Sound pressure is a variable overpressure that occurs in an elastic medium when a sound wave passes through it. The unit of measurement is pascal (Pa).
The instantaneous value of sound pressure at a point of the medium changes both with time and when moving to other points of the medium, therefore, the root-mean-square value of a given value associated with the sound intensity is of practical interest:
Where:
- - sound intensity, W / m²;
- - sound pressure, Pa;
- - specific acoustic impedance of the medium;
- - averaging over time.
When considering periodic oscillations, the amplitude of sound pressure is sometimes used; so for sine wave
where is the amplitude of sound pressure.
Sound pressure level (born SPL, s ound p ressure l evel) - measured on a relative scale, the sound pressure value, referred to the reference pressure = 20 μPa, corresponding to the hearing threshold of a sinusoidal sound wave with a frequency of 1 kHz:
db
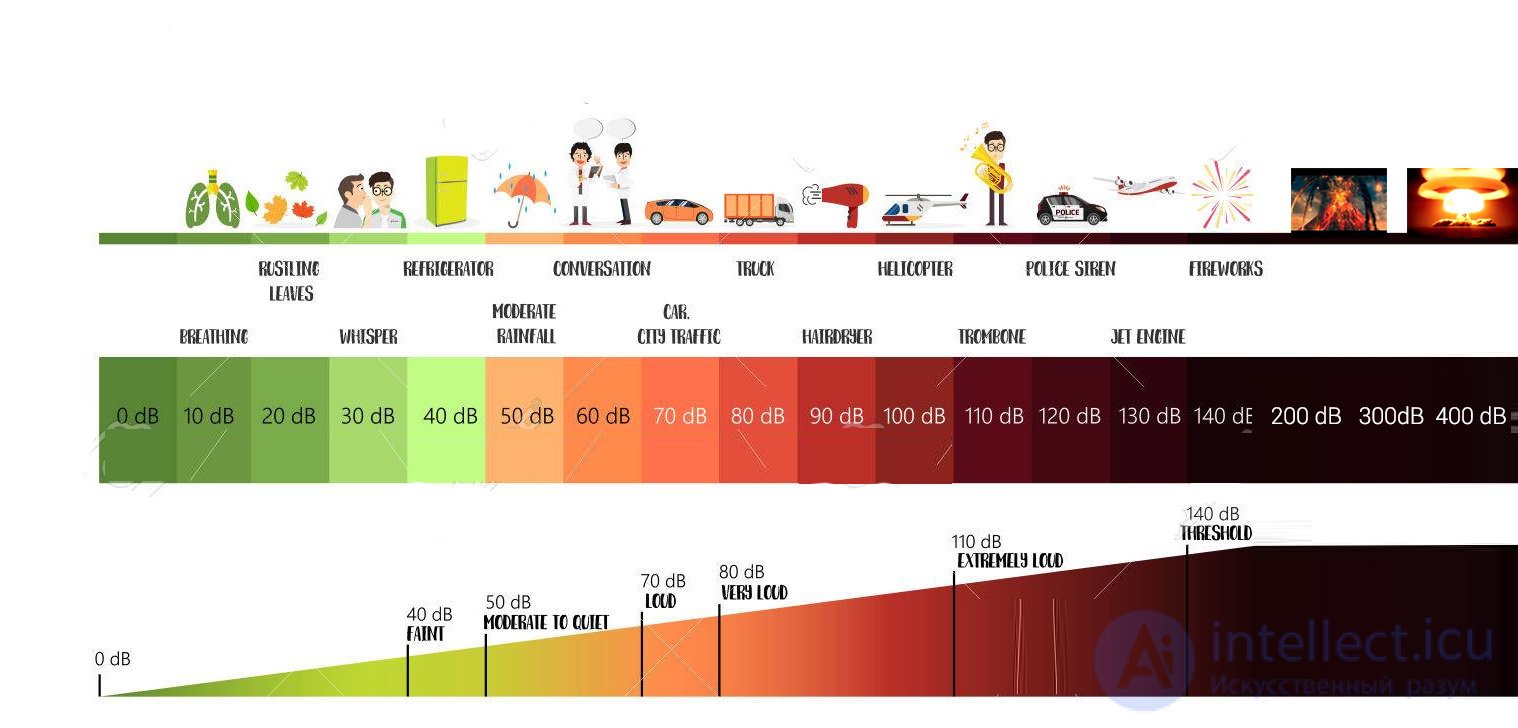
Sound pressure levels from various sources
- 0 dB SPL - special measuring chamber;
- 5 dB SPL - almost nothing is heard;
- 10 dB SPL - almost inaudible - whisper, ticking of the clock, quiet rustling of leaves;
- 15 dB SPL - barely audible - the rustling of leaves;
- 20 dB dB SPL - barely audible - the level of natural background in open areas in the absence of wind, the norm of noise in residential premises;
- 25 dB SPL - quiet - rural area away from the roads;
- 30 dB SPL - quiet - wall clock;
- 35 dB SPL - well heard - muffled conversation;
- 40 dB SPL - well audible - quiet conversation, establishment (office) without noise sources, background sound level during the day in a city room with the windows closed facing the courtyard;
- 50 dB SPL - clearly audible - a conversation of medium volume, a quiet street, a washing machine;
- 60 dB SPL - noisy - a normal conversation, the norm for offices;
- 65 dB SPL - noisy - loud conversation at a distance of 1 m;
- 70 dB SPL - noisy - loud conversations at a distance of 1 m, typewriter noise, noisy street, a vacuum cleaner at a distance of 3 m;
- 75 dB SPL - noisy - cry, laughter from a distance of 1 m; noise in the railway car;
- 80 dB SPL - very noisy - a loud alarm clock at a distance of 1 m; scream; motorcycle with a silencer; the noise of a running truck engine;
- 85 dB SPL - very noisy - a loud cry, a motorcycle with a silencer;
- 90 dB SPL - very noisy - loud cries, pneumatic jackhammer, heavy diesel truck at a distance of 7 m, freight wagon at a distance of 7 m;
- 95 dB SPL - very noisy - a subway car at a distance of 7 m;
- 100 dB SPL - extremely noisy - loud car signal at a distance of 5-7 m, blacksmith shop, very noisy factory;
- 110 dB SPL - extremely noisy - the noise of a working tractor at a distance of 1 m, loud music, a helicopter;
- 115 dB SPL - extremely noisy - sandblaster at a distance of 1 m, a powerful car subwoofer;
- 120 dB SPL - almost unbearably painful threshold, thunder (sometimes up to 120 dB), jackhammer, vuvuzel at a distance of 1 m;
- 130 dB SPL - pain - siren, noise of boilers riveting;
- 140 dB SPL - trauma to the inner ear - takeoff of a jet aircraft at a distance of 25 m, the maximum volume at a rock concert;
- 150 dB SPL - contusion, injuries - rocket taking off to the moon with a crew, at a distance of 100 m, a jet engine at a distance of 30 m, competitions in car sound systems;
- 160 dB SPL - shock, injury, rupture of the eardrum possible - a shot from a gun close to the ear; shock wave from a supersonic aircraft or an explosion with a pressure of 0.002 MPa;
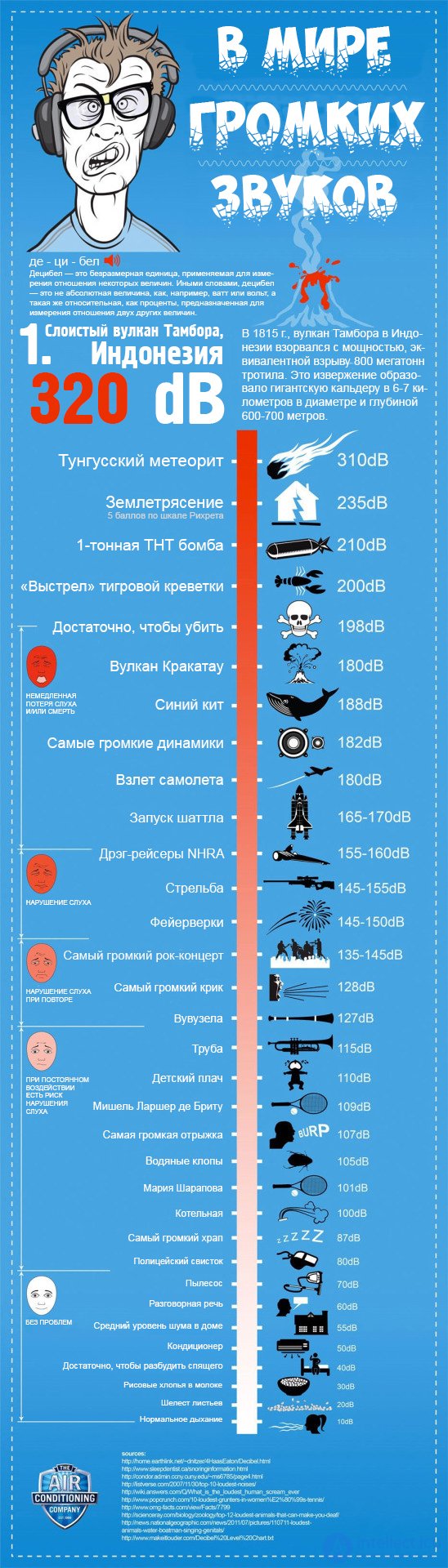
- During the eruption of the Krakatau volcano, 172 dB were recorded over a distance of 160 km.
- 168 dB SPL - shock, injury, rupture of the eardrum possible - a shot from an M1 Garand rifle at a distance of 1 m;
- 170 dB SPL - flash noise grenade, air shock wave pressure of 0.0063 MPa;
- 180 dB SPL - flash noise grenade, air shock wave with pressure of 0.02 MPa, prolonged sound with such pressure causes death;
- 190 dB dB SPL - air shock wave pressure of 0.063 MPa;
- 194 dB SPL - air shock wave with a pressure of 0.1 MPa, equal to atmospheric pressure; possible rupture of the lungs;
- 200 dB SPL - air shock wave pressure of 0.2 MPa; death is possible;
- 210 dB SPL - air shock wave pressure of 0.63 MPa;
- 220 dB SPL - air shock wave with pressure of 2 MPa;
- 230 dB SPL - air shock wave pressure of 6.3 MPa;
- 240 dB SPL - air shock wave pressure of 20 MPa;
- 249.7 dB SPL - maximum pressure of 61 MPa air shock wave in the explosion of trinitrotoluene. The pressure of shock waves in a conventional explosion may be greater (maximum pressure of detonation), but this will not be an air, but an initial explosive shock wave formed by the expansion of detonation products;
- 260 dB SPL - shock wave pressure of 200 MPa;
- 270 dB SPL - shock wave pressure of 632 MPa;
- 280 dB SPL - shock wave pressure of 2000 MPa;
- 282 dB SPL - 2500 MPa - maximum pressure of an air shock wave during a nuclear explosion. The maximum pressure of the reaction products at the time of a nuclear explosion is much greater - up to 100 million MPa.
- 300 dB SPL - 20 000 MPa - the average detonation pressure of conventional explosives; Perhaps the pressure was similar during the explosion of a Tunguz meteorite.
- 374 dB SPL - 100 million MPa - pressure in a nuclear charge at the time of a nuclear explosion;
- 2367 dB SPL - 4.63309 × 10113 Pa - Planck pressure.
Pressure above 140 dB SPL can cause rupture of the eardrum, barotrauma and even death.


Comments
To leave a comment
Basic Physics
Terms: Basic Physics