Lecture
A first-order equation y ' = f ( x, y ) is called homogeneous with respect to x and y if the function f ( x, y ) is homogeneous: f ( λx, λy ) = f ( x, y ) .
A homogeneous function can be represented as a function of 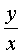 :
:
.
Using substitution 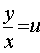 (because
(because 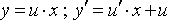 ) The differential equation y ' = f ( x, y ) reduces to an equation with separable variables:
) The differential equation y ' = f ( x, y ) reduces to an equation with separable variables:
Comments
To leave a comment
Mathematical analysis. Differential equations
Terms: Mathematical analysis. Differential equations