Lecture

Currently, industrial robots are used in virtually all industries. In developed countries, a whole generation of people has already grown, which has not seen production without the use of industrial robots. The robot is already an integral part of human life and our portal decided to mark the most significant events that influenced the development of robotics and robotic technologies in the world.
1959 - Development of the first industrial robot
 | The first industrial robot was created by self-taught inventor George Devol. The robot weighed two tons and was controlled by a program recorded on a magnetic drum. The creators used hydraulic drives, and the accuracy of the manipulator was 0.254 mm. As a result, US Patent No. 2988237 was issued and then Unimation was founded. |
1961 - Unimation introduced the first robot
 | The world's first industrial robot was introduced on the production line of the General Motors plant in New Jersey. The robot was involved in the processes (movement) of products in the production of scenes for shifting gears, as well as window handles. The cost price of the technology was about $ 65,000, but Unimation sold it for only $ 18,000. The control program was recorded on a magnetic drum, the weight of which was 1814 kg. |
1962 - The first cylindrical robot is installed.
 | 6 Versatran robots from AMF (American Machines Foundry) were installed at the Ford plant in Guangzhou, USA. The name Versatran was definitely from the words "versatile transfer". |
1967 - The first industrial robot in Europe is installed.
 | The first industrial robot in Europe was installed at a metallurgical plant - Uppsland Väsby, Sweden. |
1968 - The first industrial robot, the hand, is created.
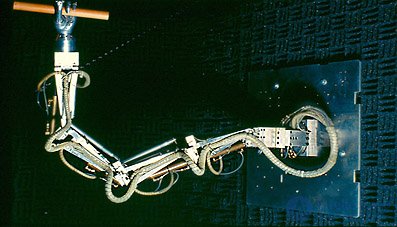 | Created the first industrial robot manipulator similar to the human hand |
1969 - The first robot to automate spot welding in the USA is introduced.
 | The introduction of Unimation robots to automate resistance welding at General Motors, USA, has increased the plant’s overall performance, as well as significantly reduced the heavy and dangerous work of people. |
1969 - Creation of the first sample of technical vision for a robot
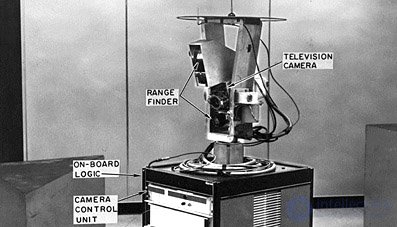 | The first technical vision for industrial robots was demonstrated at the Stanford Research Institute |
1969 - The appearance of the first painting robots in the world
 | The Norwegian corporation Trallfa has developed the first industrial painting robots for their own consumption. The main impetus for the development of this area was the shortage of labor in this period. |
1969 - Unimation begins to market in Japan
 | Unimation signs an agreement with Kawasaki Heavy Industries of Japan to produce and sell industrial robots in Asian markets. That Kawasaki is considered to be the pioneer of Japan in the field of robotics. In 1969, Kawasaki produced the first industrial robot ever created in Japan. The robot was called - Unimate Kawasaki 2000. |
1970 - Hitachi (Japan) creates intelligent technical vision
 | The robot was able to determine for the first time the dimensions of the products and their location. |
1971 - The first robotic line is installed at Daimler Benz factory.
 | The first production line using welding robots in Europe was supplied by KUKA to Daimler Benz, Sindelfingen. |
 | The first national association of manufacturers of industrial robots in Japan, JIRA, was created. Later it was renamed JARA. |
 | KUKA breaks the agreement on the use of Unimate robots and starts developing its own robots. Industrial robot KUKA Famulus, was the world's first six-axial manipulator with the use of an electric drive for all axes. |
 | Stanford arm is a robotic arm designed to assemble small products using touch sensors and back pressure sensors. The management of this robot was carried out using a mini-computer. Later, the founder of this robot, Professor Sheiman founded the company Viacarm Inc to promote and implement this technology in manufacturing plants. |
1974 - The appearance of the first industrial controller for robot control
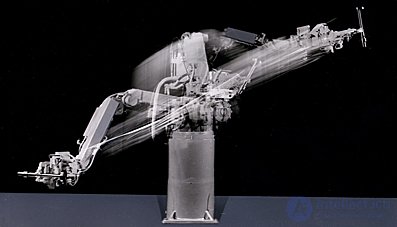 | By order of the company Cincinnati Milacron Corporation, the world's first industrial robot programmable controller was created. The robot was named T3. |
1974 - The first arc welding robot was introduced in Japan.
 | Kawasaki Corporation, using Unimate technology, has created a robot for automating arc welding of a frame for Kawasaki motorcycles. For the first time in robotic welding, touch and collision sensors were used. |
1974 - A digital microprocessor was first used in a robot controller.
 | The industrial robot IRB 6 from ASEA (the future ABB), was the first manipulator controlled by the S1 controller, which used an 8-bit Intel microprocessor. The amount of processor memory was 16Kb. The S1 had 16 digital I / Os and was programmed with 16 keys and a four-digit digital display. |
1975 - The first industrial robot with a lifting capacity of up to 60 kg was created.
 | With the emergence of demand in the automotive industry for robots with higher payloads, ABB created the world's first industrial robot with a payload of up to 60 kg. For the first time this robot was used at the Saab plant, Sweden. |
1976 - For the first time a robot in space
 | The robot arm was first used in the Viking 1 and 2 space probes. |
1978 - The first industrial robot Reis was created.
 | The first industrial six-axis Reis robot with its own controller RE15 was created. |
1978 - The first universal PUMA assembly robots from Unimation and Vicarm
 | With the support of General Motors, PUMA robots (Unimation / Vicarm) were introduced to automate the assembly processes. This has reduced a significant proportion of people involved in such operations. |
1978 - Development of the first SCARA robots
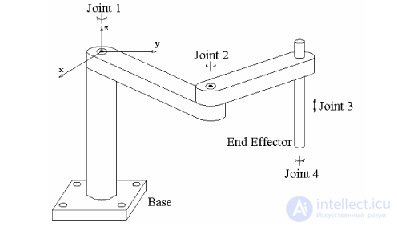 | In 1978, Hiroshi Makino from Yamanashi University, Japan, developed the SCARA robot. It was a technological breakthrough, as Scara robots were the optimal solution for some technological operations associated with the rapid movement of products. |
 | The tasks of spot welding automation opened a new era in robotics with the use of electric gearboxes, which replaced the hydraulic drives. The company Nachi, Japan developed the first robot based on gearboxes. |
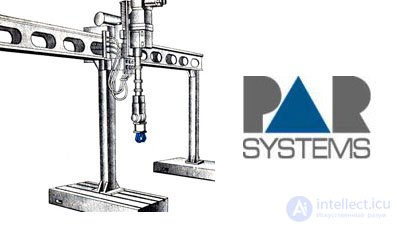 | Portal robots provide much greater reach than classic base robots and can replace several of these robots at once. |
1981 - Production of the first Puma robots in Europe
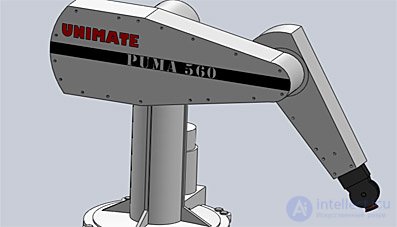 | The Finnish company Nokia has launched the production of industrial robots under license from Unimation. In the 1980s, about 1500 robots with the trade name Puma were released, among them was the popular model Puma-560. |
 | Especially for robotic sentences, IBM has created a powerful and easily applicable programming language. |
 | Adept has introduced a new type of SCARA robots with electric motors on the market. The new design has made robots simpler and more reliable while maintaining high speed. |
1985 - KUKA creates a new Z-shape manipulator.
 | The new Z form significantly added flexibility and versatility to the manipulator, providing three translational and three rotational movements. This is the configuration that most manufacturers currently use. |
1985 - For the first time, robots began to make robots.
 | The first to use their own industrial robots to create robots was Fanuc |
1992 - ABB introduced a fundamentally new S4 controller.
 | S4 significantly significantly facilitated the creation of work programs of the robot due to a convenient external interface. |
1994 - The appearance of the first controller to control two robots at the same time
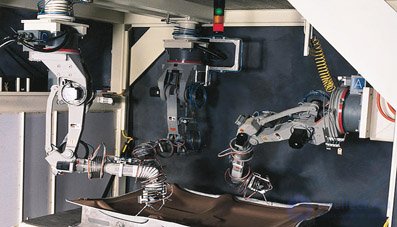 | Motoman created the first controller (MRC), which provided simultaneous control of two robots and control up to 21 axes. MRC also allowed the editing of programs using an ordinary personal computer. |
1996 - KUKA released the first Windows-based controller.
 | For the first time, the controller offered the user a clear Windows interface, as well as a 6d mouse to simplify and speed up the process of creating control programs. |
1998 - ABB introduced the world's first robot Spider
 | ABB has created the fastest robot for the first time applying Delta design, or as it is today called spider design. This robot was named FlexPicke, and with its creator Raymond Clavel. This robot was able to move 120 items per minute, and its speed reached 10 meters / sec. |
2003 - The robot went to Mars
 | The Mars Exploration Rover mission began in 2003 from the moment it was sent from two robotized rovers, to explore Mars and geology. |
2003 - The first robot attraction
 | KUKA, the first manufacturer of industrial robots, introduced the Amusement Ride, called the Robocoaster. Robocaster is used in amusement parks and specializes in extreme spinning thrill-seekers. |
2004 - Motoman introduced the first controller controlling up to 38 axes
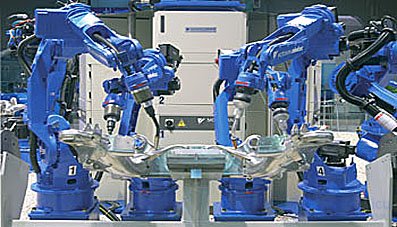 | Motoman, Japan introduced an improved controller (NX100), which provided simultaneous control of four robots, up to 38 axes. The NX100 received a touchscreen and was based on the WindowsCE operating system. |
2006 - KUKA introduced the first lightweight robot.
 | KUKA, together with the DLR (Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics, Germany) created the first robot made of aluminum, which, with a load capacity of 7 kg, had a weight of 16 kg. The first similar robot with similar characteristics weighed 2000 kg. |
2006 - Creation of a humanoid industrial robot
 | Motoman, Japan produced the first humanoid robot with 13 axes. This robot is very well manifested itself in operations for the assembly of products. |
2007 - The first industrial robot with a loading capacity of 1000 kg
 | KUKA was the first in the world to create a 1000 kg industrial robot. It significantly expanded the scope of industrial robots, in effect creating a new class in reach and carrying capacity. |
2008 - The first industrial robot with a carrying capacity of 1200 kg
 | In 2007, the Fanuc M-2000iA became the most lifting and reachable industrial robot in the world. His wrist allowed to hold products weighing up to 1200 kg. |
2009 - Motoman created a controller capable of synchronously controlling up to 8 robots
 | Yaskawa Motoman, Japan, introduced an improved controller (DX100), which provided up to eight robots with synchronous control, up to 72 axes. |
2011 - The first humanoid robot in space
 | The first robot humanoid Robonaut (R2B) was sent to the International Space Station. |
Comments
To leave a comment
Artificial Intelligence. Basics and history. Goals.
Terms: Artificial Intelligence. Basics and history. Goals.