Lecture
In this article we will analyze the distribution of IP addresses and their use by continents over the past 10 years.
Data was collected using IP2Location [1] databases from 2007 to 2016.
In the Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4), IP addresses consist of 32 bits, which can support 4,294,967,296 (2 ^ 32) unique host addresses in theory. We represent 4 bytes of IP - address using dotted decimal notation, which use a decimal number for each byte, for example, 192.168.1.1.
The IP address can be divided into 2 parts, the network part and the receiving side. The network portion of the IP address identifies the network to which the host is connected. Thus, all interfaces attached to the same network have the same network prefix. The size of the network prefix is not always the same due to different classes. The IP addressing scheme divides the total IP address space into five classes; A, B, C, D, and E. We can determine in advance which address ranges belong to each class by examining only a few bits of the address.
Initially, all IPv4 address spaces were managed directly by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), a non-profit organization. In 1992, the Internet Engineering Task Force ( IETF ) recommended numbered Internet resources managed by subsidiaries at the regional level. Several Regional Internet Registrars ( RIRs ) were created to take on this regional distribution and management role of IP address assignment. Today, there are five RIR- APNIC , ARIN , RIPE NCC , LACNIC and AfriNIC , which are responsible for all continents.
We used Hilbert's Blind to represent the topology of IP address assignment using continents. In a nutshell, the Hilbert curve is a continuous fractal space-filling curve that retains its location, and location and this was the main reason that we chose this concept to display diagrams.
The Hilbert curve map is square, since it is a matrix in the form of power 2. The card contained IP address information in the range 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 located in 256 blocks, in 16 x 16 matrix form. In the matrix, each block contains information on the geolocation of the 1st octet of the IP address. We now learned that each block represents octet range information (8.xxx, for example). Please note that the position of the blocks is not in a linear sequence from left to right due to the fractal filling space, as described in the Hilbert curve. We made a trace overlay so that you can see where the octets are located on the map.
The 1st position [0,0] contains information about a range of 0.xxx octets, and then [0.1] which contains a range of 1.xxx octets, and then [0.2] which contains a range of 14.xxx octets, so on and so on. You may notice that the adjacent blocks are neither located in line by line, nor column by column basis. In order to better illustrate the filling of the Hilbert curve, please see below the navigation pattern.
 Chart 1: Hubert Curve
Chart 1: Hubert Curve
We group geolocation information across 7 continents, namely in North America , South America , Europe , Africa , Asia , Oceania and Antarctica . There are two additional groups, the Unassigned and Reserved IP Address. The unassigned group refers to IP addresses that were not allocated at the time the data was compiled. Reserved refers to IPs that are IP protected from the IETF.
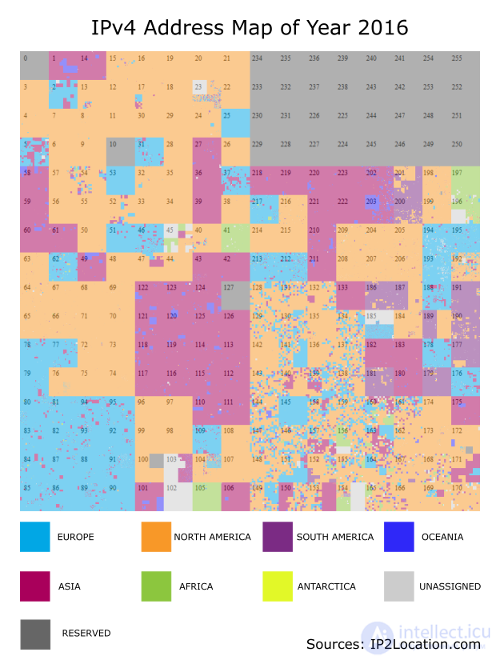
Chart 2: IP Address Space Allocation with Gilbert's Expansion
An IPv4 depletion address is a depletion of the pool of unallocated IPv4 addresses. At the time of writing, all RIRs, except AFRINIC, have announced the exhaustion of the IP address of the pool in their registries.
In 2016 maps, we observed some unallocated address ranges, but this may be due to the RIRA reservation for future use, such as for the transition to IPv6. The only class A that is still available 102.0.0.0/8 is controlled by AFRINIC.
Based on the maps from 2007-2012 and in Table 1, we observed a significant increase in the number of IP addresses assigned in Asia by APNIC. In recent years, this trend has decreased due to the exhaustion of IP addresses.
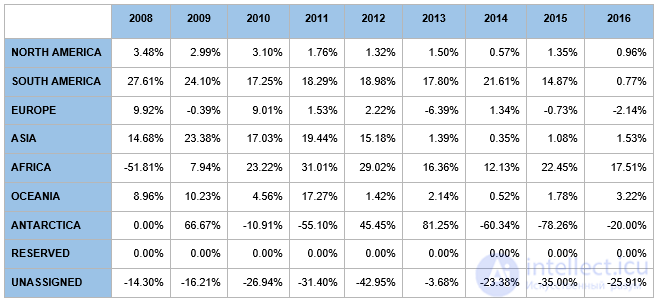
Table 1: Changes in IP Address Distribution by Year
However, we also observed the use of IP addresses in Asia from ranges assigned to other registries, such as RIPE NCC, ARIN and AFRINIC. In some cases, this was related to the business of the owner of the IP address, such as launching a distributed CDN or several regional data centers. It is also likely that Asian organizations are renting address ranges from LIRs due to strong demand for IPv4 address and depletion in APNIC.
We created an animated GIF so that you can see how the distribution of IP addresses evolved over the years from 2007 to 2016.
Comments
To leave a comment
Computer networks
Terms: Computer networks