Lecture
Pricing - setting the price of a product or service. There are two main pricing systems: market pricing based on the interaction of supply and demand and centralized state pricing based on pricing by government agencies. In a market economy, the process of choosing the final price is made depending on the cost of production, prices of competitors, the ratio of supply and demand and other factors.
Price and pricing are the most important concepts of a market economy. The most common words, the price we call the amount of money that the buyer gives to the market in exchange for the goods sold by the seller. Thus, the price - the main characteristic of the product from the point of view of a market economy.
There is no universally accepted definition of such a complex economic category as price. One of the most successful figurative definitions can be called the following: the price is determined by the cost of the manufacturer and the art of the seller. The price is intended to reflect the interests of all market participants: the manufacturer must refund the invested funds and make a profit; the buyer must justify the cost of the purchased goods, having in turn benefited from its use.
Pricing is one of the key factors of a market economy and the most difficult part of marketing work. The commercial success of any manufacturer of goods or services is largely determined by the choice of pricing strategy and tactics. The difficulty lies in the fact that the price at a particular point in time may depend on many factors - not only economic, but also political, social, and psychological.
The optimal price for a product or service:
There are several main goals that a manufacturer of goods or services can pursue when setting prices:
In the practice of economic entities, various types of prices for goods are applied:
The price of a product in a certain market is not a constant value even within a small period. Prices are subject to change and fluctuations depending on a number of factors, ranging from political and macroeconomic events to fashion and weather. Some of these factors may be predicted, while others are probabilistic or unpredictable. In this regard, when pricing it is important to understand which factors influence the determination of prices, the extent to which the manufacturer can use the positive and level the influence of negative factors.
Internal factors affecting the formation of prices by the manufacturer:
External factors to consider when pricing:
Pricing strategy formation involves a number of stages:
The following directions of pricing strategies are distinguished:
In this case, it is possible to apply different pricing strategies when selling the same product in different markets (for example, in the domestic and export markets).
With the most general approach, pricing methods can be divided into three groups - cost-oriented, demand-driven, and competitor-oriented.
Cost-oriented methods are good because there is no need to collect information about the state of the market and the magnitude of the demand; all the data necessary for pricing to the manufacturer is represented by its accounting department. The simplest option involves determining the cost of goods with the accrual of the established rate of return. This method is used mainly in cases where products are intended for export; when the main consumer of products is the state; or when products are sold through participation in tenders. If such a product is sold on the open domestic market, then the estimated price is compared with the current market price. According to the results of such a comparison, a decision is made on the advisability of producing a certain type of product.
A modification of the method, taking into account the dependence of production costs on the volume of production, is the method of analysis of the control point. In this case, in the conditions of a known market price for a product, the minimum allowable volume of output is determined, allowing to reach zero profit. If the manufacturer has the technological ability to produce a greater number of products, then a decision is made to start production; otherwise, the manufacturer refuses to release.
Demand-oriented methods (consumer assessment methods) are based on knowledge of need and predictive estimates of consumer perception of goods. In this case, it is considered that the buyer determines for himself the value of the offered goods and relates it to the asking price. At the same time come to the fore advertising campaigns, marketing strategies for product promotion, the formation of its image. In the interests of the manufacturer to ensure product differentiation according to technical and consumer qualities, design, targeting; and, accordingly, high price elasticity.
Parametric pricing methods are also widely used (the method of specific indicators, the method of structural analogy). They are used when the price of actually sold products with a certain set of consumer properties is known; at the same time, with general similarity, the new products differ from the previous ones by any parameters. In this case, the price of a new product can be calculated on the basis of the previous price by applying correction factors that take into account the “improvement” of a new product relative to the old one (for example, an increase in the strength of the yarn; or an increase in the net volume of the refrigerator) . It should be borne in mind that, in general, the percentage of price increase should lag somewhat behind the percentage of increase in quality, otherwise the competitiveness of products will be lost.
Competitor-oriented methods allow you to set prices based on the current prices in the market. This takes into account the conditions of competition, the ratio of the quality of a competing product and its value. Depending on the chosen marketing strategy, the price is set slightly higher or slightly lower than that of competitors.
For each trading company control and analysis of pricing is very important. Why?
The scheme of control and analysis of pricing in enterprises
You can control the pricing process in commercial, non-profit, state-owned enterprises. Including employees themselves, who directly commit transactions for the purchase, sale of goods and services for the needs of organizations. These are hired personnel who may be part of the company's management team (directors, top managers, supervisors, deputies, etc.), and lower-level specialists (sales managers, purchasing managers, etc.).
An example of pricing in enterprises
The organization (the owner of the business) instructed the supply department (supply manager) to purchase a wholesale batch of water heating tanks in the amount of one hundred pieces, for further retail sales of these tanks. The supply manager is challenged. Find and buy this equipment at the lowest price, and the sales manager should sell at the highest price, thereby making the organization (business owner) a profit. But, as a business owner will be able to check at the lowest price the product was purchased or not. Statistics show that 80% of Russian enterprises have kickback schemes. The price of water tanks at the dealer with a maximum discount of 35% for a volume of 100 pieces is 9,750 rubles per unit, the retail price of such a tank in the city is 15,000 rubles. The purchasing manager buys 10,000 rubles each, the difference of 250 rubles goes into the pocket to the purchasing manager. Then the equipment goes to the warehouse of the organization (business owner). Where already the sales department (sales manager) is instructed to sell these tanks with a wrap of 40%, the sale price of the tank was 15,000 rubles, while the sales manager was announced that he could make a discount of up to 10% on these tanks at his discretion. It turns out that the sales manager has the opportunity to play on the difference in discounts. Which again allows the sales manager to put the difference in his pocket.
Below is a pricing control scheme and its subordinates.
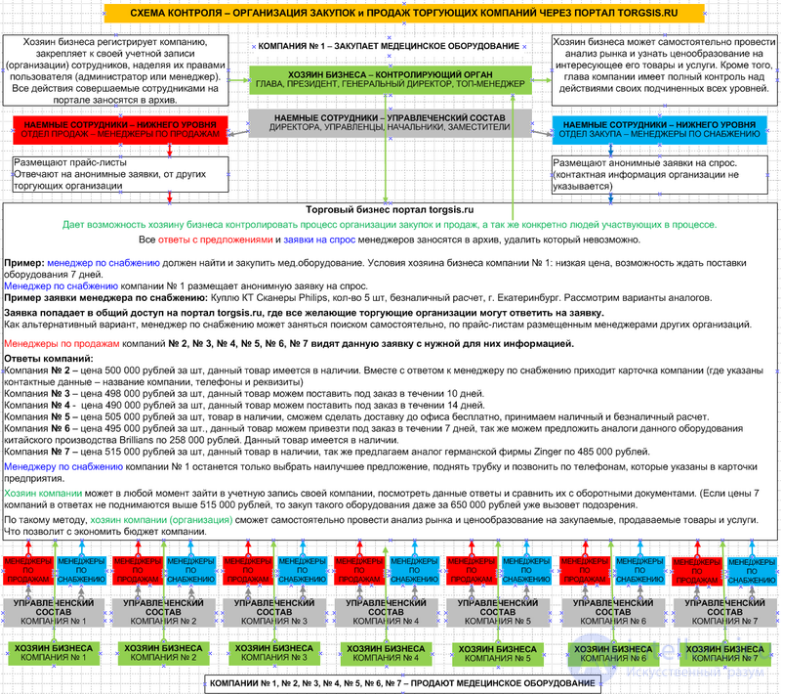
This diagram shows the whole process of control and interaction between organizations that sell and buy on the trade business portal. It is anonymous requests for demand, without specifying the contact details of companies that promote healthy competition.
Такая схема работы выгодна обеим сторонам, у продавцов отпадает надобность в холодном прозвоне и поиске клиентов, а у покупателей в поиске лучшей цены, что делает эту схему привлекательной в разрезе сегодняшнего дня. Когда цена на один и тот же товар может сильно колебаться из-за 1000 торгующих организаций одним и тем же продуктом.
Хозяин бизнеса (контролирующий орган) — имеет полный доступ к архиву данных, он в любой момент может проверить работу своих сотрудников и самостоятельно провести анализ ценообразования на закупаемый товар либо услугу, сравнив документооборот своей компании с ценами, предлагаемыми на рынке товаров и услуг.
Покупающая сторона (менеджер по снабжению) оставив такую заявку, будет дальше заниматься своими насущными делами. Его не будут тревожить лишними звонками из других компаний, предлагать (навязывать) купить у них товар. Ему просто через какое-то время, нужно проверить ответы, выбрать самый подходящий по всем условиям и созвониться с предлагающей стороной.
Предлагающая сторона (менеджер по продажам) не может знать, какой компании именно он отвечает (предлагает) и сколько конкурирующих компаний ответило помимо него. Заведомо зная это, менеджер постарается дать конкурентоспособную цену, что приводит к снижению цены, а не к её повышению.
Comments
To leave a comment
Pricing
Terms: Pricing