Lecture
Surface-active substances (surfactants) play an important role in the food industry. These compounds have the ability to reduce the surface and interfacial tension between different substances - for example, between water and oil - which helps stabilize emulsions, foams, suspensions and dispersions. Due to these properties, surfactants are widely used in food production to improve texture, taste, appearance and shelf life.
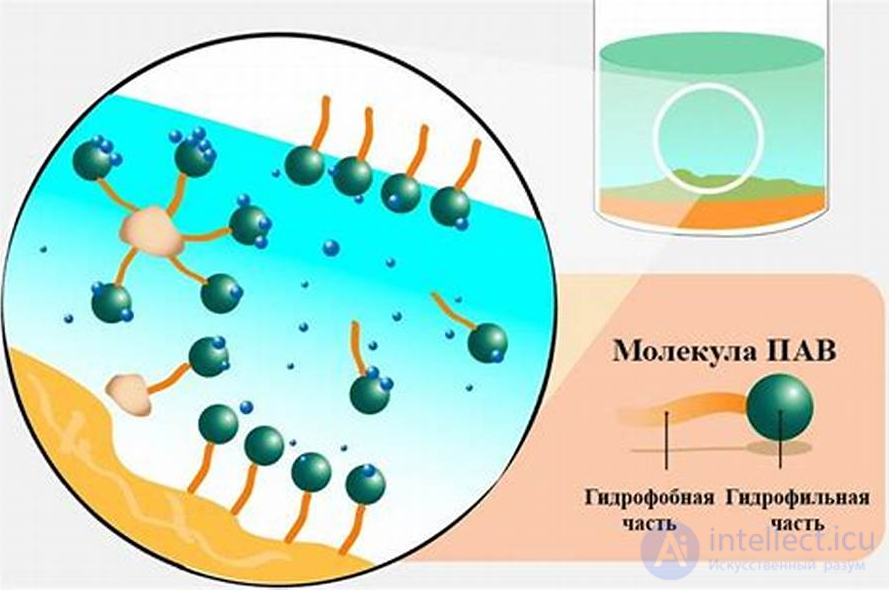
Surfactants are molecules containing both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (fat-loving) parts. This allows them to act as intermediaries between immiscible phases - water and fat. The main classes of surfactants:
Anionic surfactants - negatively charged, rarely used due to their aggressive action;
Cationic surfactants - positively charged, often used as antiseptics;
Nonionic surfactants - uncharged, the safest and most common in the food industry;
Amphoteric surfactants — can behave as cationic or anionic depending on the pH of the environment.
Application of surfactants in the food industry
1. Emulsifiers
This is the most common type of food surfactants. They are used to create and stabilize emulsions — for example, in mayonnaise, ice cream, creams, sauces.
Examples:
Lecithin (E322) — a natural emulsifier from eggs and soy;
Mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (E471) — obtained from vegetable oils;
Polysorbates (E432–E436) — synthetic non-ionic surfactants.
2. Foaming agents and defoamers
Surfactants can both create foam and suppress it. This is important, for example, in the production of whipped desserts and drinks with foam (foaming), or, conversely, during heat treatment, where excess foam interferes (foam suppression).
3. Wetting and solubility
Some surfactants improve the solubility of powders (e.g. cocoa, coffee) in water by reducing surface tension and facilitating dissolution.
Cooking features
Thermal stability
Some surfactants are sensitive to high temperatures: they can break down or lose activity. Therefore, in cooking, preference is given to stable emulsifiers such as lecithin and E471.
pH influence
The acidity of the environment affects the activity of surfactants, especially amphoteric ones. For example, in acidic sauces or marinades, surfactants can change their properties, which is important to consider when selecting additives.
Combination with other ingredients
Surfactants can interact with proteins, starch and fats. For example, in baking, emulsifiers improve the crumb structure and prolong the freshness of bread.
Safety and standards
Only those surfactants that have undergone toxicological assessment and are recognized as safe are used in the food industry. In the European Union and Russia, permitted surfactants have the status of food additives (E-codes), and their dosage is strictly regulated.
Conclusion
Surfactants are an integral part of modern food production. They allow the creation of stable products with improved organoleptic properties. However, when using them, it is important to take into account technological features, compatibility with other ingredients and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Comments
To leave a comment
Пищевая химия
Terms: Пищевая химия