Lecture
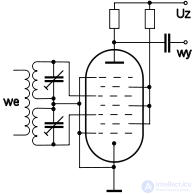

Nonod ( enneod , heptagride ) is an electron tube with nine electrodes — an anode, cathode, and seven grids.
Such lamps were created for a specific scheme, in order to reduce the number of "cylinders" in the device.
So, one of the nonodes released in the USSR - 6Л1П had a special discontinuous hysteresis anode characteristic and was intended to work as a nonlinear element in high-speed amplitude discriminators, binary storage devices, computational and "key" circuits, limiters.
For normal purposes - radio reception, radio transmission, amplification of signals in such a number of grids there is no need.
Even more specific is the domestic nine-electrode "grid-beam" lamp type 6Л2Г, designed for special electronic circuits.
Formally, a nonodode can be considered a “normal” receiving-amplifying lamp EQ-80 (and its 12-volt analogue UQ-80) with triple control and containing tri-control grids separated by three shielding grids (connected together) and one common anti-dinatron grid (Germany, Siemens, 1950) [1] .
Comments
To leave a comment
Radio tubes and ion devices
Terms: Radio tubes and ion devices