Lecture
Teletraffic Theory (from Greek Tele - far and English Traffic -
movement) - movement, load, i.e. movement and maintenance of flows
messages in switched networks.
The subject of teletraffic theory is the quantitative side.
message flow processes in switching systems. Under
the switching system will understand the search stage, station or network. how
and any other mathematical theory, teletraffic theory does not operate with
switching systems themselves, and with their mathematical models.
The mathematical model of the teletraffic system includes the following three
main elements:
1. Incoming call flow - P;
2. Scheme of the switching system - S;
3. Discipline call flow service - D
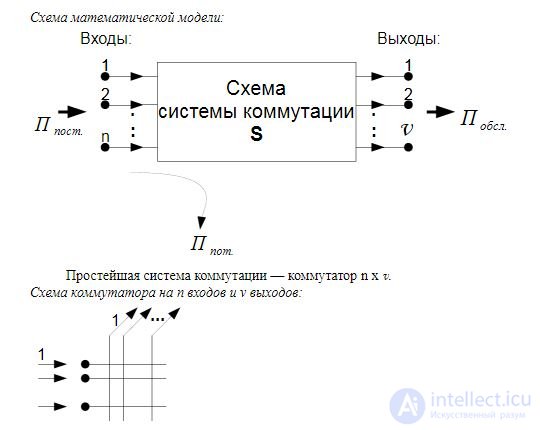
Switching systems are studied in the course of the same name and are divided into: fully accessible and incomplete; single and multilink.
Call flow is a sequence of homogeneous events occurring at certain time intervals. Service discipline characterizes the interaction of the call flow with the switching system.
The discipline of service is characterized by:
• How to service calls (lossy, waiting, combined);
• Order of call service (in order of occurrence, in a random order, etc.);
• Search modes for circuit outputs (free, group, individual);
• Laws of changing the duration of call service (indicative law, constant or arbitrary duration of service);
• And other characteristics (availability of priorities, constraints, etc.)
In the scientific literature for the compact recording of mathematical models, the notation proposed by D. Kendall is used.
Mathematical model is denoted by a sequence of characters:
1. The first symbol indicates the function of the distribution of the intervals between calls (i.e. the call flow);
2. The second symbol is the distribution function of the call service duration;
3. The third symbol is a diagram;
4. Subsequent symbols characterize the discipline of service.
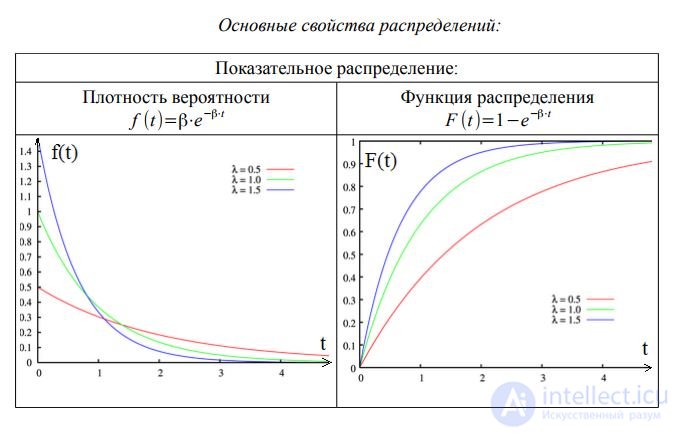
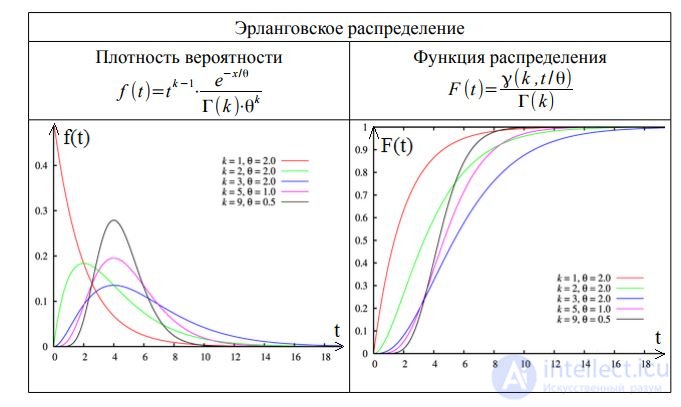
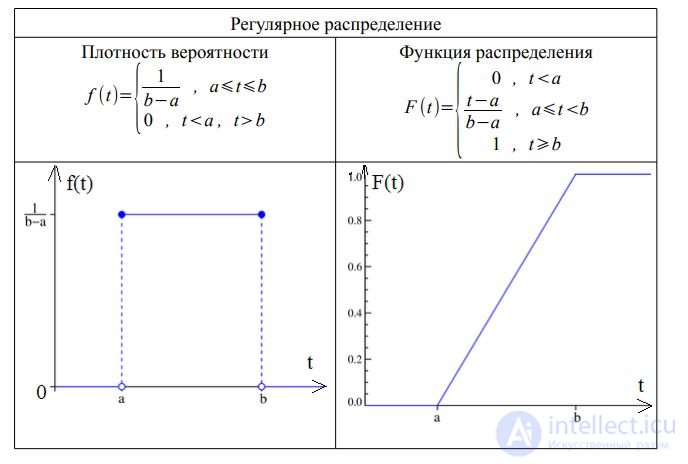
The distribution is indicated by the following symbols:
• M - indicative (exponential) distribution;
• E - Erlang (gamma) distribution;
• D - regular (deterministic - Latin determinave - determine, condition) - a stream with constant intervals between calls;
• G is an arbitrary distribution.
For the multidimensional case, arrows are placed above the symbols, for example:
_
M
An example of writing a mathematical model: M / M / S. Such a record indicates that an arbitrary scheme S receives a call flow with an exponential function of the distribution of the intervals between calls (the first character M). The distribution function of the service duration is exponential (second symbol M). If the circuit of the switching system is a fully accessible bundle of v lines, then v is written instead of S. Building a mathematical model that adequately reflects a real switching system is not a trivial task.
Correctly constructing a mathematical model is half the battle.
The main goal of teletraffic theory is to develop methods for assessing the quality of functioning of switching systems.
The main tasks of teletraffic theory are the problems of analysis, synthesis and optimization.
The task of the analysis is to find the functional relationship between the quality of service P, the parameters of the incoming call flow P, the scheme S and the discipline of service D. P = f (P, S, D)
The task of synthesis is to find the structural parameters of switching systems for given flows, discipline and quality of service. S = f (P, P, D)
The optimization problem usually consists in minimizing the volume of equipment of the switching systems for given flows, discipline and quality of service. K (S) = f (P, P, D) → min
We will deal in the course mainly in the tasks of analysis.
The main mathematical apparatus of the theory of teletraffic is probability theory, mathematical statistics and combinatorics.
The founder of the teletraffic theory is the Danish scientist Agner Krarup Erlang (1878 - 1929, who worked in the Copenhagen telephone company since 1908). A great contribution to the theory was made by Soviet scientists, especially the Soviet mathematician A. Ya. Khinchin (1894-1959).
With other scientists, we will meet in the process of studying the course.
Comments
To leave a comment
Teletraffic Theory
Terms: Teletraffic Theory