Lecture
Economic (from other Greek οἶκος - house, household, housekeeping and ν μος, territory of economic management and rule, law , literally "house management rules") [1] - economic activities of the society, as well as the totality of relations the system of production, distribution, exchange and consumption.
For the first time in scientific work the word "economy" appears in the IV. BC er in Xenophon, who calls her "natural science." Aristotle contrasted economics with chrematistics, a branch of human activity related to the extraction of benefits [2] . In modern philosophy, the economy is considered as a system of social relations, considered from the perspective of the concept of value. The main function of the economy is to constantly create suchweights that are necessary for the livelihoods of people and without which society cannot develop. The economy helps to meet the needs of a person in a world of limited resources.
The economy of society is a complex and all-encompassing organism that ensures the vital activity of every person and society.
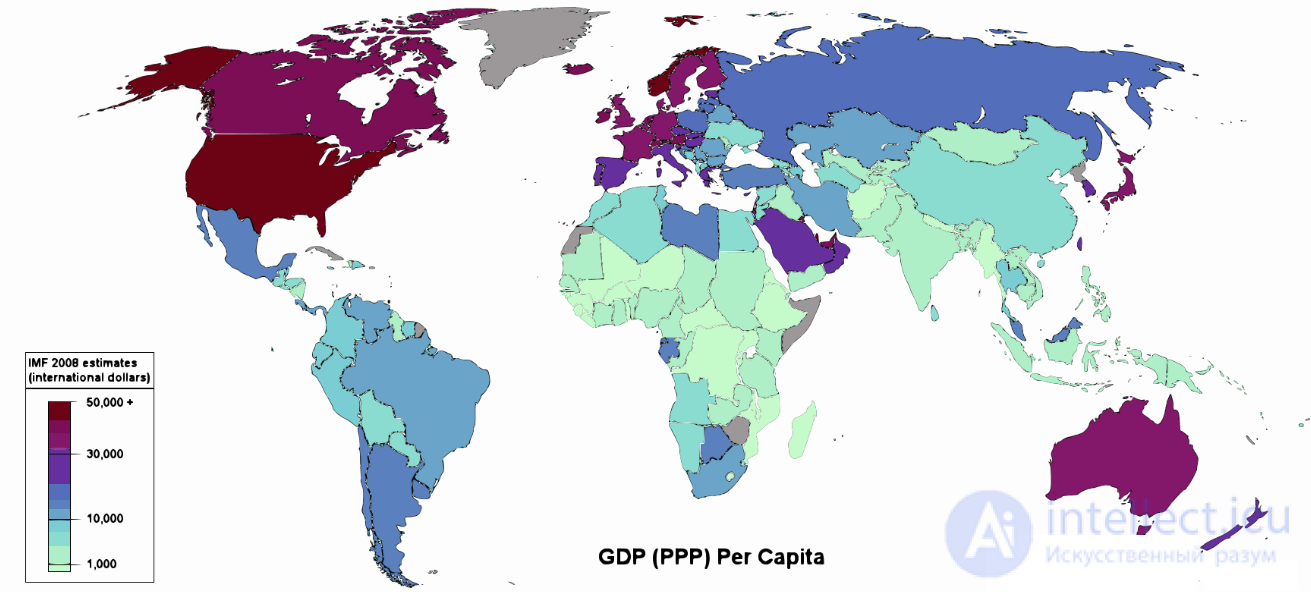
World economy: GDP (popps) per capita
In economic science, the division of economic activity into micro, macroeconomic levels of production and the world economy has been adopted.
Main article: Economy
Depending on the forms of ownership, the state and private sectors are distinguished.
Depending on the specific types of economic activity, the real sector of the economy, non-productive, financial, is distinguished.
There are the following main forms of the economy:
Economic growth is defined as the increase in real production in the national economy for a certain period of time (for a month, quarter, year). Unlike economic development, economic growth is a quantitative indicator. Real production is usually understood as real (that is, cleared of inflation factors) gross domestic product (GDP), less commonly real gross national product (GNP), net national product (NNP), or national income (ND). Economic growth is closely linked to an increase in overall well-being: an increase in life expectancy, quality of care, level of education, reduced working hours, etc.
There are extensive and intensive factors of economic growth.
In primitive society, the level of economic development was low, ensuring consumption on the verge of physical survival. At first, primitive people obtained livelihoods through hunting and gathering, but as a result of the Neolithic revolution, agriculture and animal husbandry arose. The development of society led to the division of labor and social inequality, there were social classes and the state. Occurred royalties.
The exchange of goods gradually developed, which was first carried out in the form of barter, but with the advent of money turned into a trade. Nevertheless, in the societies of the Ancient world and the Middle Ages, subsistence farming prevailed. In many states of antiquity there was a so-called palace economy, based on a combination of planned economy (allowing for large public works, such as irrigation, the construction of palaces and pyramids) and natural economy.
From the end of the 15th century, the Epoch of great geographical discoveries began, which led to the fact that the world economy developed and the era of primitive accumulation began.
From the last quarter of the 18th century, an industrial revolution began, which led to the fact that in the most developed countries the majority of the population by the end of the 19th century were no longer engaged in agriculture, but in industry. Capitalism became the predominant economic system, and the process of transforming a traditional society into a modern, agrarian society into an industrial society took place.
In the twentieth century, a command-and-control socialist economy was created in a number of countries. In other countries, the development of capitalism took place. In the second half of the 20th century, the scientific and technological revolution began, as a result of which industrial society in the most developed countries began to turn into a post-industrial one.
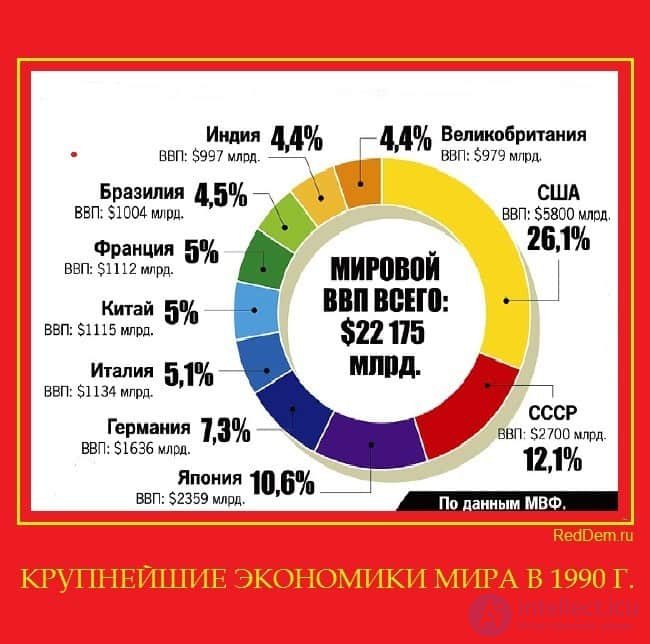
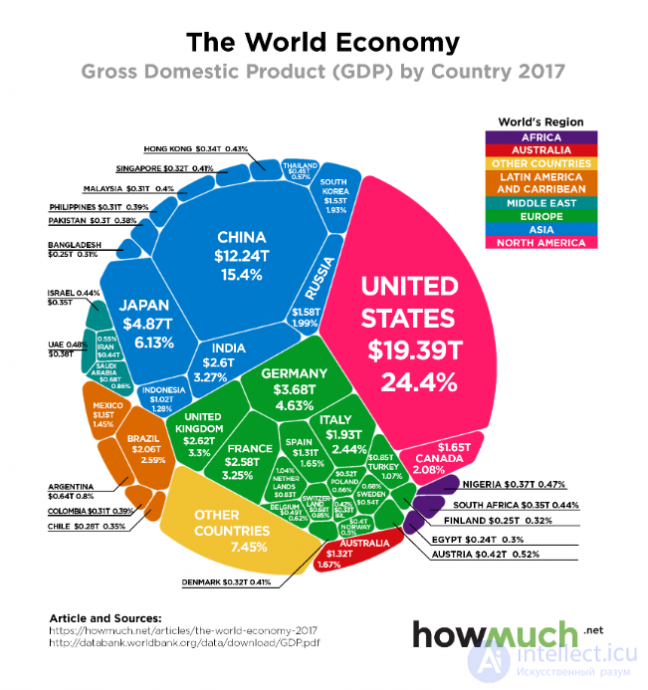
The largest economies of the world
The largest economies of the world in 2008 in terms of GDP (in millions of US dollars) according to the IMF data [3] :
| A place | A country | GDP (million $) |
|---|---|---|
| The whole world | 62,909,274 [4] | |
 European Union European Union |
16,282,230 [4] | |
| one |  USA USA |
14,657,800 |
| 2 |  PRC PRC |
5,878,257 |
| 3 |  Japan Japan |
5,458,872 |
| four |  Germany Germany |
3,315,643 |
| five |  France France |
2,582,527 |
| 6 |  Great Britain Great Britain |
2,247,455 |
| 7 |  Brazil Brazil |
2,090,314 |
| eight |  Italy Italy |
2,055,114 |
| 9 |  Canada Canada |
1 574 051 |
| ten |  India India |
1,537,966 |
| eleven |  Russia Russia |
1,465,079 |
| 12 |  Spain Spain |
1,409,946 |
| 13 |  Australia Australia |
1 235 539 |
| 14 |  Mexico Mexico |
1,039,121 |
| 15 |  The Republic of Korea The Republic of Korea |
1 007 084 |
Comments
To leave a comment
Economic theories
Terms: Economic theories