits:
Disadvantages:
Of course, this list cannot be considered complete. Above were listed exclusively the most popular products and their basic characteristics, from which, if desired, you can choose something worthwhile.
Recently, containerization systems such as Docker or Kubernetes have been used more and more. They allow you to automatically deploy prepared OS images mainly for the purpose of automatic testing and for CI systems. Containers are very similar to virtual machines, but they do not require a hypervisor, but only the corresponding engine:
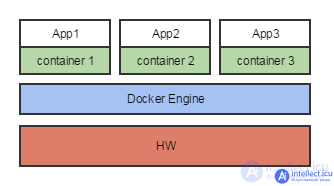
Containerization ( virtualization at the operating system level , container virtualization , zone virtualization ) is a virtualization method in which the kernel of the operating system supports several isolated instances of user space instead of one. These instances (commonly called containers or zones ) are, from the user's point of view, completely identical to a single instance of the operating system. For Unix-based systems, this technology is similar to an improved implementation of the chroot mechanism. The kernel provides full isolation of containers, so programs from different containers cannot affect each other.
Unlike hardware virtualization, in which the hardware environment is emulated and a wide range of guest operating systems can be launched, an instance of the operating system with the same kernel as the host operating system can be started in the container (all host containers use a common kernel). At the same time, during containerization, there are no additional resource overheads for emulating virtual equipment and launching a full-fledged instance of the operating system, characteristic of hardware virtualization.
There are implementations focused on creating almost full-fledged copies of operating systems (Solaris Containers, Virtuozzo containers, OpenVZ), as well as options that focus on isolating individual services with a minimal operating environment (jail, Docker).
All the same, virtual machines and emulators have their strengths and weaknesses, which does not allow us to put an equal sign between them and traditional methods of testing the functionality and performance of the developed software.
продолжение следует...
Часть 1 Emulators of operating systems. Virtualization, Emulation, Containerization
В чем разница между эмуляцией и симуляцией?
Вы хотите дублировать поведение старого калькулятора HP, есть два варианта:
Вы пишете новую программу, которая рисует дисплей и клавиши калькулятора, и когда пользователь нажимает на клавиши, ваши программы делают то же, что и старый калькулятор. Это симулятор
Вы получаете дамп прошивки калькулятора, затем пишете программу, которая загружает прошивку и интерпретирует ее так же, как микропроцессор в калькуляторе. Это эмулятор
Simulator пытается дублировать поведение устройства. Эмулятор пытается дублировать внутреннюю работу устройства.
Comments
To leave a comment
Operating Systems and System Programming
Terms: Operating Systems and System Programming