Lecture
Example: Let the attribute “Employee number” be defined on the domain of three-digit integers, then it can be presented in the form of a table:
|
Employee number |
|
100 |
|
105 |
|
... |
|
523 |
The value of this attribute is set, and therefore the order of the elements is not important and duplicates are not allowed.
The title of the table is the name of the attribute.
The value of the table is called its extension.
Consider another case: attribute - salary.
Here the order of the records and the presence of duplicates can be significant. In this case, the attribute is represented by an extended set, which can be represented as a special table:
|
Salary |
|
100 |
|
200 |
|
150 |
|
80 |
|
100 |
|
Salary |
|
|
100 |
one |
|
200 |
2 |
|
150 |
3 |
|
80 |
four |
|
100 |
five |
Numbers (1) - (5) indicate the order (position of values in the complex). This table defines the second type of presentation.
An entity type as an attribute aggregate can be represented as a table:
Employee number |
Surname |
Salary |
|
100 |
Ivanov |
100 |
|
105 |
Petrov |
200 |
|
... |
... |
... |

Relational tables are designed to apply the mathematical apparatus of the theory of relations, that is, operations on sets.
Tables of records are intended, first of all, to store time - version support tables.
Relationship types can be represented as a separate table. The intensional (definition) of this table consists of intensions of the entities involved in the communication. Extension type of communication - tuples of the implementation of the entities involved in the relationship.
Connection type is a relationship, not a record type.
Example: consider the link "works":
Works (employee, company)
Both the employee and the company are sets, therefore the communication implementation works , there is an employee and company subset of the Cartesian product of sets.
No |
Surname |
Address |
Floor |
Company name |
Dislocation |
|
123 |
Ivanov |
Sumy |
M |
Wescom |
Kharkov |
|
705 |
Petrova |
Sverdlov |
F |
Wescom |
Kharkov |
|
324 |
Smith |
New York |
F |
Ibm |
New York |
Link type is a relationship, not a record type. Duplicates are not permitted.
Representation of the type of entity.
Vertices are attribute types, and arcs are aggregates of attribute type pairs.
More than one aggregate can be built on one pair of attributes. Dougie can be called.
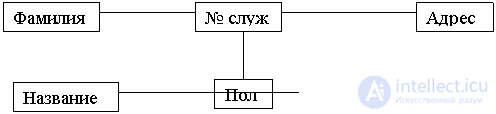
Moving along arcs we get an aggregate that forms an entity.
With the help of the graph can be represented and implementation.
The vertices of the graph can be both sets and extended sets.
With the help of graphs can be represented and types of relationships .
Vertices are an entity type.
Dougie is a type of connection.
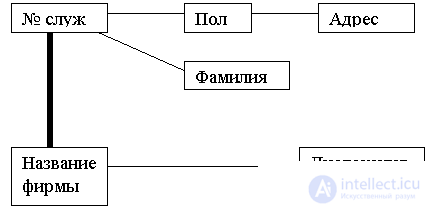
The arc works like other arcs, but its semantics is different.
Comments
To leave a comment
Databases - Data models
Terms: Databases - Data models