Lecture
Below is a list of the outstanding problems of modern physics. . Some of these problems are theoretical. This means that existing theories fail to explain certain observable phenomena or experimental results. Other problems are experimental, and this means that there are difficulties in creating an experiment to test the proposed theory or to investigate a phenomenon in more detail.
The following problems are either fundamental theoretical problems or theoretical ideas for which there are no experimental data. Some of these problems are closely interrelated. For example, extra dimensions or supersymmetry can solve the hierarchy problem. It is believed that the complete theory of quantum gravity is able to answer most of the listed questions (except for the island stability problem).
Disintegration of the metastable vacuum
Why does the predicted quantum vacuum mass have little effect on the expansion of the Universe?
Quantum gravity
Is it possible to combine quantum mechanics and general relativity into a single self-consistent theory (perhaps this is quantum field theory)? [2] Is space-time continuous or is it discrete? Will a self-consistent theory use a hypothetical graviton or will it be entirely a product of the discrete structure of spacetime (as in loop quantum gravity)? Are there deviations from the predictions of GR for very small or very large scales or in other extraordinary circumstances that follow from the theory of quantum gravity?
Black holes, the disappearance of information in a black hole, Hawking radiation
Do black holes produce heat radiation, as theory predicts? Does this radiation contain information about their internal structure, as the duality implies — gauge invariance implies, or not, as Hawking’s original calculation suggests? If there are no black holes that can continuously evaporate, then what happens to the information stored in them (quantum mechanics does not provide for the destruction of information)? Or will the radiation stop at some point, when there is not much left of the black hole? [3] . Is there any other way to study their internal structure, if such a structure exists at all?

Spacetime dimension
Are there additional dimensions of space-time in nature besides the four known to us? [1] If so, how many? Is the “3 + 1” dimension (or higher) an a priori property of the Universe, or is it the result of other physical processes, as, for example, the theory of causal dynamic triangulation suggests? Can we experimentally “observe” higher spatial dimensions? Is the holographic principle, according to which the physics of our “3 + 1” -dimensional space-time is equivalent to physics on a hypersurface with the dimension “2 + 1”?
Inflationary Model of the Universe
Is the theory of cosmic inflation correct, and if so, what are the details of this stage? What is a hypothetical inflaton field responsible for rising inflation? If inflation occurred at one point, is this the beginning of a self-sustaining process due to inflation of quantum mechanical collars that will continue in a completely different place, remote from this point?
Multiverse
Are there physical reasons for the existence of other universes that are fundamentally unobservable? For example: are there any quantum-mechanical “alternative stories” or “many worlds”? Are there “other” universes with physical laws that are the result of alternative ways of breaking the apparent symmetry of physical forces at high energies, which are probably incredibly far away from cosmic inflation? Could other universes influence ours, causing, for example, anomalies in the temperature distribution of the background radiation [4] ? Is the use of the anthropic principle to solve global cosmological dilemmas justified?
The principle of cosmic censorship and the chronology protection hypothesis
Can singularities that are not hidden behind the event horizon and known as “bare singularities” arise from realistic initial conditions, or can some version of Roger Penrose's “cosmic censorship hypothesis”, which is supposed to be impossible, be proved? [5] Similarly, whether there are closed timelike curves that occur in some solutions of the equations of general relativity (which suggest the possibility of time travel in the opposite direction) are excluded by the theory of quantum gravity, which combines the general theory of relativity with quantum mechanics, as suggested by the defense hypothesis chronology "Stephen Hawking?
Time axis
What can phenomena tell us about the nature of time, which differ from each other by going back and forth in time? What time is different from space? Why are CP-invariance violations observed only in some weak interactions and nowhere else? Are CP-invariance violations a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics, or are they a separate time axis? Are there exceptions to the causality principle? Is the past the only possible one? Is the present moment physically different from the past and the future, or is it simply the result of the characteristics of consciousness? How did people learn to negotiate what is the present moment? (See also below Entropy (time axis)).
Locality
Are there non-local phenomena in quantum physics? If they exist, are they not limited in the transmission of information, or: can energy and matter also move along a non-local path? Under what conditions are non-local phenomena observed? What does the presence or absence of non-local phenomena for the fundamental structure of space-time entail? How does this relate to quantum coupling? How can this be interpreted from the standpoint of the correct interpretation of the fundamental nature of quantum physics?
Future of the universe
Is the Universe moving in the direction of the Big Freezing, the Big Gap, the Big Grip or the Big Bounce? Is our Universe part of an infinitely repeating cyclical model?
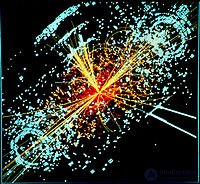
Unsolved questions of elementary particle physics are divided into two classes. The first is what everything consists of and why it is built as it was built, as well as the search for possible new particles and interactions. The second is how already known phenomena are formed from already known particles.
Higgs mechanism
How many Higgs bosons are there? Are they described in the Standard Model?
Hierarchy problem
Why is gravity such a weak force? It becomes large only on the Planck scale, for particles with an energy of the order of 10 19 GeV, which is much higher than the electroweak scale (energy of 100 GeV is dominant in low-energy physics). Why are these scales so different from each other? What prevents the values of the electroweak scale, such as the Higgs boson mass, from obtaining quantum corrections on the scale of the Planck order? Is the solution to this problem super-symmetry, additional measurements, or simply anthropic fine tuning?
Magnetic monopole
Were there particles - carriers of the "magnetic charge" in any past epoch with higher energies? If so, are there any today? (Paul Dirac showed that the presence of some types of magnetic monopoles could explain charge quantization.)
Proton Decay and the Great Unification
How can three different quantum-mechanical fundamental interactions of quantum field theory be combined? Why is the lightest baryon, which is a proton, absolutely stable? If the proton is unstable, then what is its half-life?
Supersymmetry
Is space supersymmetry implemented in nature? If so, what is the mechanism of supersymmetry breaking? Does supersymmetry stabilize the electro-weak scale, preventing high quantum corrections? Is dark matter composed of light supersymmetric particles?
Generation of matter
Are there more than three generations of quarks and leptons? Is the number of generations related to the dimension of space? Why do generations exist at all? Is there a theory that could explain the presence of mass in some quarks and leptons in separate generations on the basis of first principles (Yukawa's theory of interaction)?
Fundamental symmetry and neutrino
What is the nature of neutrinos, what is their mass and how did they shape the evolution of the Universe? Why is there more substance detected in the Universe than antimatter [9] ? What invisible forces were present at the dawn of the Universe, but disappeared from view during the development of the Universe?
Elementary particles
Are there bosons consisting of four or more quarks? Are there fermions consisting of five or more quarks? If so, what are their properties? If not, why not? [ten]
Quantum chromodynamics
What are the phase states of strongly interacting matter and what role do they play in space? What is the internal structure of nucleons? What properties of strongly interacting matter does QCD predict? What controls the transition of quarks and gluons to pi mesons and nucleons? What is the role of gluons and gluon interactions in nucleons and nuclei? What determines the key features of QCD and what is their relationship to the nature of gravity and space-time?
Atomic nucleus and nuclear astrophysics
What is the nature of nuclear forces that binds protons and neutrons into stable nuclei and rare isotopes? What is the reason for the connection of simple particles into complex nuclei? What is the nature of neutron stars and dense nuclear matter? What is the origin of elements in space? What are nuclear reactions that drive stars and cause them to explode?
Island of stability
What is the hardest of stable or metastable nuclei? [eleven]
Quantum mechanics and the correspondence principle (sometimes called quantum chaos)
Are there any preferred interpretations of quantum mechanics? How does a quantum description of reality, which includes such elements as a quantum superposition of states and the collapse of a wave function or quantum decoherence, lead to the reality we see? One can formulate the same thing with the help of the measurement problem: what is the “dimension” that causes the wave function to fall into a certain state?
Physical information
Are there physical phenomena, such as black holes or the collapse of the wave function, which irrevocably destroy information about their previous states?
Theory of Everything ("Theory of the Great Association")
Is there a theory that explains the values of all fundamental physical constants? [12] Is there a theory that explains why the standard model's gauge invariance is as it is, why does observable spacetime have 3 + 1 dimensions, and therefore the laws of physics are as they are? Do "fundamental physical constants" change over time? Are any particles in the standard model of elementary particle physics actually composed of other particles that are so strongly coupled that they cannot be observed at modern experimental energies? Are there fundamental particles that have not yet been observed, and if so, what are they and what are their properties? Are there any unobservable fundamental forces that the theory suggests explaining other unsolved problems in physics?
Gauge invariance
Are there really non-abelian gauge theories with a gap in the mass spectrum?
CP symmetry
Why isn't CP symmetry preserved? Why does it persist in most of the observed processes?
Semiconductor physics
The quantum theory of semiconductors cannot accurately compute a single semiconductor constant.
The quantum physics
Unknown exact solution of the Schrödinger equation for many-electron atoms
When solving the problem of scattering of two beams on one obstacle, the scattering cross section is infinitely large
Statistical physics
There is no systematic theory of irreversible processes, which makes it possible to carry out quantitative calculations for any given physical process.
Quantum electrodynamics
Are there gravitational effects caused by zero col- erations of the electromagnetic field? [20]
It is not known how in the calculations of quantum electrodynamics in the high-frequency region to simultaneously fulfill the conditions for the finiteness of the result, relativistic invariance, and the sum of all alternative probabilities equal to one.
Biophysics
There is no quantitative theory for the kinetics of conformational relaxation of protein macromolecules and their complexes.
There is no complete theory of electron transfer in biological structures.
Superconductivity
It is impossible to theoretically predict, knowing the structure and composition of a substance, whether it will go to the superconducting state with decreasing temperature.
Solid state physics
It is impossible to even approximately calculate the magnetization, heat capacity, electrical conductivity and other macroscopic quantities based on the known structure of the crystal, the electron shells of atoms in the crystal, and other parameters of the microworld for highly magnetic substances (ferromagnets, antiferromagnets, and ferrimagnetic materials)
Existence of the universe
What is the origin of the matter, energy and space-time that formed the Universe / Multiverse?
Baryon asymmetry of the Universe
Why in the observable universe there is much more matter than antimatter? [eleven]
The problem of cosmological constant
Why does zero vacuum energy not lead to a large value of the cosmological constant? What cancels this dependence?
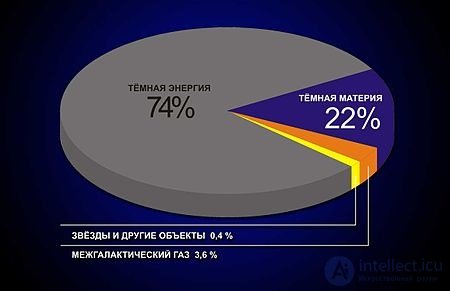
Dark energy
What is the cause of the observed accelerated expansion of the Universe (de Sitter phase)? Why is the energy density of the dark component of the energy - the value of the same order as the density of the substance at the present time, whereas these two phenomena have evolved completely differently over time? Maybe it is because we are observing at the right time? Is dark energy a cosmological constant, or is it a dynamic field — some kind of quintessence, such as phantom energy?
Dark matter
What is dark matter? Is it related to supersymmetry? Is the phenomenon of dark matter related to one or another form of matter, or is it really an extension of gravity?
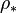 and dark matter density
and dark matter density 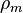 horizontally delayed time factor
horizontally delayed time factor 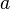 . Two straight lines intersect in the current era.
. Two straight lines intersect in the current era. Dark flow
What is the reason for the coordinated movement of a large group of galaxy clusters to a single point in the Universe? [28]
Entropy (time direction)
Why did the universe have such low entropy in the past, resulting in a difference between the past and the future and the second law of thermodynamics? [29] .
Horizon problem [9]
Why is the part of the Universe remote from us so homogeneous, whereas the Big Bang theory predicts the measurable anisotropy of the celestial sphere more than it is observed? A possible approach to the solution are the hypotheses of inflation and variable speed of light.
The relic radiation isotropy
Some common features of the microwave radiation of the sky at distances of more than 13 billion light years seem to indicate the presence of both the movement and orientation of the solar system. Is this a consequence of systematic processing errors, contamination of the results with local effects or an inexplicable violation of the Copernican principle?
Form of the universe
Что такое 3-многообразие сопутствующего пространства, то есть сопутствующее пространственное сечение Вселенной, неофициально называемое «формой» Вселенной? Ни её кривизна, ни топология в настоящее время неизвестны, хотя кривизна скорее всего «близка» к нулю на наблюдаемых масштабах. Гипотеза космической инфляции предполагает, что форма Вселенной может быть неизмеримой, но с 2003 года ком***а Жана-Пьера Люмине и другие группы полагают, что Вселенная может иметь форму додекаэдрического пространства Пуанкаре. Является ли форма Вселенной неизмеримой, представляет собой пространство Пуанкаре или имеет другое 3-многообразие?
Gravitational waves
Можно ли гравитационные волны обнаружить экспериментально? [30] [31]
Термодинамика Вселенной
Почему в наблюдаемой части Вселенной в настоящее время отсутствует термодинамическое равновесие? [32]
Нарушение симметрии электрослабого взаимодействия
Каков механизм, ответственный за нарушение электрослабой калибровочной симметрии, дающий массу W и Z бозонам? Является ли он простым механизмом ХиггсаСтандартной модели [33] или же природа использует сильную динамику при нарушении электрослабой симметрии, как это предлагается в теории техниколор?
Масса нейтрино
Какой механизм отвечает за генерацию массы нейтрино? Является ли нейтрино античастицей самой себе? Или это и есть античастица, которая просто не может соединиться и аннигилировать с нормальной частицей из-за её нестабильного состояния?
Кварки
Why exactly three colors? Why exactly three generations of quarks? Is the coincidence of the number of colors and the number of generations random? Is this number coincidental with the dimension of space in our world? Where does such a spread in the masses of quarks come from? What are quarks made of? How do quarks stack into hadrons?
The ratio of inertial mass / gravitational mass for elementary particles
In accordance with the principle of equivalence of the general theory of relativity, the ratio of inertial mass to gravitational for all elementary particles is an equal unit. However, there is no experimental confirmation of this law for many particles. In particular, we do not know what the weight of a macroscopic piece of antimatter of known mass will be.
Proton spin crisis
По первоначальной оценке Европейской группы по мюонному сотрудничеству, на три основных («валентных») кварка протона приходится около 12 % от общего объёма спина. Можно ли пересчитать остаток глюонов, которые связывают кварки, а также образуют «море» пар кварков, которые постоянно создаются и аннигилируют?
Квантовая хромодинамика (КХД) в непертурбативном режиме
Уравнения КХД остаются нерешёнными на энергетических масштабах, соответствующих описанию атомных ядер, и, среди прочего, в основном численные подходы, кажется, начинают давать ответы на этот предельный случай. Подходит ли КХД для описания физики ядра и его компонентов?
Удержание цвета
Почему никогда не были зафиксированы свободный кварк или глюон, а только объекты, построенные из них, например, мезоны и барионы? Каким образом эти явления вытекают из КХД?
Сильная CP-проблема и аксионы
Почему сильное ядерное взаимодействие инвариантно к чётности и зарядовому сопряжению? Является ли теория Печчеи — Квинн решением этой проблемы?
Гипотетические частицы
Какие из гипотетических частиц, предсказываемых суперсимметричной теорией и другими известными теориями, на самом деле существуют в природе?
Теория Редже
Почему все наблюдаемые в эксперименте траектории Редже являются прямолинейными и имеют приближенно равные наклоны? [34] [35]
Радиус протона
Радиус протона, определённый в экспериментах по измерению лэмбовского сдвига в атоме водорода с заменой электрона на мюон (0,8409 фм), оказался меньше радиуса протона, определённого в экспериментах по рассеянию электронов на протонах (0,879 фм) [36] .
Магнитный момент мюона
Экспериментальное значение магнитного момента мюона не соответствует теоретическому .
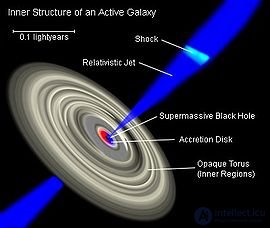
Струи аккреционных дисков
Почему некоторые астрономические объекты, окружённые аккреционным диском, такие как активные ядра галактик, испускают релятивистские струи, излучаемые вдоль полярной оси? [38] . Почему у многих аккреционных дисков существуют квази-периодические коле***ния? Почему период этих коле***ний имеет масштаб, обратно пропорциональный массе центрального объекта? Почему иногда существуют обертоны, и почему у разных объектов обертоны имеют различные соотношения частоты?
Солнечная цикличность
Какова природа циклов солнечной активности; каков механизм обращений магнитного поля Солнца, Земли?
Проблема нагрева короны
Почему солнечная корона (атмосферный слой Солнца) намного горячее, чем поверхность Солнца? Почему магнитное пересоединение совершается на много порядков быстрее, чем предсказывают стандартные модели?
Гамма-всплески
Каково происхождение этих краткосрочных всплесков высокой интенсивности?
Сверхмассивные чёрные дыры
Какова причина отношения М-сигма между массой сверхмассивной чёрной дыры и дисперсией скорости галактики? [40]
Наблюдаемые аномалии
Аномалия «Гиппарха»: Каково фактическое расстояние до Плеяд?
Аномалия сближения (англ.)русск.: Почему наблюдаемая энергия спутников, совершающих гравитационный манёвр, отличается от предсказываемых теорией значений?
Проблема вращения галактик: Является ли тёмная материя ответственной за различия в наблюдаемых и теоретических скоростях вращения звёзд вокруг центра галактик, или же причина в чём-то ином?
Сверхновые
Каков точный механизм, посредством которого имплозии умирающих звёзд становятся взрывом?
Космические лучи сверхвысоких энергий
Почему некоторые космические лучи обладают невероятно высокой энергией (так называемые частицы OMG ), учитывая, что вблизи Земли нет источников космических лучей с такой энергией? Почему некоторые космические лучи, испускаемые далёкими источниками, имеют энергию выше предела Грайзена-Зацепина-Кузьмина? [41] [42]
Замедление времени пульсара
Почему выбросы пульсаров на больших космологических расстояниях не проявляют предсказанное свойство замедления времени?
Скорость вращения Сатурна
Почему магнитосфера Сатурна проявляет (медленно меняющуюся) периодичность, близкую к той, на которой вращаются облака планеты? Какова истинная скорость вращения глубоких внутренних слоёв Сатурна?
solar system
Отсутствует законченная теория, объясняющая происхождение Солнечной системы и Земли.
Аморфные тела
Какова природа перехода между жидкой или твёрдой и стекловидной фазами? Какие физические процессы приводят к основным свойствам стекла?
Холодный ядерный синтез
Каково объяснение спорных докладов об избыточном тепле, излучении и трансмутациях?
Криогенная электронная эмиссия
Почему в отсутствие света увеличивается эмиссия электронов фотоэлектронного умножителя при уменьшении его температуры?
Высокотемпературная сверхпроводимость
What is the mechanism that causes some materials to exhibit superconductivity at temperatures well above 50 kelvins?
Sonoluminescence
What is the cause of the emission of short flashes of light when a liquid bubble collapses, excited by sound?
Turbulence
Is it possible to create a theoretical model to describe the statistics of a turbulent flow (in particular, for its internal structure)? [55] Under what conditions is there a smooth solution of the Navier – Stokes equations? This is probably the last unsolved problem of classical or Newtonian physics.
Quasi biennial cycle
What is the nature of a coli *** with a period of about 26 months, arising in the equatorial stratosphere?
Half year cycle
What is the nature of a collective *** with a six-month period, manifested, in particular, in the form of the “Indian summer” effect?
Equilibrium temperature gradient
The theory of turbulent heat transfer in the atmosphere gives an equilibrium vertical temperature gradient of –9.8 K / km, while the experiment gives a value almost 40% less!
Negative viscosity
What is the physical mechanism of negative viscosity phenomena?
Fireball
What is the nature of this phenomenon? Is ball lightning an independent object or is it energized from outside? Do all ball lightning have the same nature or are there different types of them?
Synaptic plasticity
It is necessary for computational and physical models of the brain, but what is the reason for this and what role does it play in the higher order processes of the extra-hippocampus and the visual cortex?
Axonal guidance
How do axons emanating from neurons find their goals? This process is crucial for the development of the nervous system, in particular, in the question of the formation of the structure of compounds in the brain.
Randomness and resistance to noise in gene expression
How do genes control our body, withstanding various external influences and internal stochasticity? There are various models of genetic processes, but we are far from understanding the whole picture, in particular, in morphogenesis, in which gene expression must be tightly regulated.
Quantitative study of the immune system
What are the quantitative properties of immune responses? What are the basic building blocks of the immune system? What role does stochasticity play?
Biopolymer physics
There is no theory that explains the experimental data on conformational and configurational changes in biopolymers.
Higgs boson (2012/2013)
Experimentally discovered Higgs boson (Large Hadron Collider at CERN)
Anomaly "Pioneers" (2012)
What causes a slight additional acceleration in the direction of the Sun of the Pioneer spacecraft? It is believed that this is a consequence of the previously ignored recoil of thermal forces.
Long gamma-ray bursts (2003)
Prolonged gamma-ray bursts are associated with the death of massive stars in some specific cases of supernova-type flares, known as hypernovas.
The problem of solar neutrinos (2002)
New understanding of neutrino physics, requiring modification of the standard model of particle physics, in particular, neutrino oscillations
Relic radiation (2000s)
Anisotropy of the microwave background radiation was measured (WMAP satellite experiment)
The Reality of Quarks (1995)
Initially, scientists considered quarks to be just another mathematical abstraction. Only the discovery of the top quark finally convinced them of the reality of the quarks.
Age Crisis (1990s)
Estimation of the age of the Universe from 3 to 8 billion years was less than the age estimate of the oldest stars in our galaxy. Refinement of estimates of the distance to stars and the introduction of dark energy into the cosmological model made it possible to increase the estimate of the age of the Universe.
Newton's law of the world
Not tested at distances less than one centimeter
Quasars (1980s)
For decades, the nature of quasars was incomprehensible. Now they are considered as a kind of active galactic nuclei, which emit tremendous energy due to matter falling into a massive black hole in the center of the galaxy.
Comments
To leave a comment
Basic Physics
Terms: Basic Physics