Lecture
The differential equation y "+ p · y '+ q · y = 0 , where p and q are constant, is called a homogeneous second-order linear equation.
The form of the general solution y 0 of a homogeneous second-order linear equation depends on the roots k 1 , k 2 of the characteristic equation:
.
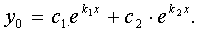
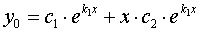 .
. 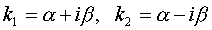 where
where 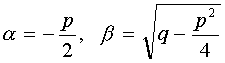 , then the general solution is:
, then the general solution is: 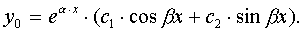
Comments
To leave a comment
Mathematical analysis. Differential equations
Terms: Mathematical analysis. Differential equations