Lecture
t E = R e S e ;
C o = C out + C w + C n ;
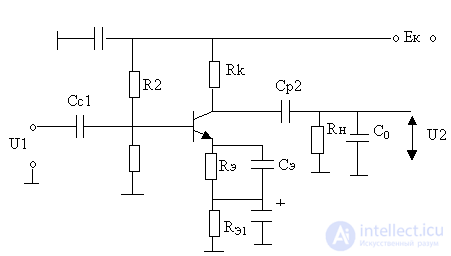
R e1 C e1 - chain of automatic shift;
R e S e - chain of high-frequency correction ;
R1, R2 is a divisor;
R n - AC resistance;
R e << R e1 ;
C e << C e1 ;
R e " (10-50) ohms
With u " (10-500) pF
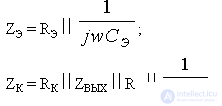
On HF, RN - decreases ( w S >> w B ), therefore S does not depend on w , therefore Z K decreases, gain decreases. This is due to the shunt effect C 0 .
From the formula (*) of the gain with the OS, it can be seen that the depth F = 1 + SZ E , will vary with frequency. Thus, with an increase in w, in the numerator, Z K - decreases, and in the denominator F decreases (OS depth), thereby ensuring a constant gain in a certain frequency band. Choosing the appropriate elements of correction , you can get the rise of the frequency response and, therefore, reduce the settling time ( t Y ).
We find the analytical expression of frequency response, phase response and PC with the corrected OOS.
R OUT >> R K ; R OUT >> R H.
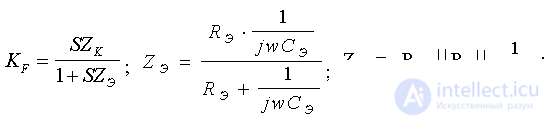
At LF R OUT >> R K ; R OUT >> R H.
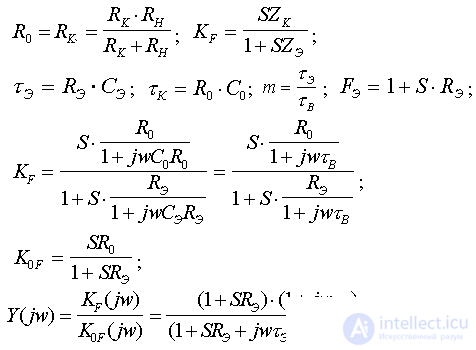
Using the accepted notation, we represent the characteristic in the form:
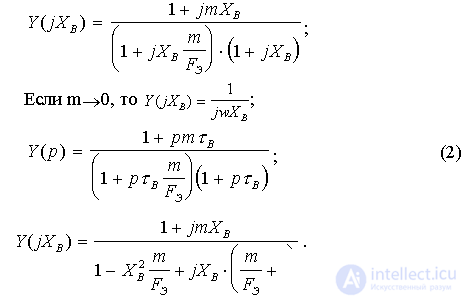
Using the Braude method, we find the optimality condition for frequency response, phase response, HRP.
The condition of optimal correction of the frequency response :
Equating the coefficients for the same degrees X B = w t B , we get:
Consequently, the bandwidth expands to the depth of the OS.
These formulas work well if R H >> R K. When intermediate cascades work, efficiency decreases.
The sequence of calculation:
1) Determine F e ;
2) Find m;
3) Find R e , C e (R e ~ 0.1R e1 ), where R e1 is the emitter stabilization resistance.
PH:
correction with the help of OOS:
1) It is sufficiently effective if R H > R K , the effect of R H is weakened due to parallel capacitive coupling;
2) corrections with the help of R E C E -chain allows to stabilize the gain
3) Allows the use of highly reliable elements (capacitors);
4) Provides multi-band cascades most effectively.
Comments
To leave a comment
Microwave Devices and Antennas
Terms: Microwave Devices and Antennas