Lecture
Qt Creator is a fully integrated development environment (IDE) that provides you with the tools for designing and developing complex applications for a variety of desktop and mobile platforms.
One of the greatest achievements of Qt Creator is that it allows the development team to work on a project on various platforms using common development and debugging tools.
But why do you need projects? To be able to build and run applications, Qt Creator needs the same information that the compiler will need. This information is specified in the build and launch project settings.
Creating a project will allow you to:
You can either create a project from scratch, or import an existing project. Qt Creator generates all the necessary files depending on the type of project being created. For example, if you choose to create an application with a graphical user interface (GUI), Qt Creator will create an empty .ui file that you can modify in the integrated Qt Designer .
Qt Creator is integrated with cross-platform build automation systems: qmake and CMake. You can also import existing projects that do not use qmake or CMake, and tell Qt Creator to simply ignore your build system.
Qt Creator comes with a code editor and Qt Designer for designing and building graphical user interfaces (GUIs) from Qt widgets.
Since it is an IDE, Qt Creator differs from a text editor in that it knows how to build and run applications. He understands C ++ and QML as code, not as plain text. This allows him to:
You can use Qt Designer to position and customize your widgets or dialogs and test them using different styles and screen resolutions. Widgets and forms created with Qt Designer are easily integrated into the program code using the Qt signal and slot mechanism, which will allow you to easily define the behavior of graphic elements. All properties set in Qt Designer can be dynamically changed in code. Moreover, features such as widget promotion and custom modules allow you to use your own widgets with Qt Designer .
You can use the editor to write code in Qt C ++ or in the declarative programming language QML.
You can use QML to create a very flexible user interface from a wide range of QML elements. QML helps developers and designers work together to create flexible user interfaces that will be distributed on portable devices such as cell phones, media players, nettops and netbooks.
QML is a JavaScript extension that provides a mechanism for declaratively assembling a tree of objects from QML elements. QML improves the integration between JavaScript and an existing Qt system based on QObject, adds support for automatic property binding, and provides network transparency at the language level.
Qt Creator provides support for building and running applications on Qt for desktops (Windows, Linux and Mac OS) and mobile devices (Symbian, Maemo and MeeGo). Build settings allow you to quickly switch between build targets.
When you build an application for a mobile device connected to your computer, Qt Creator generates an installation package, installs it on the device, and starts it.
You can send the installation package to the Ovi Store. Packages for Symbian devices must be signed.
Qt Creator is integrated with a set of useful tools, such as version control systems and a Qt emulator.
The recommended way to develop a project is to use a version control system. Qt Creator uses version control console clients to access your repositories. The following version control systems are supported:
The features you have in Qt Creator depend on the version control system. Basic features are available for all supported systems. These include comparing files with the latest version in the repository and displaying the difference, viewing the version history and details of the changes, annotating the files, and accepting and discarding the changes.
To test Qt applications designed for mobile devices in a similar environment, you can use the Qt emulator. You can change the device information about its settings and environment.
The Qt emulator is installed as part of the Nokia Qt SDK. After installation, you can select it as the build target in Qt Creator.
Qt Creator can help you debug your applications. It provides interfaces to the GNU Symbolic Debugger (gdb) and Microsoft Console Debugger (CDB) for debugging common C ++ applications and internal debuggers for Java Script. This includes the ability to connect mobile devices to your computer and debug programs running on them.
Qt Creator displays raw information provided by debuggers in an explicit and concise way in order to simplify the debugging process as much as possible without limiting the debugger capabilities.
Qt Creator is available in binary packages for the following operating systems:
To build Qt Creator itself from source, you need:
Supported Mobile Platforms
You can develop applications for the following mobile platforms:
The following table summarizes the support for operating systems to build applications for mobile platforms.
operating system | Platform | ||
Workspace | Symbian | Maemo | |
Windows | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Linux | Yes | Not | Yes |
Mac os x | Yes | Not | Not |
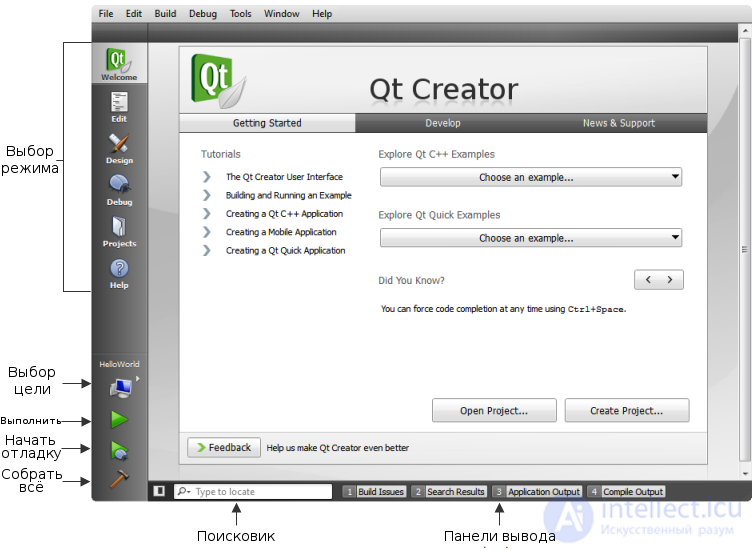
Starting Qt Creator opens Start mode where you can:
To switch to another Qt Creator mode, you can use the mode switch.
Qt Creator has been translated into several languages. If the system language is one of the supported ones, it will be selected automatically. To change the language, select Tools> Options ...> Environment and select a language in the Language field. Changes will take effect after restarting Qt Creator.
The mode switch will allow you to quickly switch between tasks such as editing the project and the source file, designing the application interface, setting up the assembly and execution of projects, and debugging your applications. To change the mode, click on the desired icon or use the corresponding keyboard shortcuts.
You can use Qt Creator in the following modes:
Certain actions in Qt Creator cause a mode change. For example, Debug > Start Debug > Start Debug will automatically switch to Debug mode.
Sidebar is available in Editor and Debug mode. Use the sidebar to view files, projects and bookmarks.
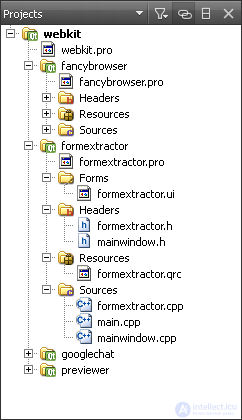
You can select the contents of the sidebar in the sidebar menu:
You can change the sidebar view in the following ways:
 or Alt + 0 ( Cmd + 0 on Mac OS X).
or Alt + 0 ( Cmd + 0 on Mac OS X).  . Select new content to view in a split view.
. Select new content to view in a split view.  .
. The sidebar shows the projects in the project tree. The project tree contains a list of all projects opened in the current session. Files of each project are grouped according to their type.
You can use the project tree in the following ways:
 and select Simplify Tree .
and select Simplify Tree .  and select Hide generated files .
and select Hide generated files .  .
. The taskbar in Qt Creator can display one of the following panels:
Output panels are available in all modes. To open the output panel, click on its name. To expand the output pane, click the Expand Output Pane button or press Alt + 9 .
To search in the Console and Console assembly views, activate them and press Ctrl + F. Enter the search string in the Search field and click the left arrow or the right arrow to search down or up.
To open the Basic Messages and Version Control panels, select Window> Output Panels .
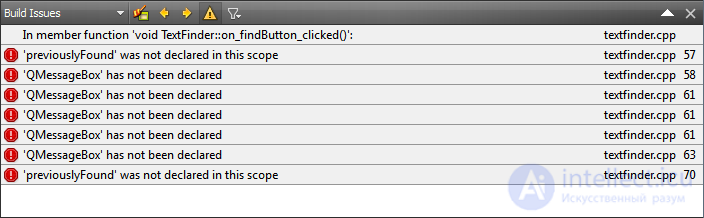
The Assembly Messages panel provides a list of errors and warnings that occurred during the assembly. This panel filters out minor compiler messages and displays errors in an ordered manner.
Clicking with the right mouse button on a line will bring up a context menu with which you can copy the contents and call up the change history from the control system for the line that caused the error message.
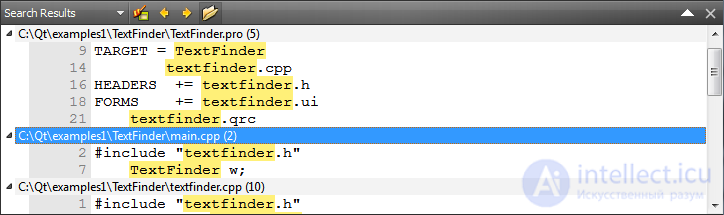
The Search Results pane displays the results of global searches, such as searches within the current document, files on disk, or in all projects.
The screenshot below shows an example of the search results for all references to a textfinder inside the "/ TextFinder" directory.
The console panel of the application displays the status of the program when it runs and debug information.
The screenshot below shows an example of the qDebug () output.
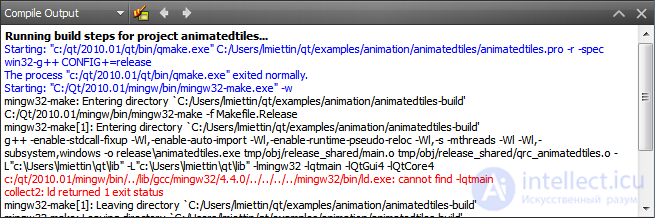
The assembly console panel provides all the compiler output. The assembly console provides a more verbose display of information compared to the Assembly messages panel.
Qt Creator is suitable not only for developers who are used to using the mouse, but also for developers who are more comfortable with the keyboard. A large set of keyboard shortcuts and a search engine help speed up the development process for your application.
Comments
To leave a comment
Cross platform programming
Terms: Cross platform programming