Lecture
Modular programming technology.
High-level languages appeared in the 60s. Computer resources (8 KB RAM, speed of 20 thousand operations per second) were insufficient, so programmers had to write programs very “cleverly” using the unconditional transfer operator. The program turned out to be confusing, had the structure of a “spaghetti dish”. As the scope of the computer expanded, the software became more complicated. Programmers solving complex problems faced the problem of the proliferation of the number and size of programs to such an extent that the further development process became practically uncontrollable, and none of the developers could say with certainty that the software that was created always performs what is required and that does not do anything that is not required. Therefore, there was a need for a new methodology for developing software projects. In 1968-1969 programming conferences were held. On the second of these, Edsger Dijkstra proposed a fundamentally new way of creating programs - structured programming. The main thing is to split the software package (when it is created) into program modules that are connected hierarchically.
|
|
|
Modular programming goals:
1. Improve the readability of programs.
2. Improve the efficiency and reliability of programs (it is easy to find and correct errors).
3. Reduce the time and cost of software development (reduced debugging time).
The division of the software package into modules is carried out in accordance with the following principles:
2.1.2. Downstream and upstream programming .
In the development of modular programs, two design methods are used - descending and ascending. In descending design, the development of a software package goes from top to bottom.
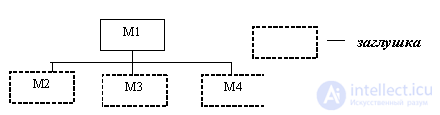
At the first stage of development, the head module is coded, tested and debugged, which is responsible for the logic of the entire software package. The remaining modules are replaced with plugs simulating the work of these modules. The use of plugs is necessary so that at the very early design stage it is possible to check the performance of the head module. In the final stages of design, all plugs are gradually replaced by working modules.
With upstream design, development goes from bottom to top. At the first stage, modules of the lowest level are developed. At the next stage, modules of a higher level are connected to them and their operability is checked. At the final design stage, a head module is developed that is responsible for the logic of the entire software package. Downstream and upstream programming methods have their advantages and disadvantages.
Disadvantages of downstream design:
The advantage of descending design - at the very beginning of the design, the head module is debugged (program logic).
The advantage of upstream programming is that you don’t need to write a stub.
Lack of upstream programming - the head module is developed at the final design stage, which sometimes leads to the need to refine the modules of lower levels.
In practice, both methods are used. The top-down design method is most often used in the development of a new software system, and the bottom-up design method is used in modifying an existing complex.
Comments
To leave a comment
Algorithmization and programming. Structural programming. C language
Terms: Algorithmization and programming. Structural programming. C language